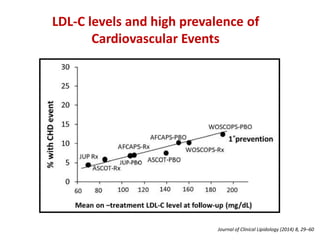
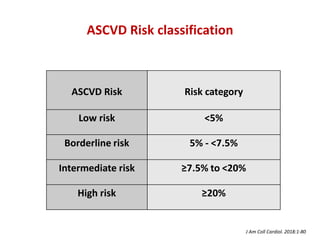
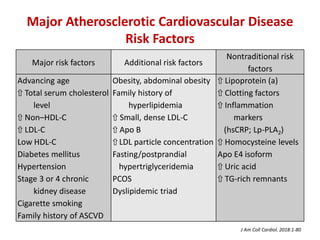
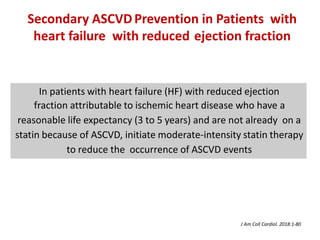
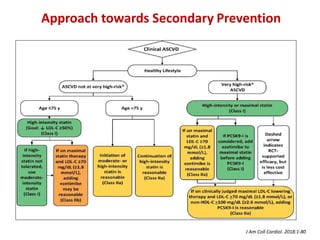
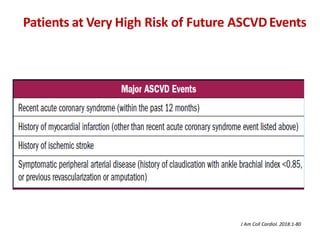
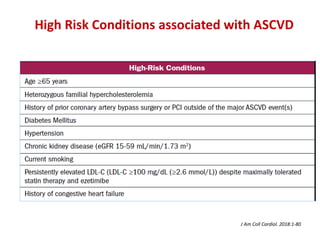
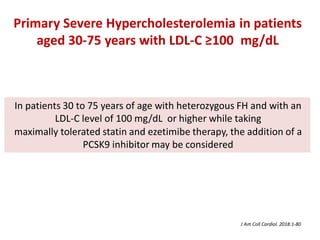
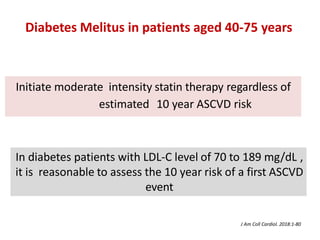
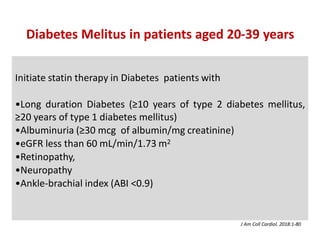
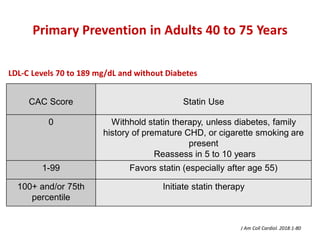
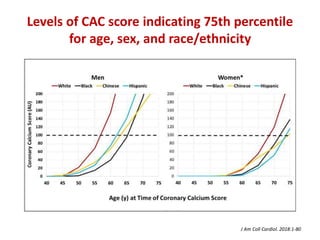
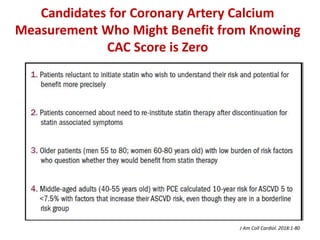
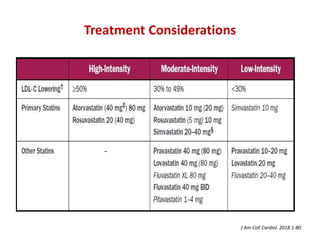
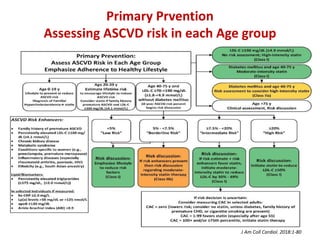
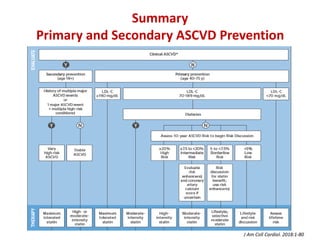
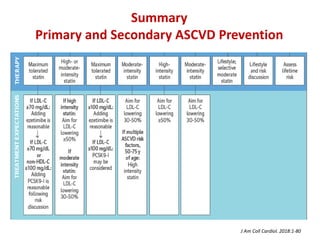
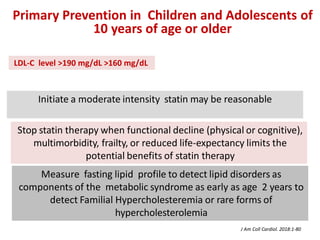
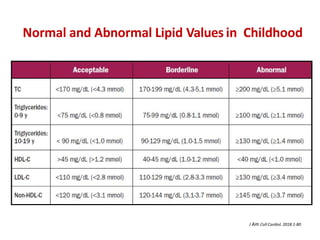
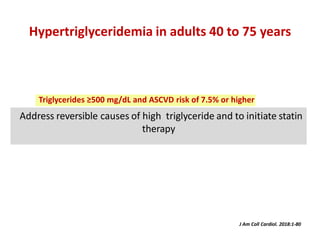
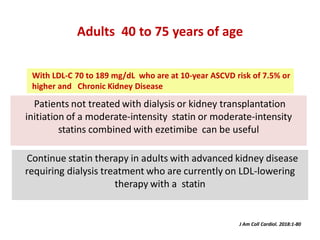
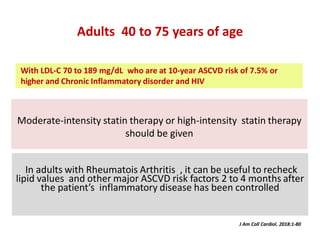
The ACC/AHA guidelines on lipid management emphasize the importance of primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) while identifying patients' risk factors for effective treatment decisions. Key recommendations include starting statin therapy based on LDL-C levels and ASCVD risk assessment, particularly in high-risk individuals, with the addition of non-statin therapies for those not meeting cholesterol targets. The guidelines stress personalized treatment plans, particularly for adults aged 40-75 and those with severe hypercholesterolemia, incorporating discussions on risk factors and coronary artery calcium scores as part of the decision-making process.