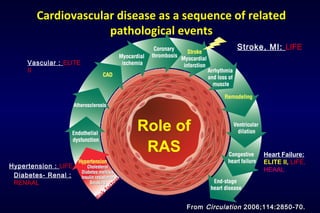
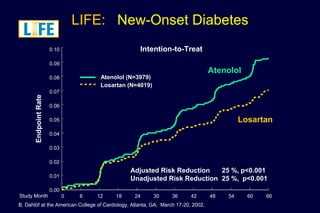
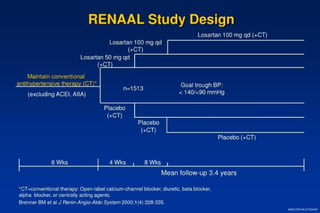
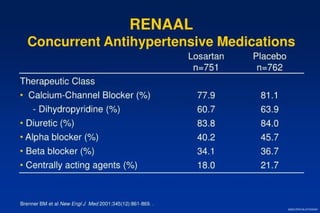
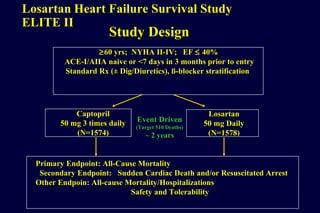
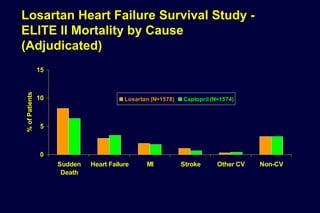
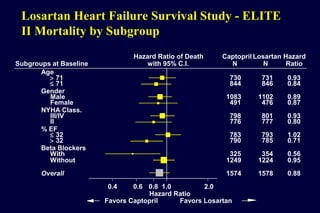
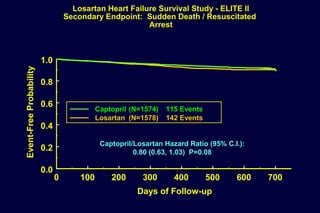
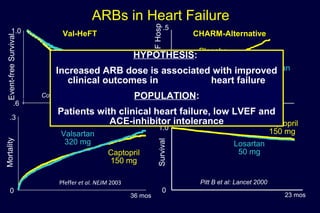
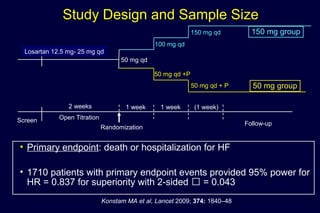
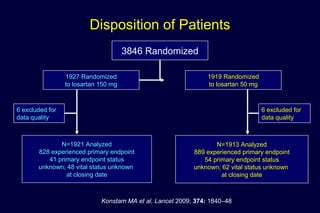
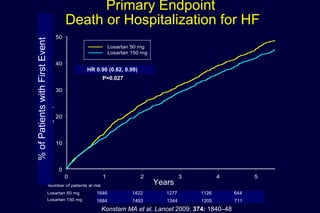
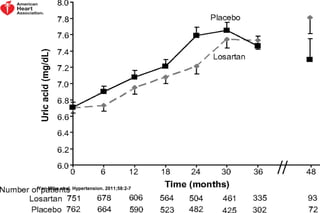
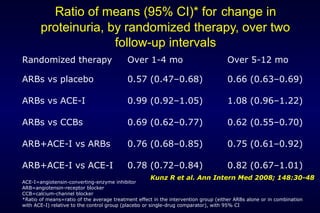
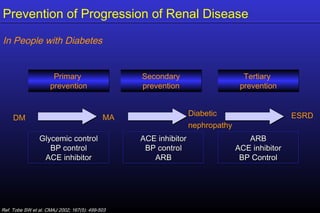
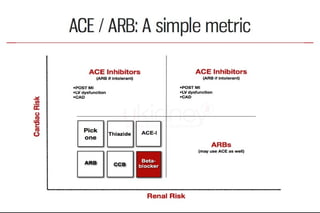
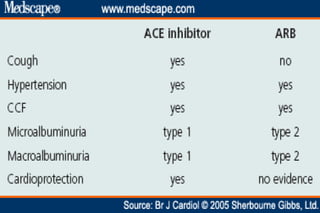
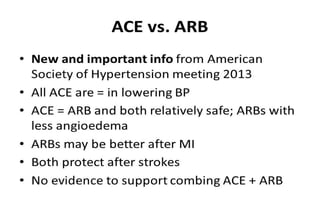
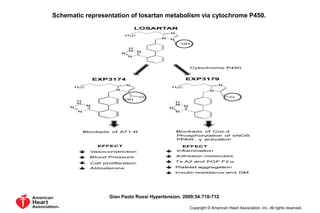
The document summarizes key findings from the LIFE study, a large clinical trial that compared losartan to atenolol for reducing cardiovascular risk in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy. The main findings were:
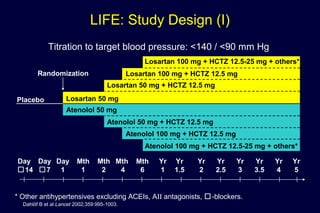
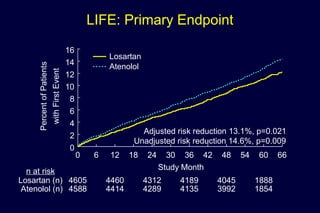
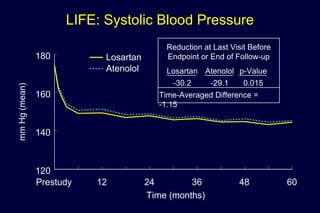
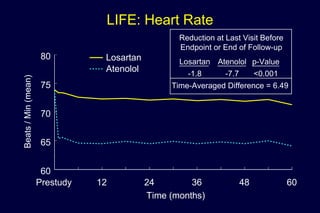
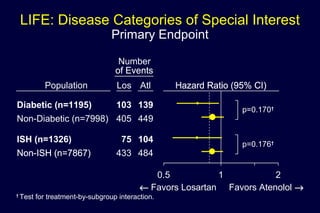
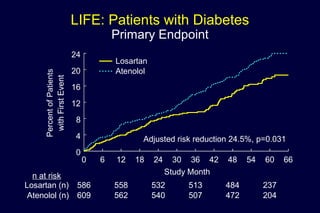
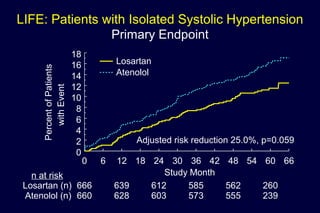
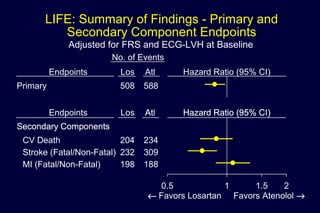
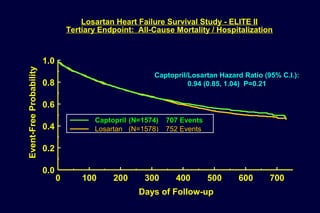
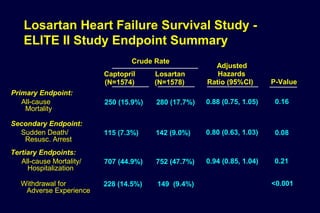
1) Losartan reduced the primary composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, stroke or myocardial infarction by 13% compared to atenolol, with comparable blood pressure reduction in both groups.
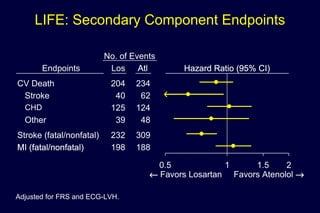
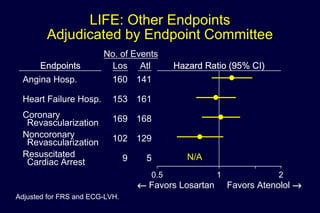
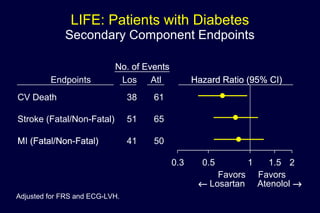
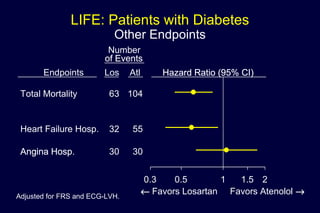
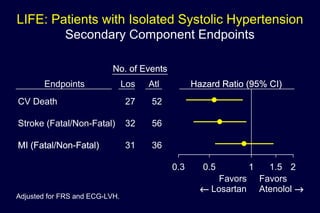
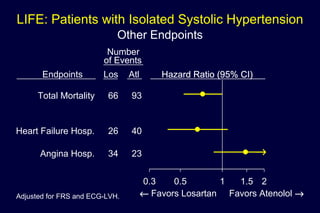
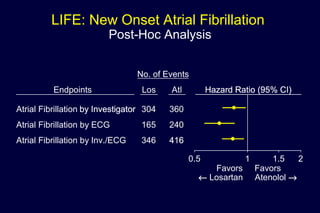
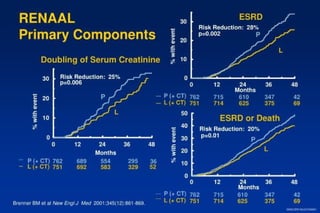
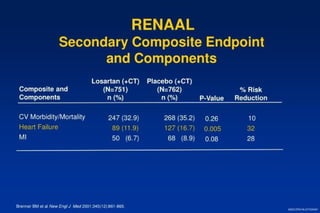
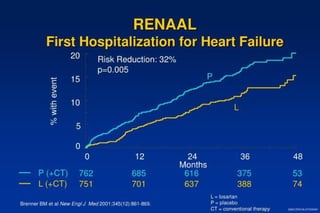
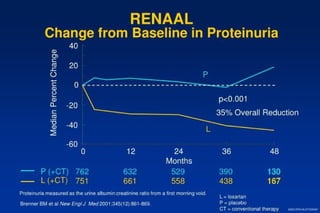
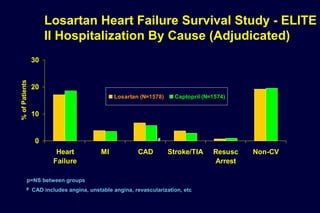
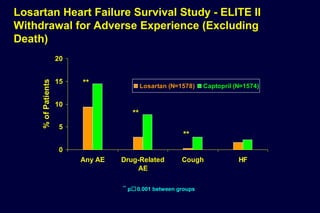
2) Secondary analyses found losartan reduced risks for several individual components of the primary endpoint including stroke and heart failure hospitalizations.
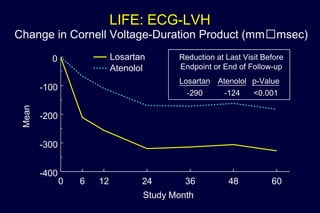
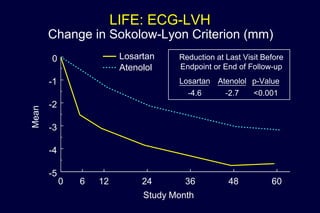
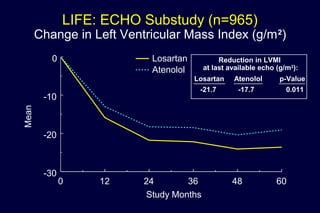
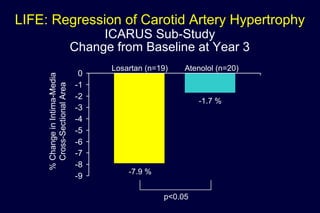
3) Losartan provided greater regression of left ventricular hypertrophy compared to atenolol based on electrocardiogram and echocardiogram assessments