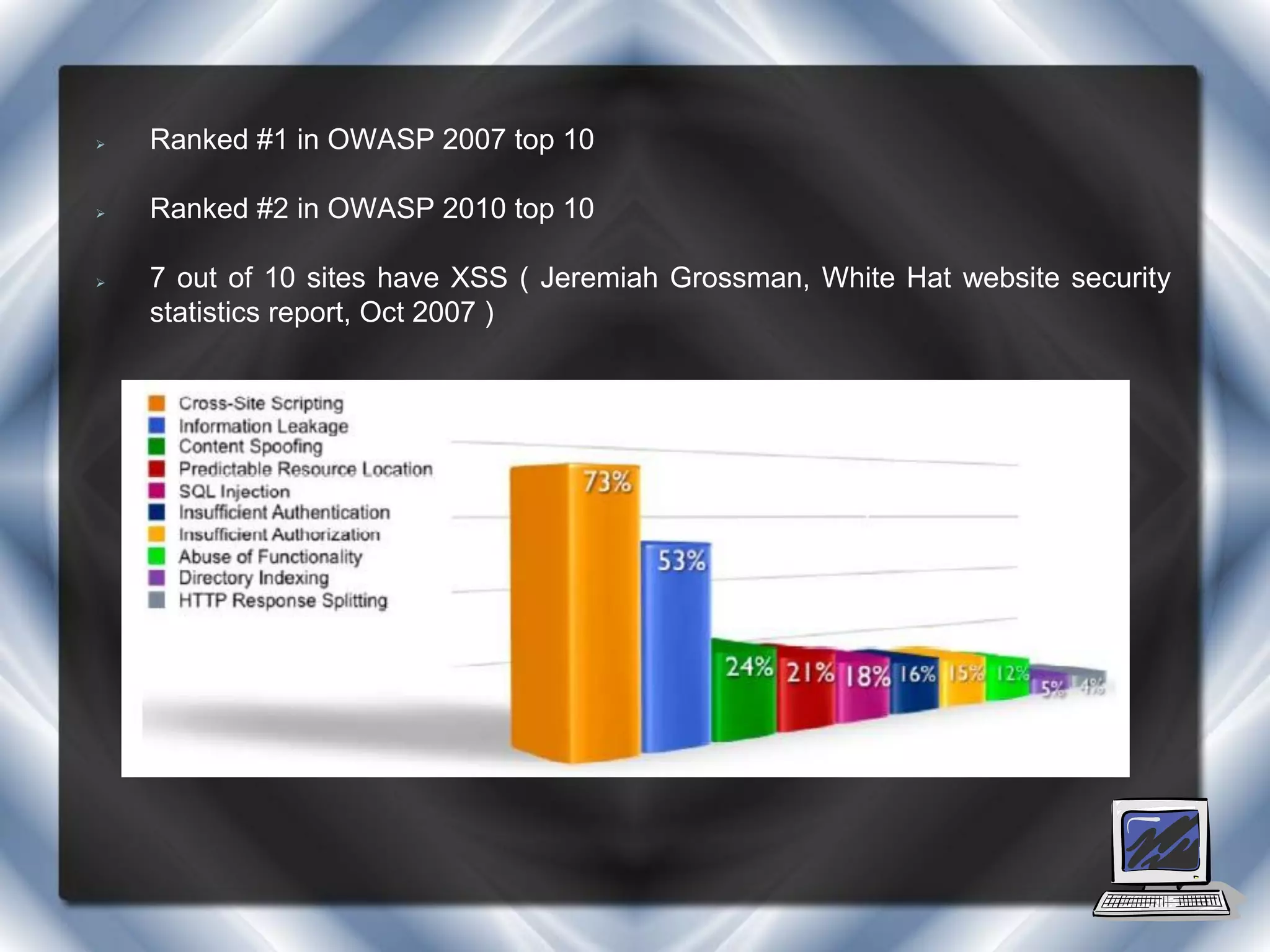
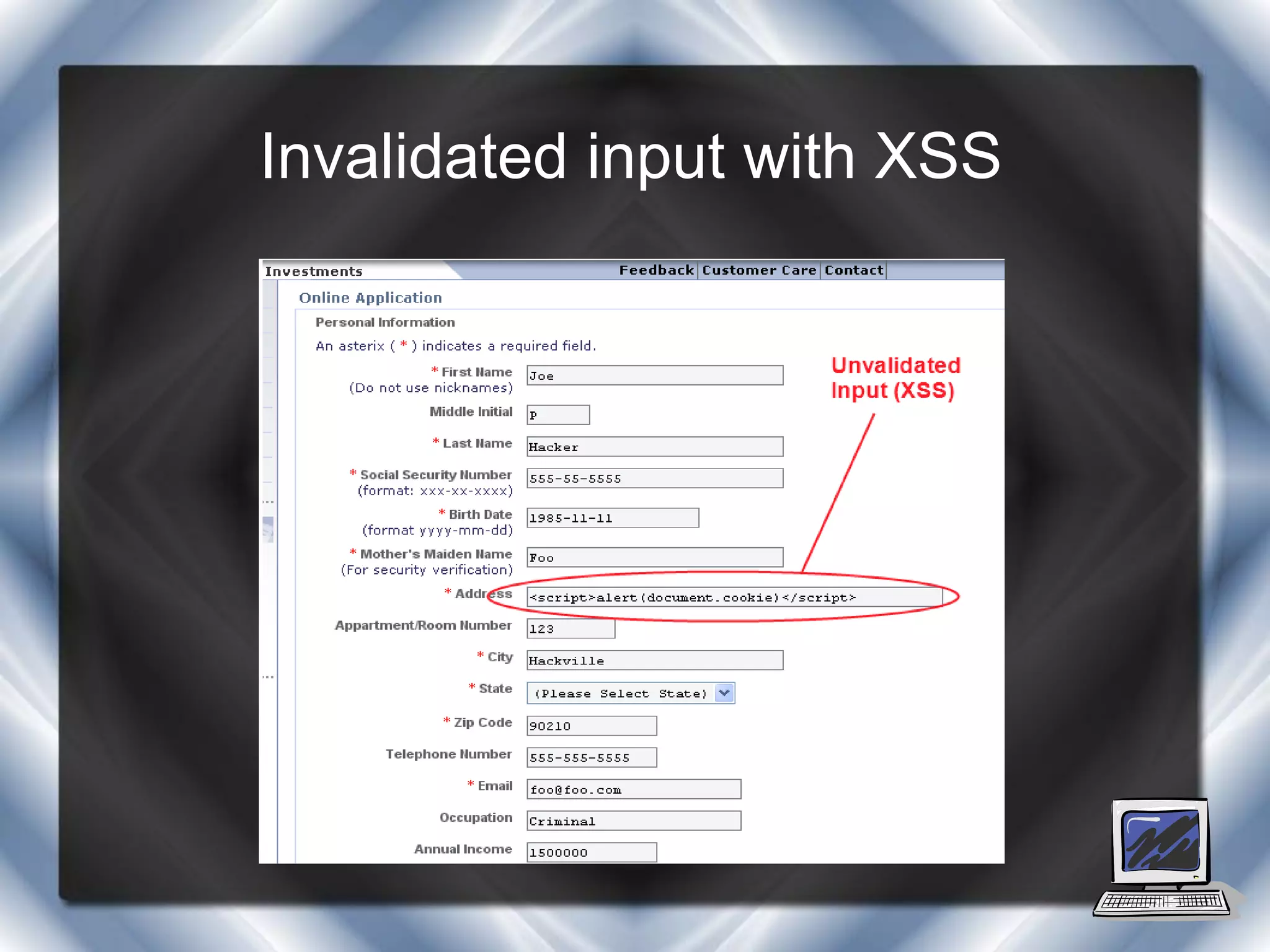
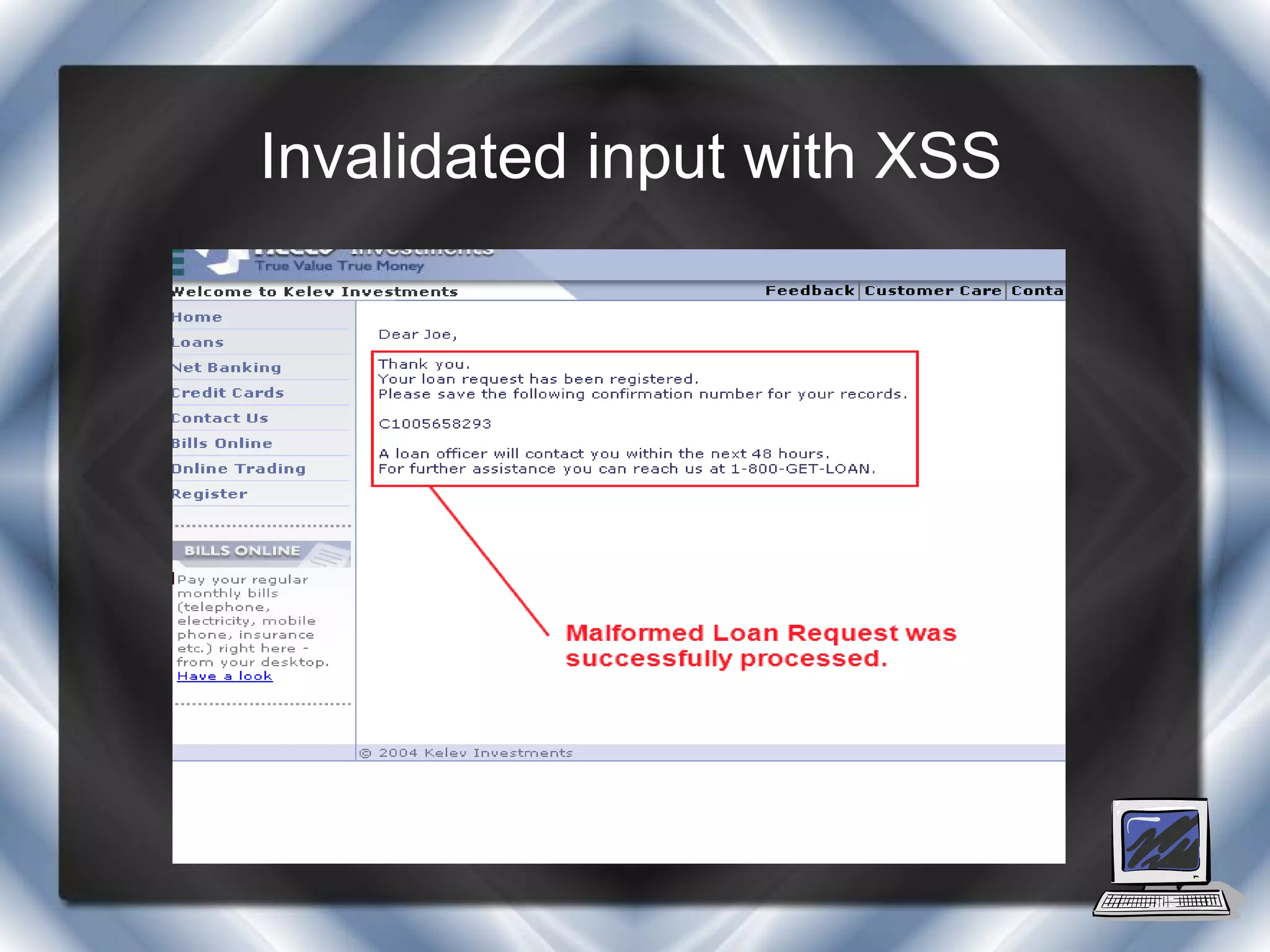
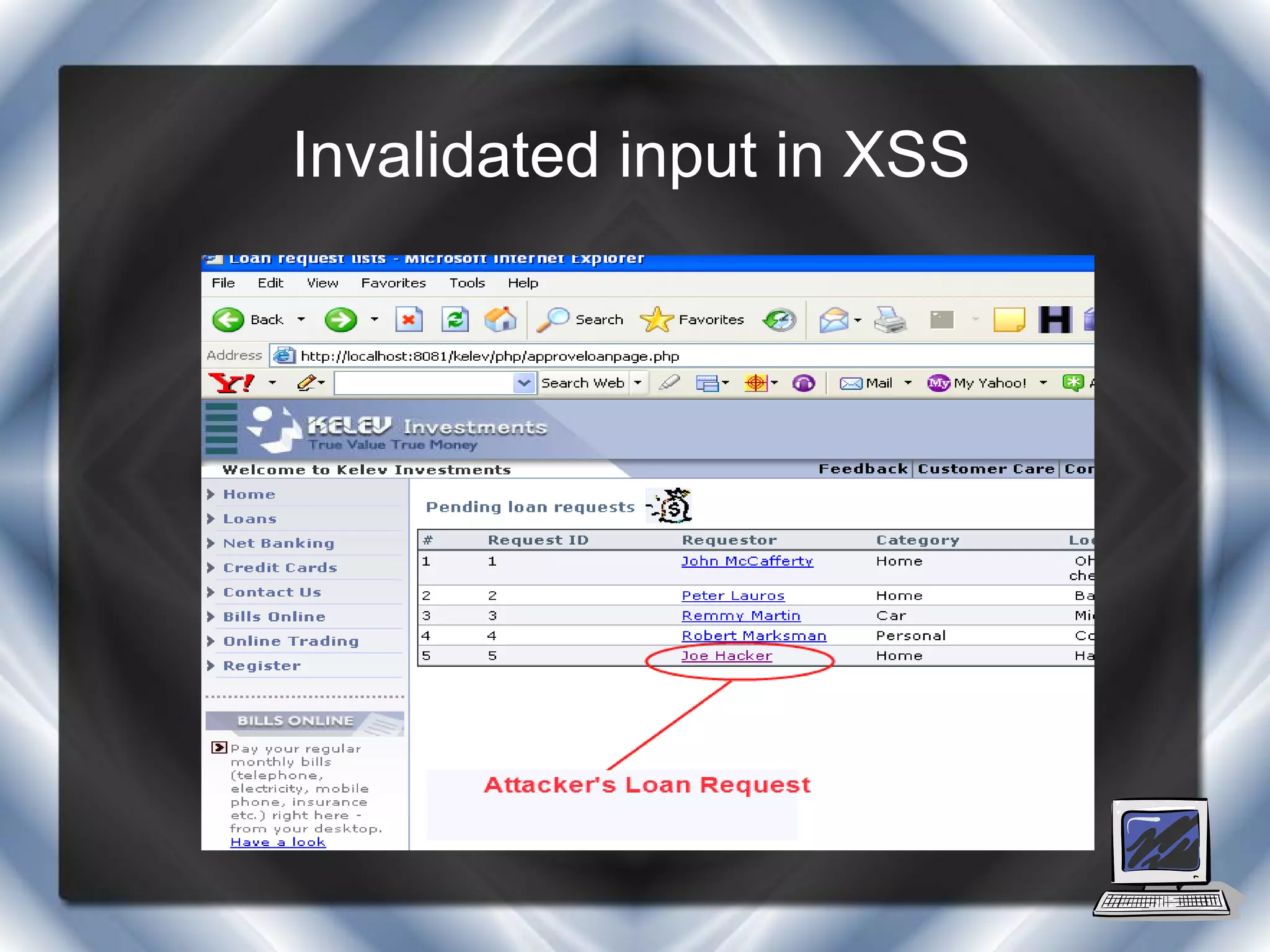
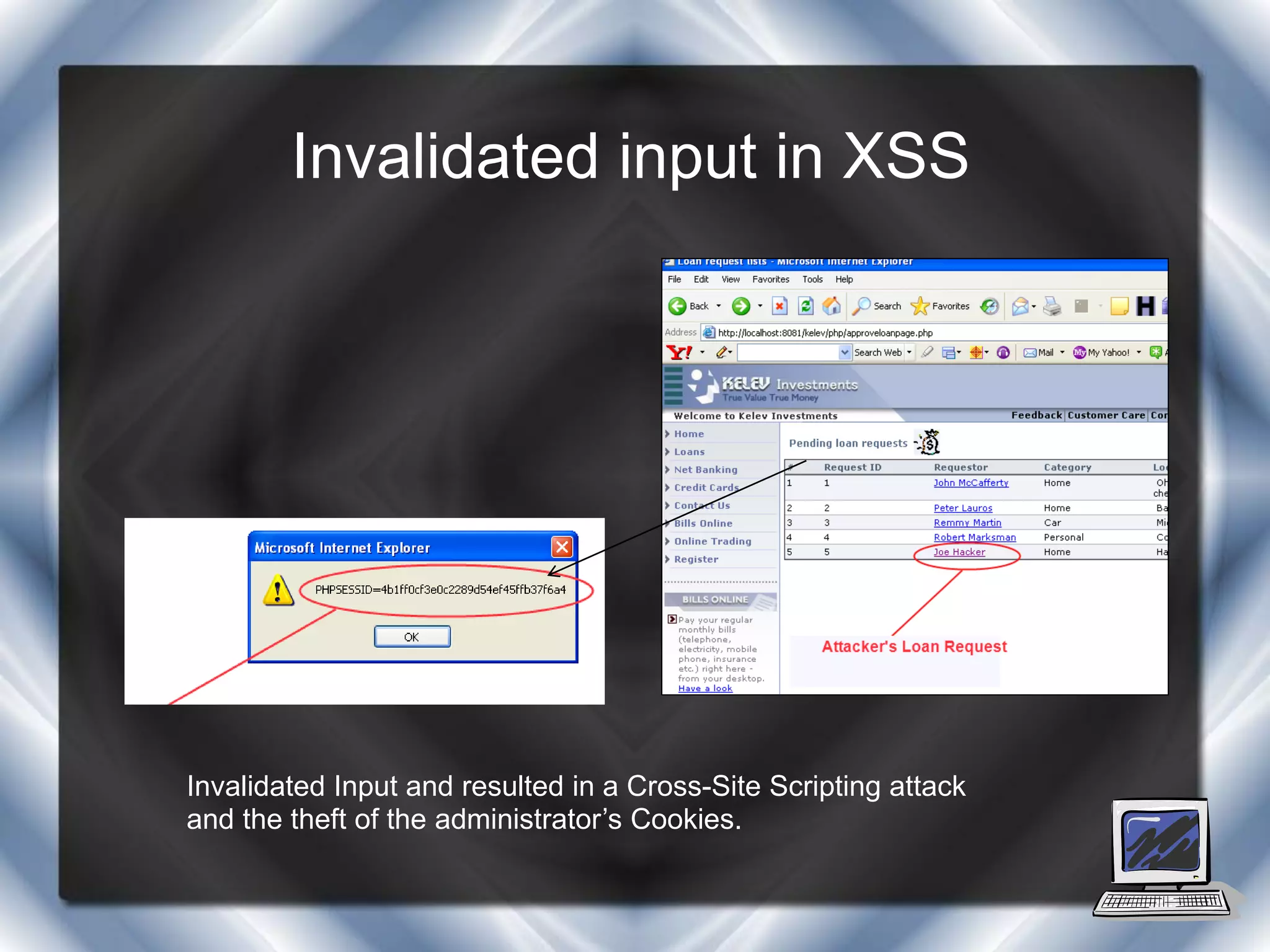
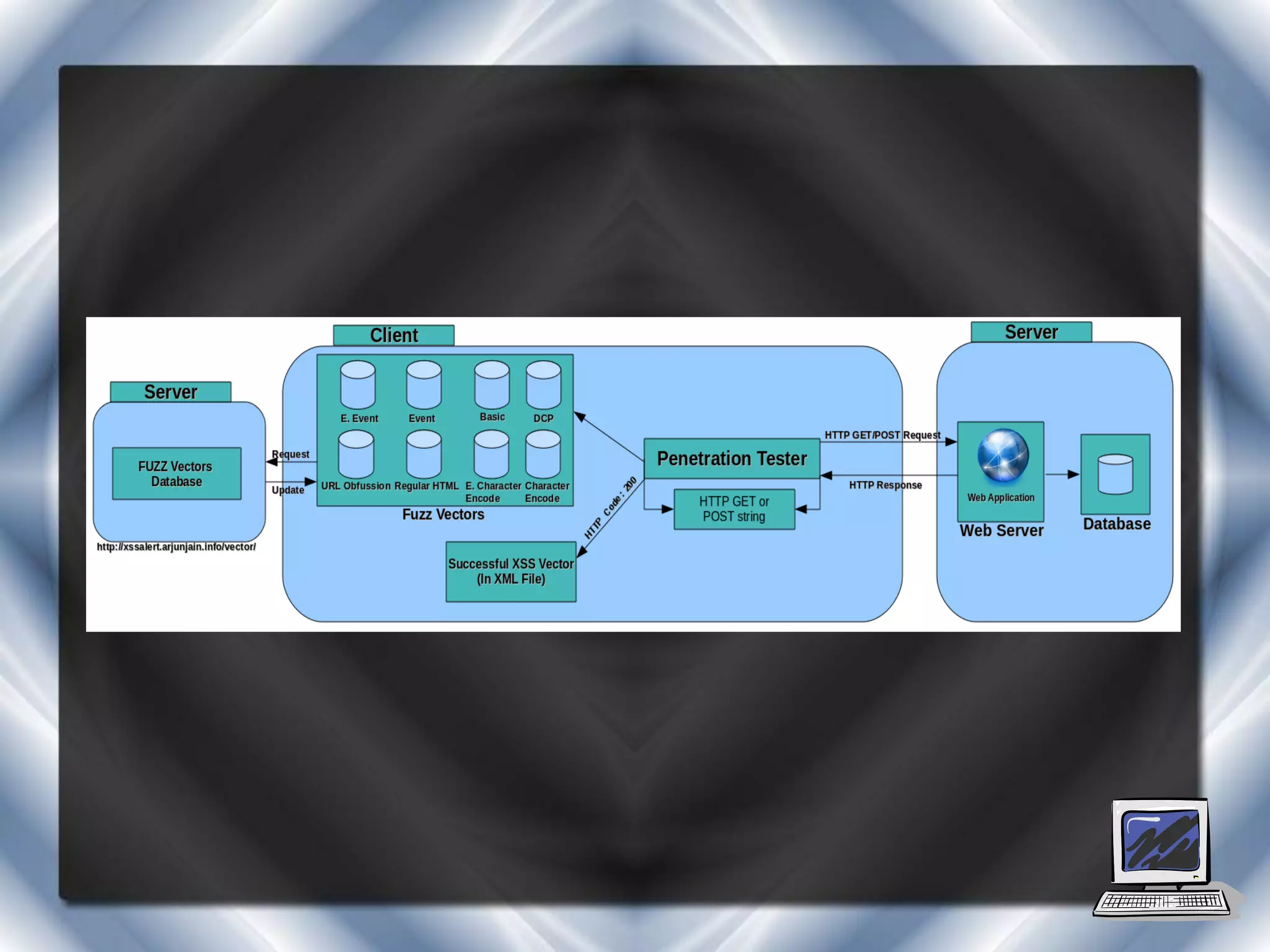
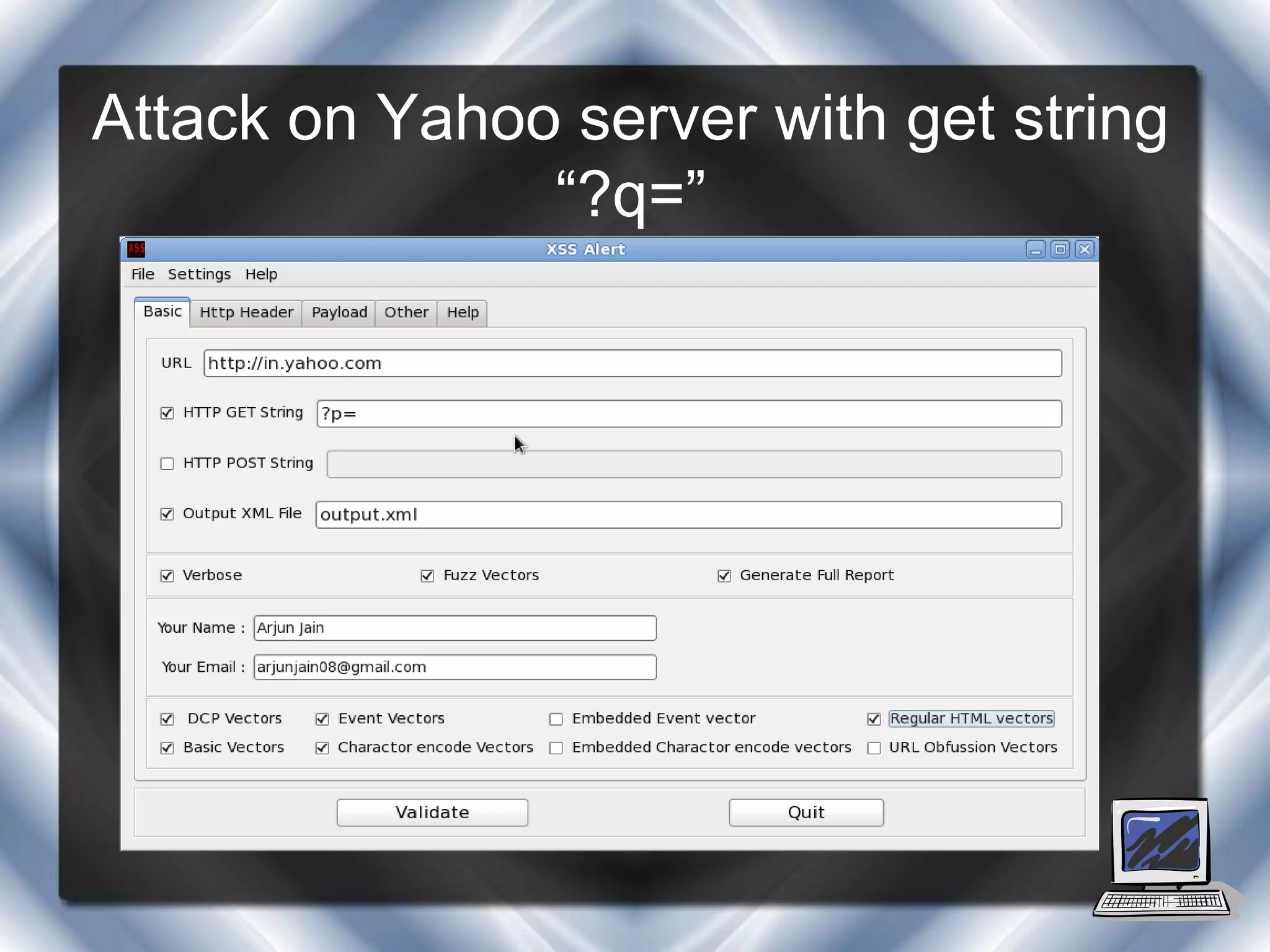
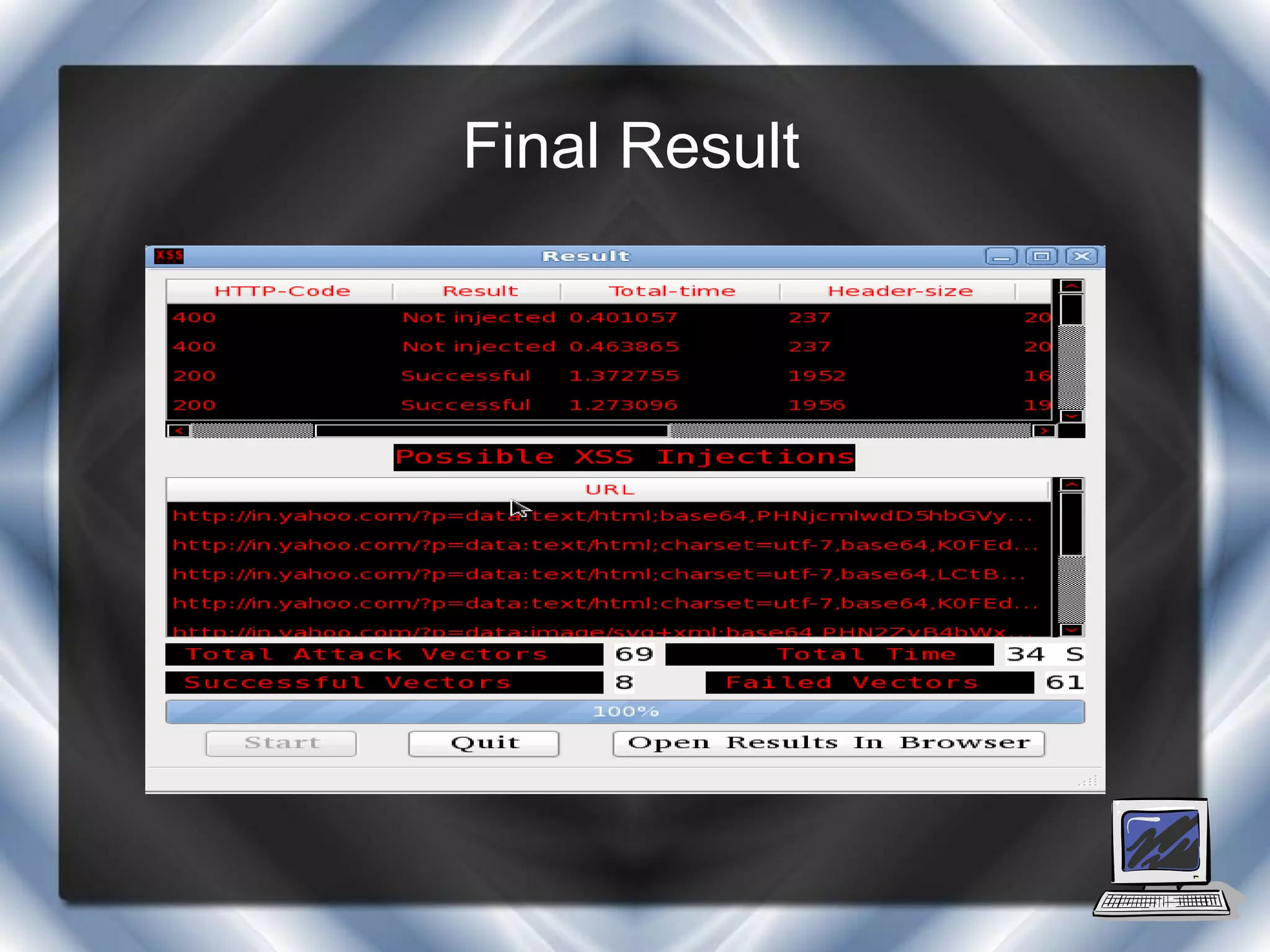
This document summarizes a presentation on cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks and the XSS Alert tool. It defines XSS as enabling attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages. It describes three types of XSS attacks and provides an example of a reflected XSS attack. It also discusses DOM security, how XSS Alert works to detect XSS vulnerabilities, and demonstrates an XSS attack on a Yahoo server.