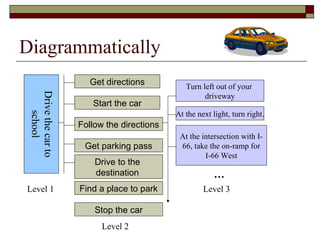
The document discusses algorithms, defining them as logical sequences of steps to solve problems and listing properties of good algorithms such as being simple, complete, correct, and having appropriate abstraction. It also provides examples of algorithms and outlines steps for developing algorithms, including analyzing the problem, designing a solution, implementing the program, testing it, and validating it works for all cases.