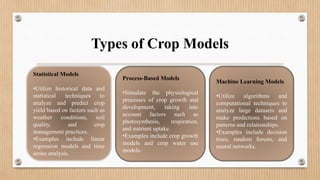
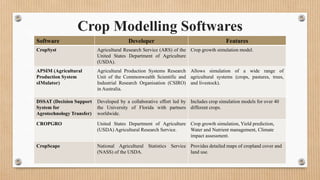
Crop modelling uses simulations and algorithms to predict crop growth and yields under various environmental conditions. It helps farmers, researchers, and policymakers make informed decisions. There are three main types of crop models: statistical models which use historical data, process-based models which simulate physiological processes, and machine learning models which analyze patterns in large datasets. Crop modelling software is used with data from remote sensing, weather, and soils to optimize crop management, assess climate change impacts, and predict yields. Popular software includes CropSyst, APSIM, DSSAT, CROPGRO, and CropScape.