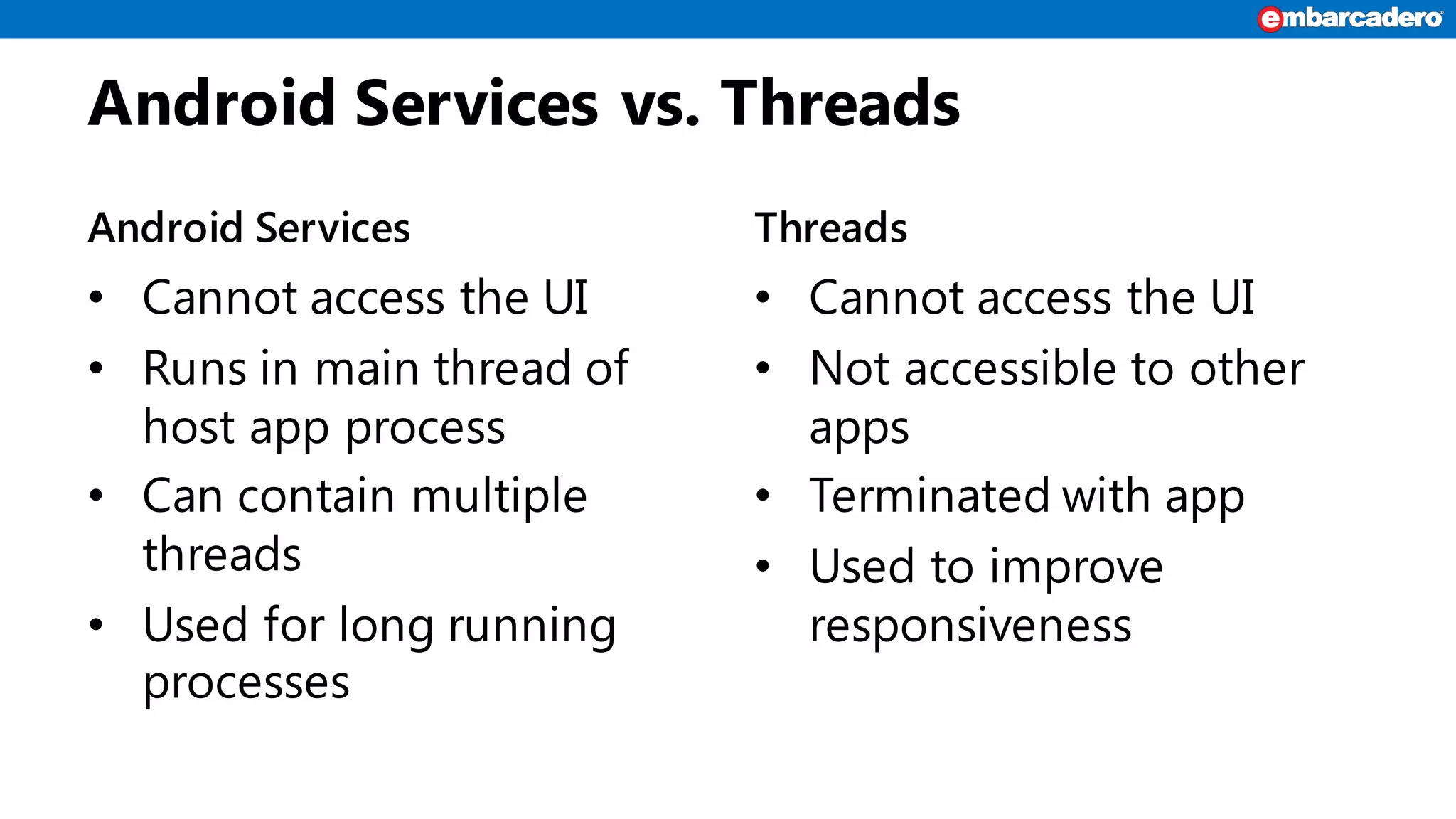
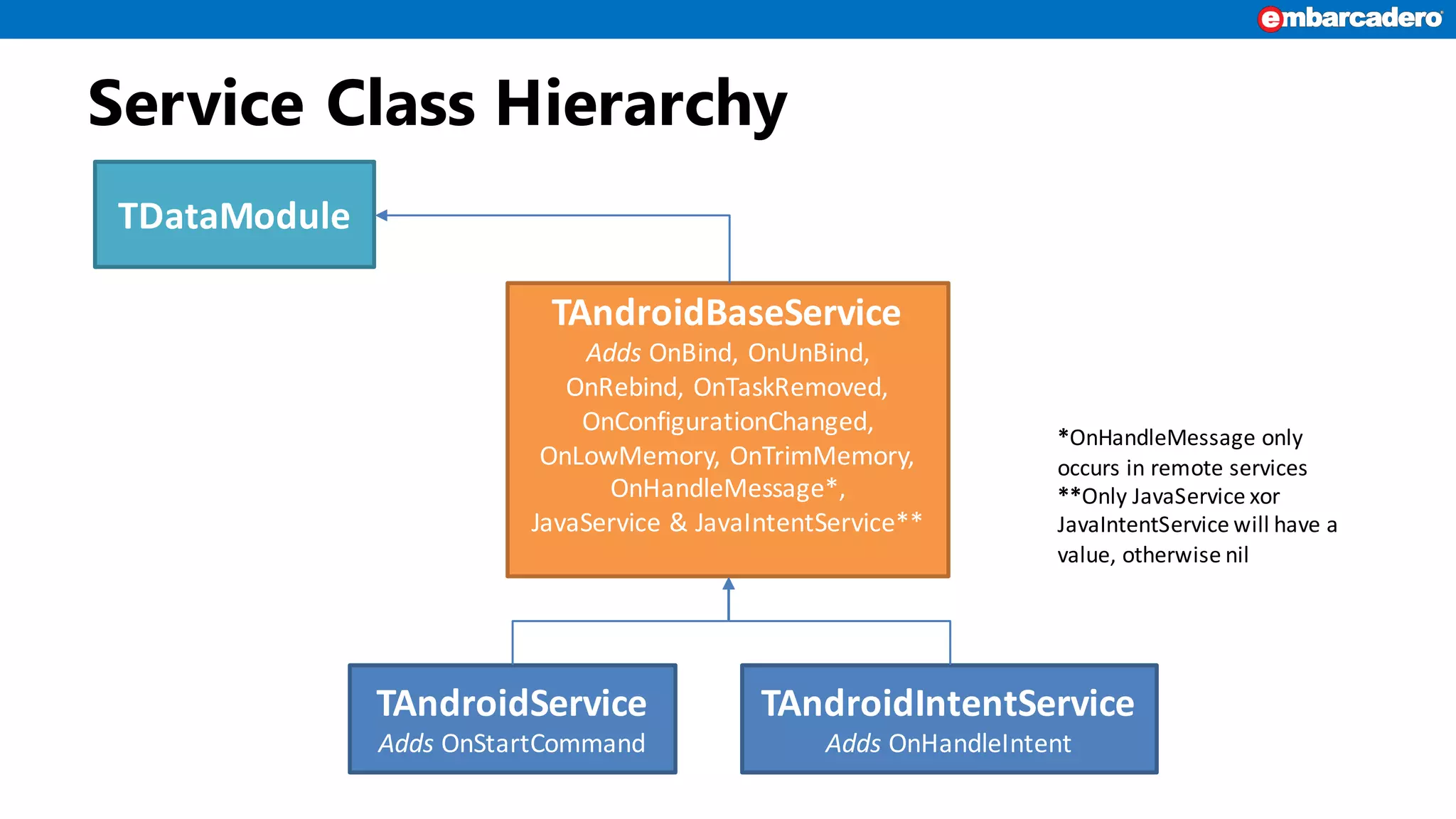
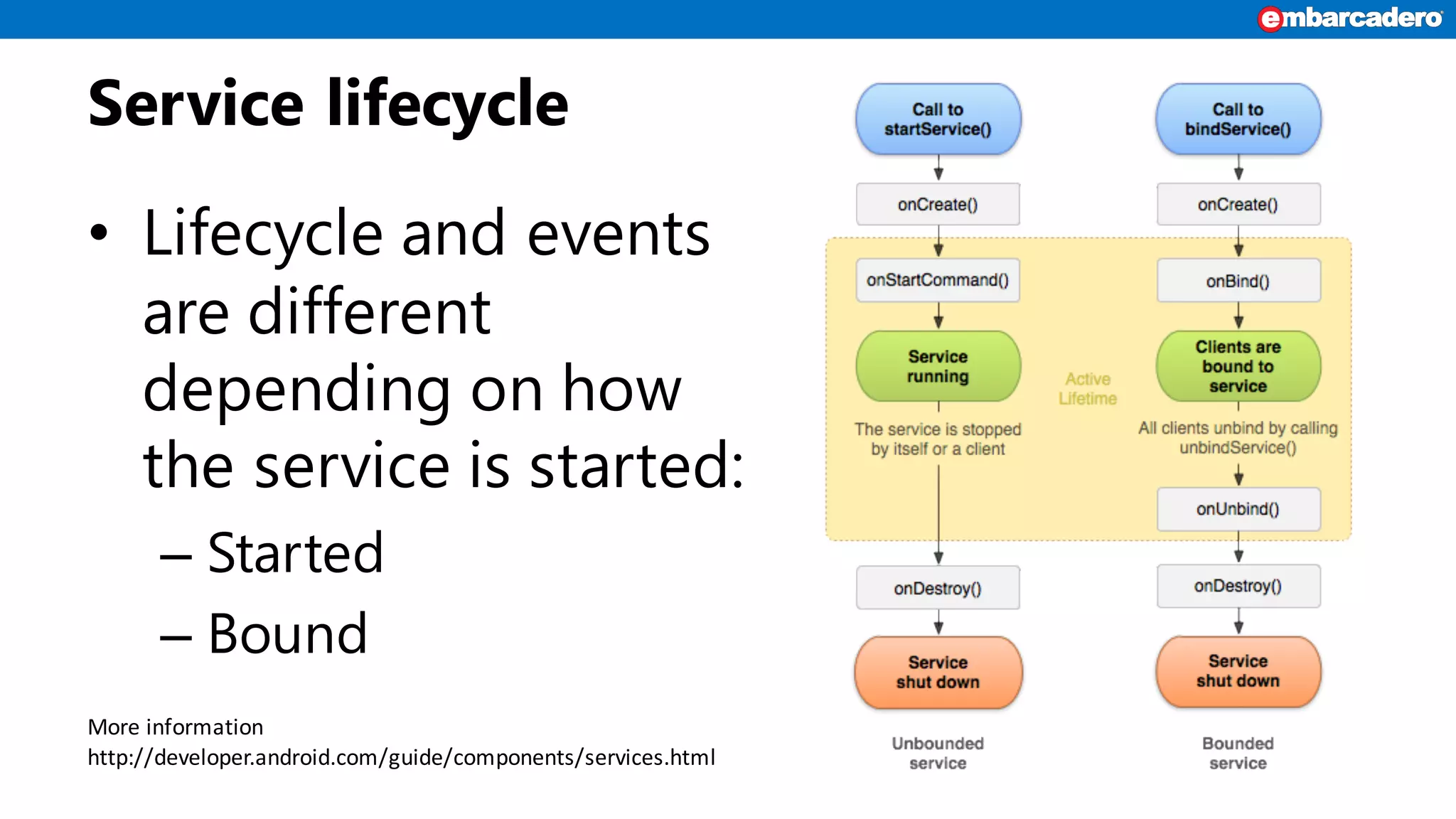
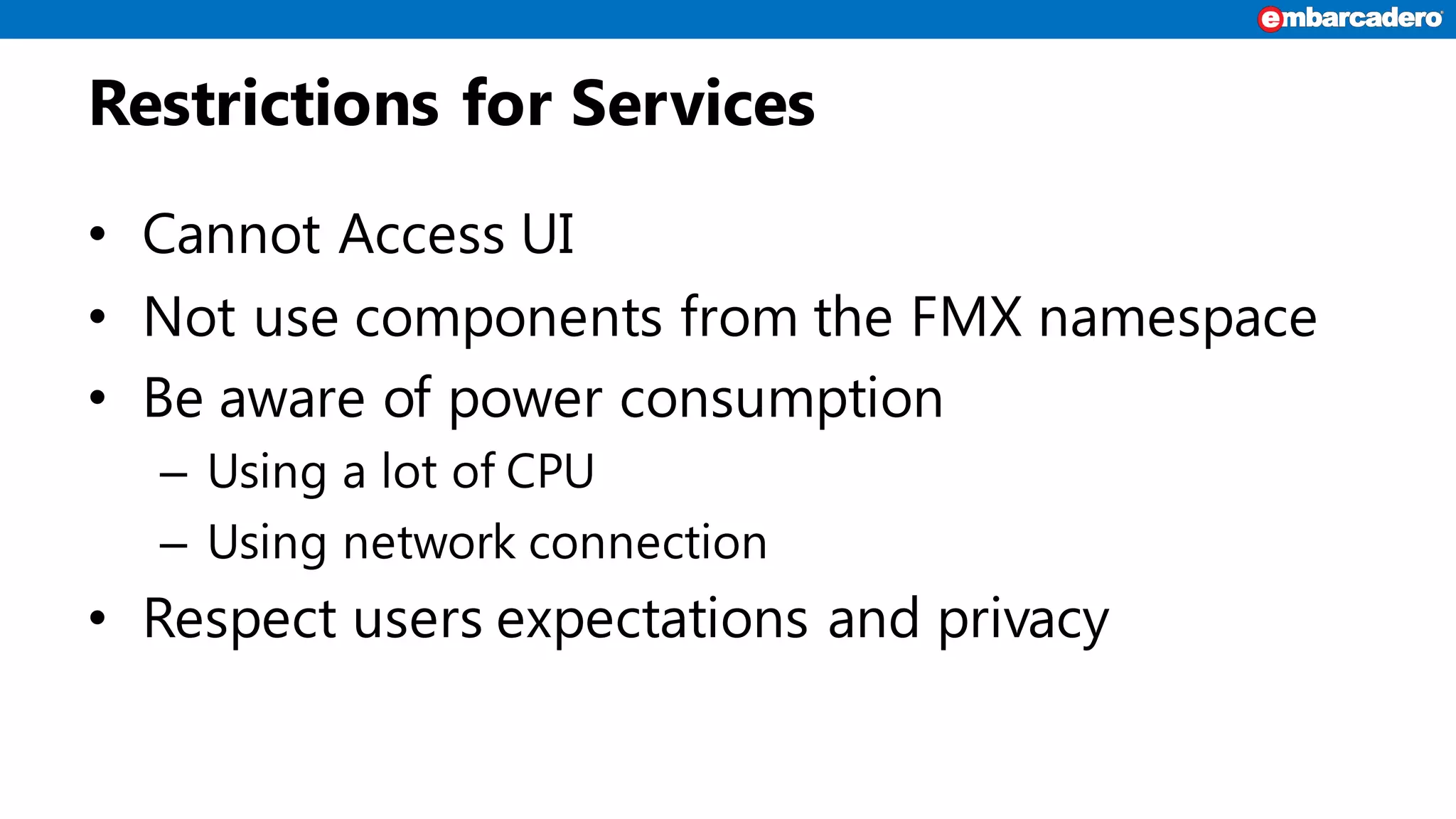
Android services enable background functionality that can run even when an app is closed, supporting multiple apps. Key types include IntentService for asynchronous tasks and local vs. remote services, with specific lifecycle management. Developers must build and reference services correctly, while considering restrictions and user privacy.