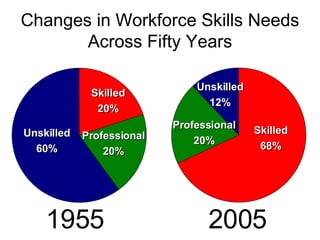
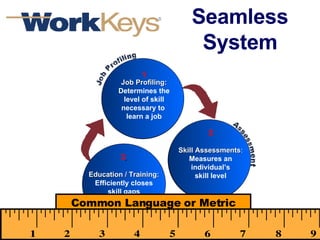
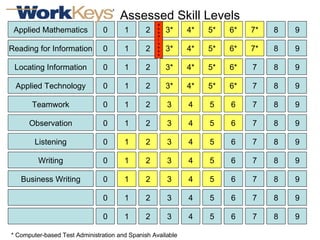
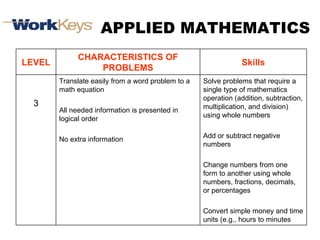
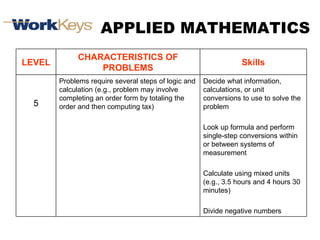
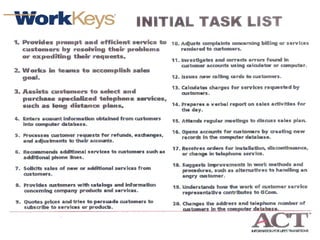
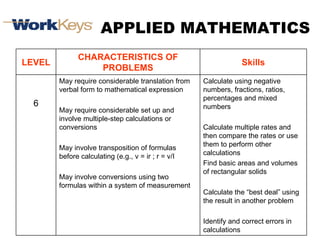
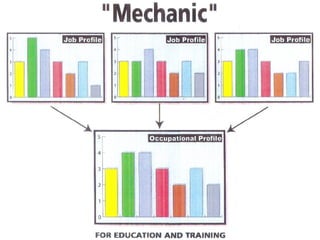
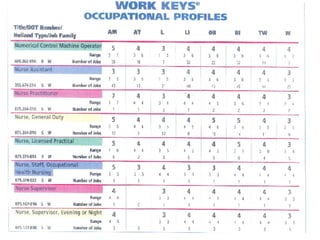
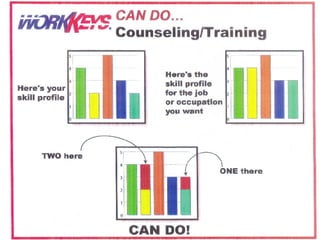
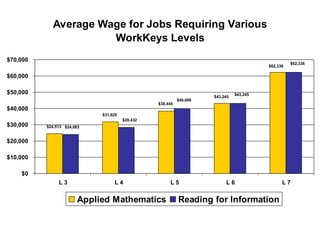
The document summarizes changes in workforce skill needs over 50 years from 1955 to 2005. Unskilled jobs decreased from 60% to 12% while skilled jobs increased from 20% to 68%. It then discusses using skills assessments to determine an individual's skill level, identify gaps, and provide targeted training to efficiently close those gaps. A common language of key skills can help define job requirements and measure worker competencies.