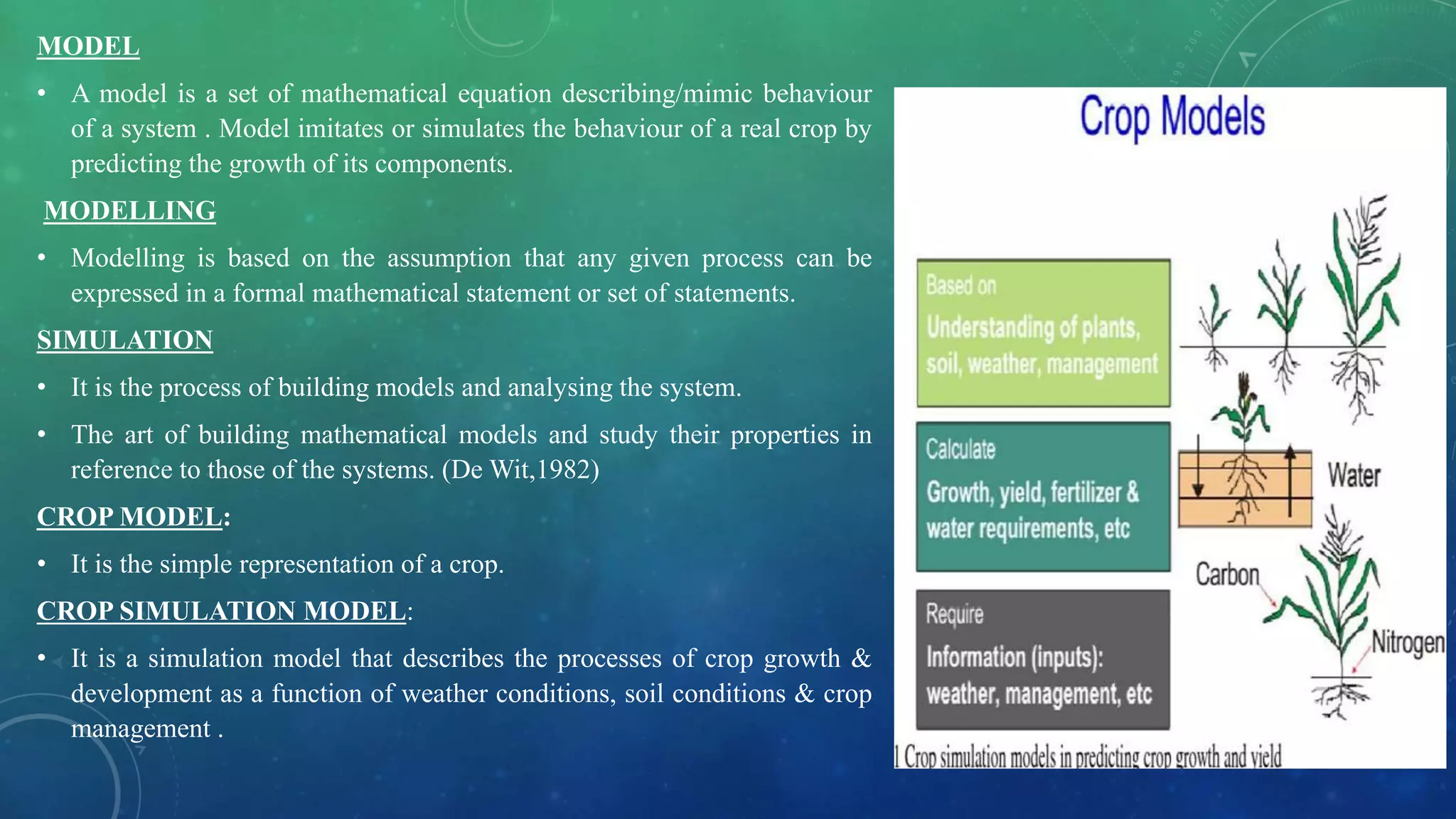
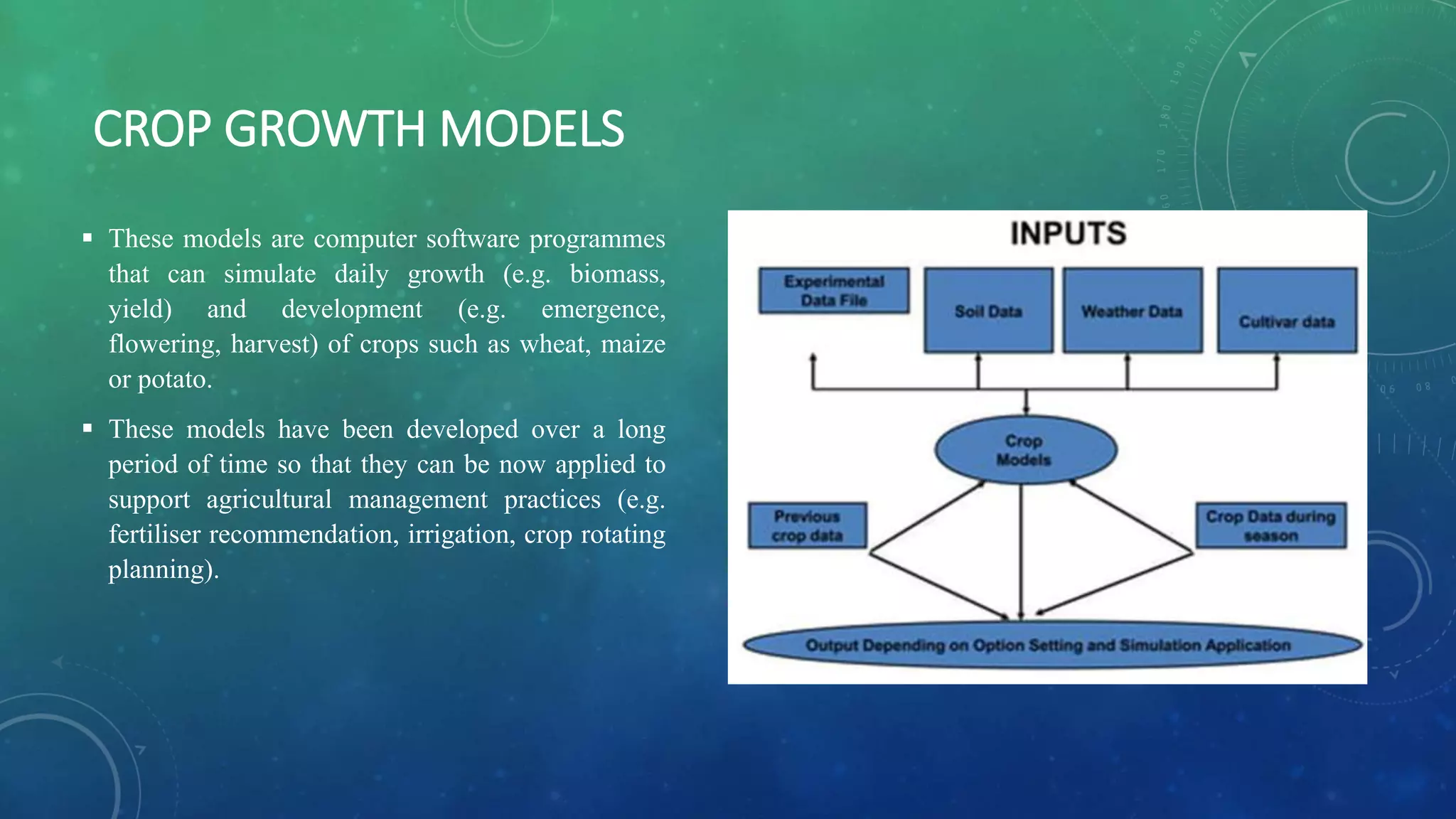
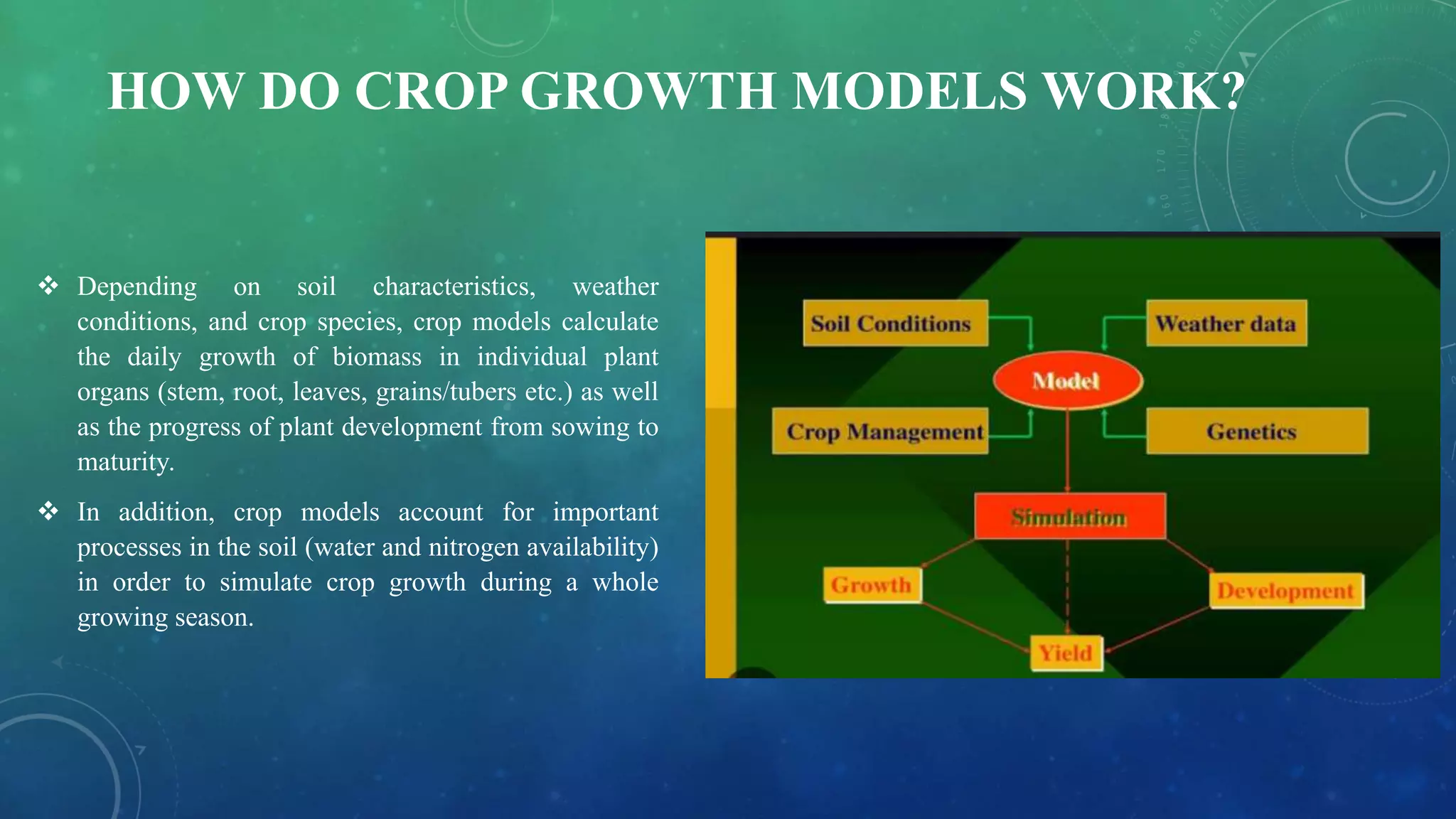
The document discusses crop growth simulation models, emphasizing their role in understanding interactions between soil, plants, and weather for optimizing crop productivity. It outlines the history, types, and applications of crop models, highlighting their importance in agricultural management, yield prediction, and adaptation to climate change. The conclusion stresses the need for properly validated models to maximize their effectiveness in supporting sustainable agriculture.