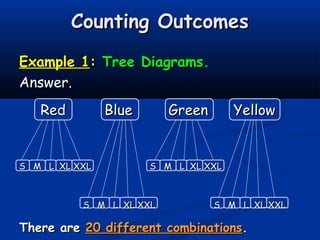
This document discusses methods for counting outcomes of probability experiments:
(1) Tree diagrams can be used to visually represent and count all possible outcomes.
(2) The Fundamental Counting Principle uses multiplication to calculate the total number of outcomes based on the number of possibilities in each part of an experiment.
Examples demonstrate how to apply these methods to problems involving combinations of options, such as clothing choices. Tree diagrams are best for directly showing outcomes, while the counting principle provides a formulaic approach.