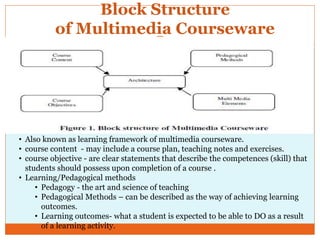
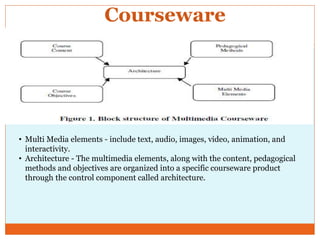
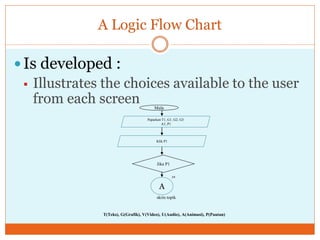
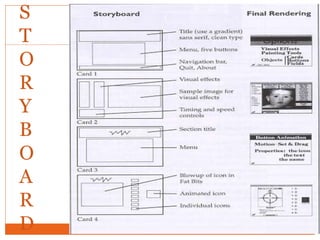
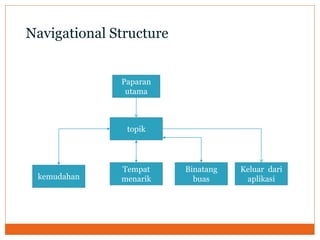
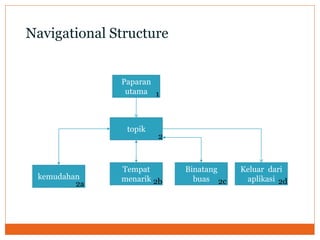
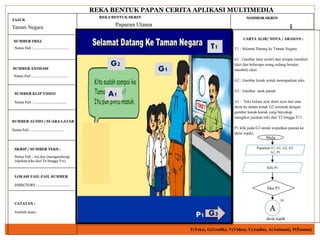
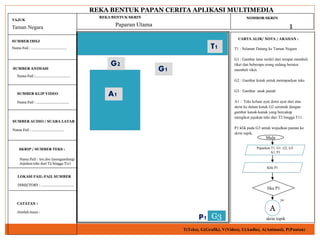
Courseware refers to educational software used for teaching or self-learning purposes. It combines course content with various multimedia elements like text, audio, images, video and interactivity. The block structure of multimedia courseware includes course content, objectives, pedagogical methods and learning outcomes. It organizes these elements along with multimedia using an architectural control component. Storyboarding is used to plan, produce and evaluate multimedia presentations by providing a written synopsis of the multimedia resources and their order in the finished presentation.