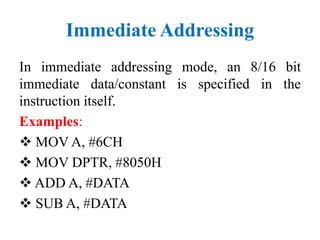
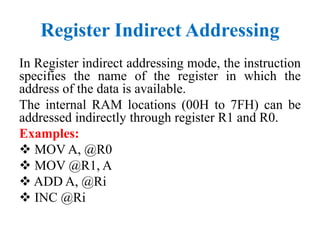
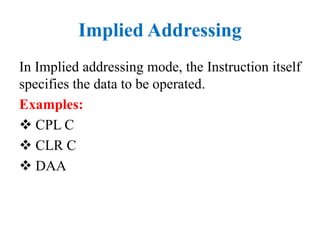
The document discusses different addressing modes used in programs. It defines addressing as the method of specifying data to be operated on by an instruction. It then describes 7 addressing modes - immediate, direct, register, register indirect, implied, relative, and indexed addressing. For each mode, it provides examples of instructions that use that addressing mode.