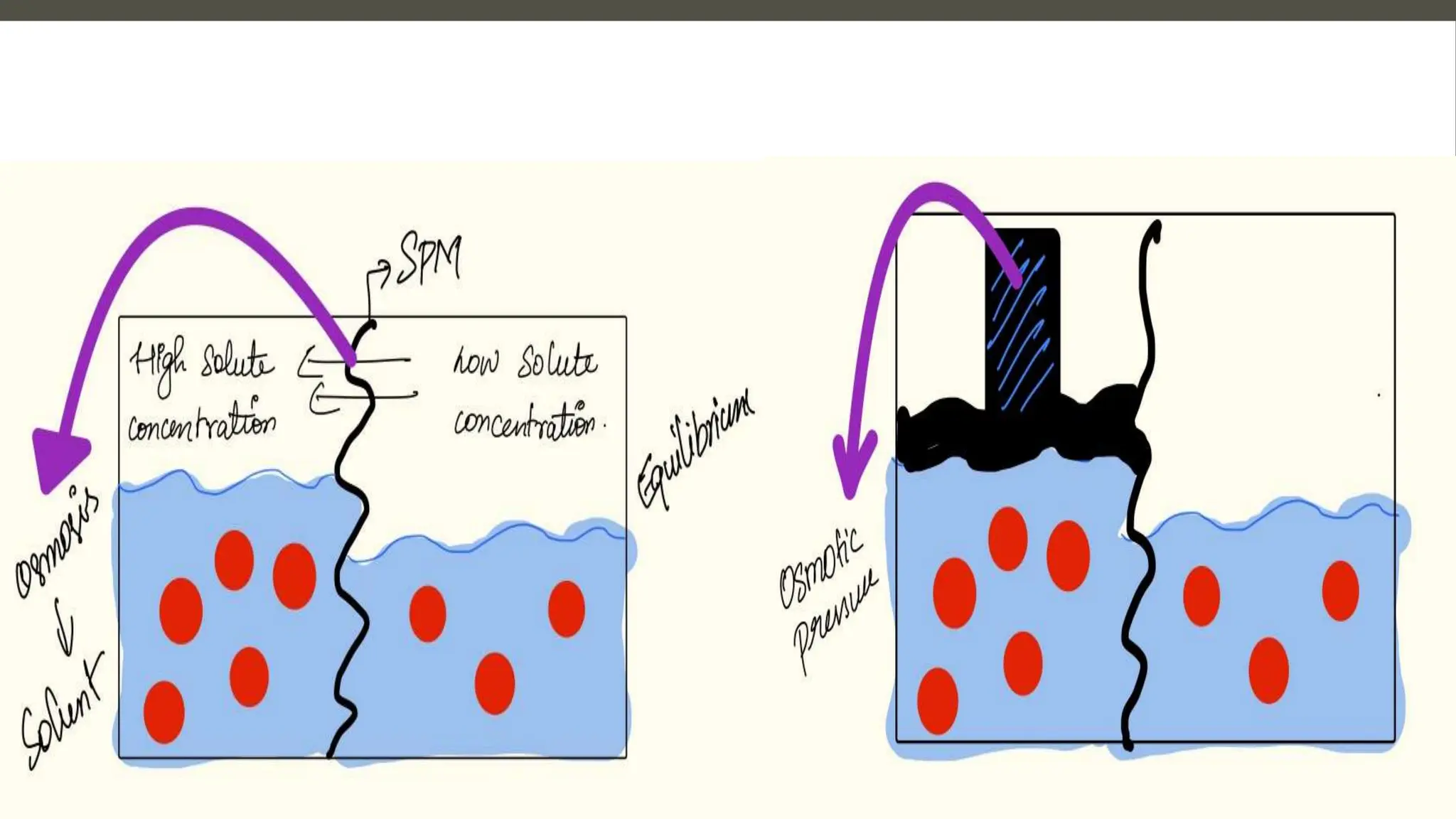
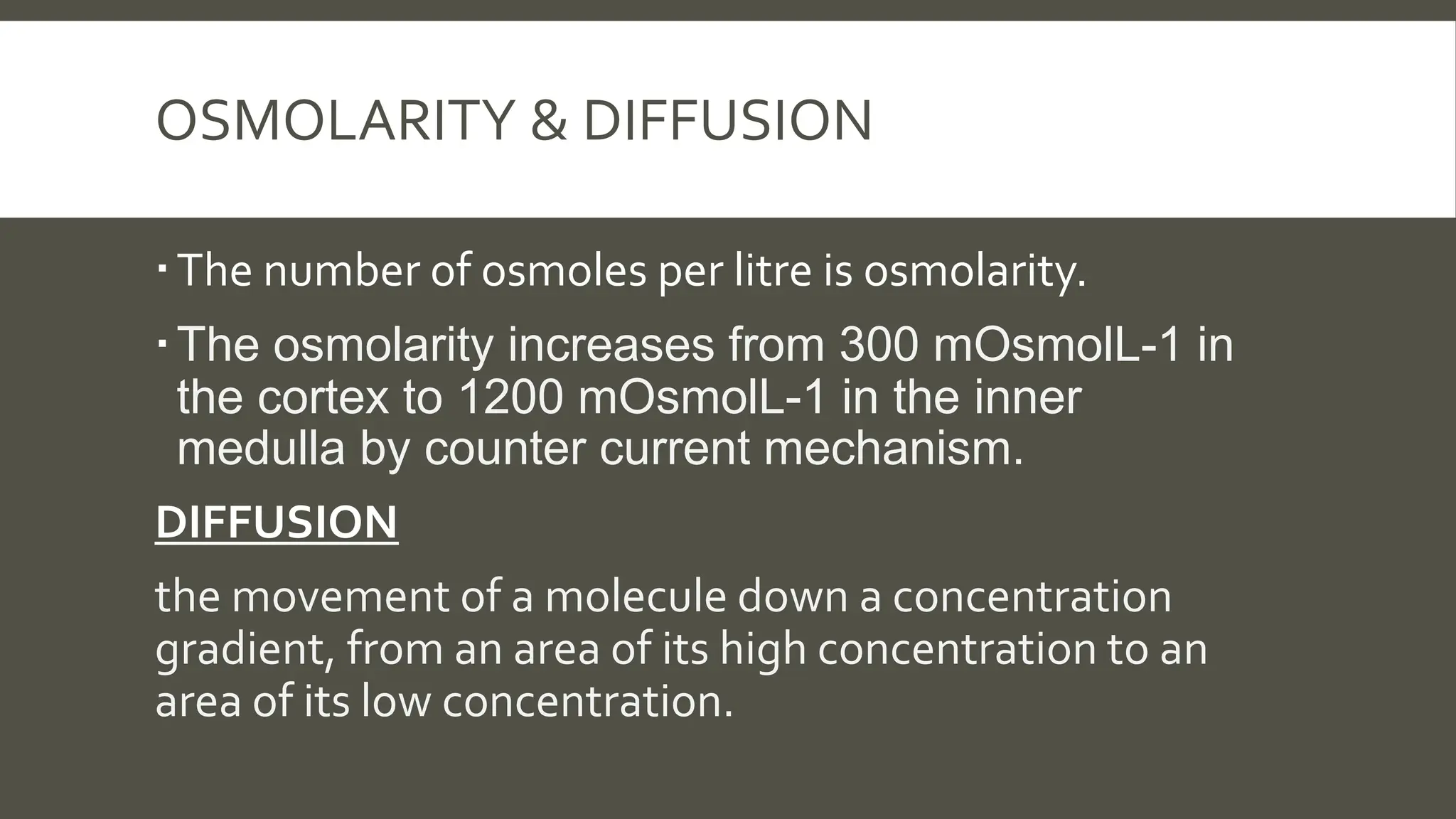
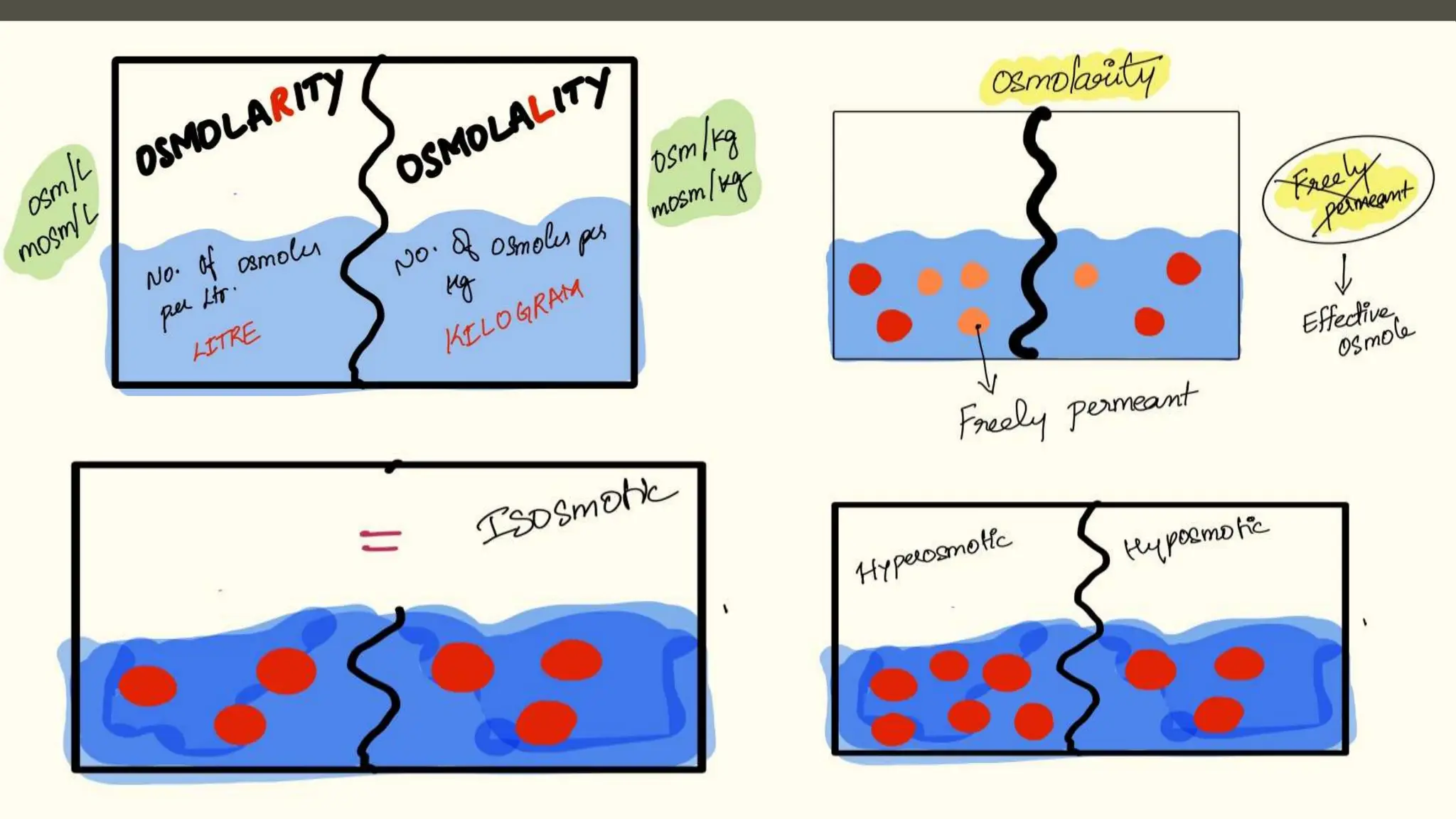
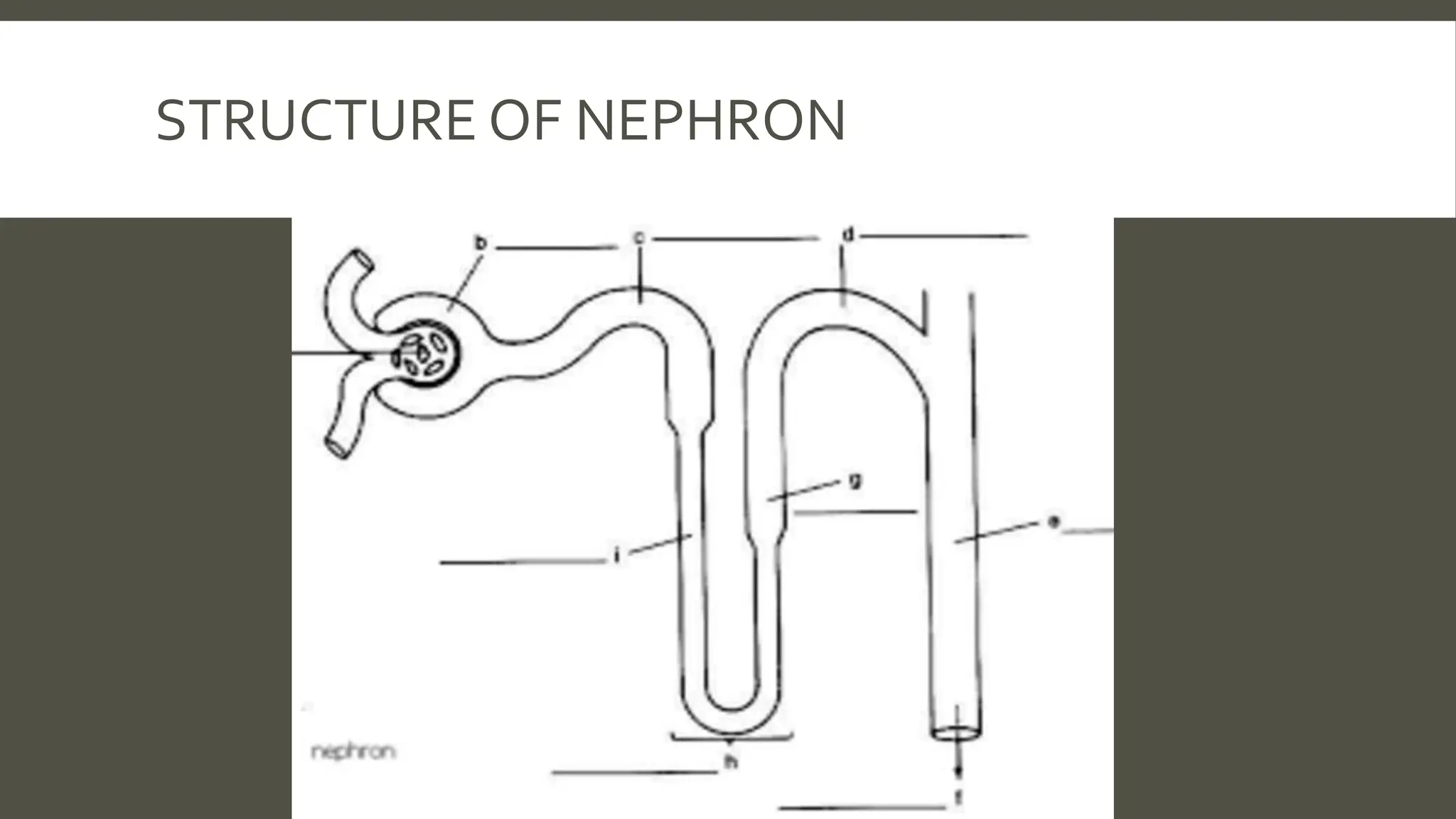
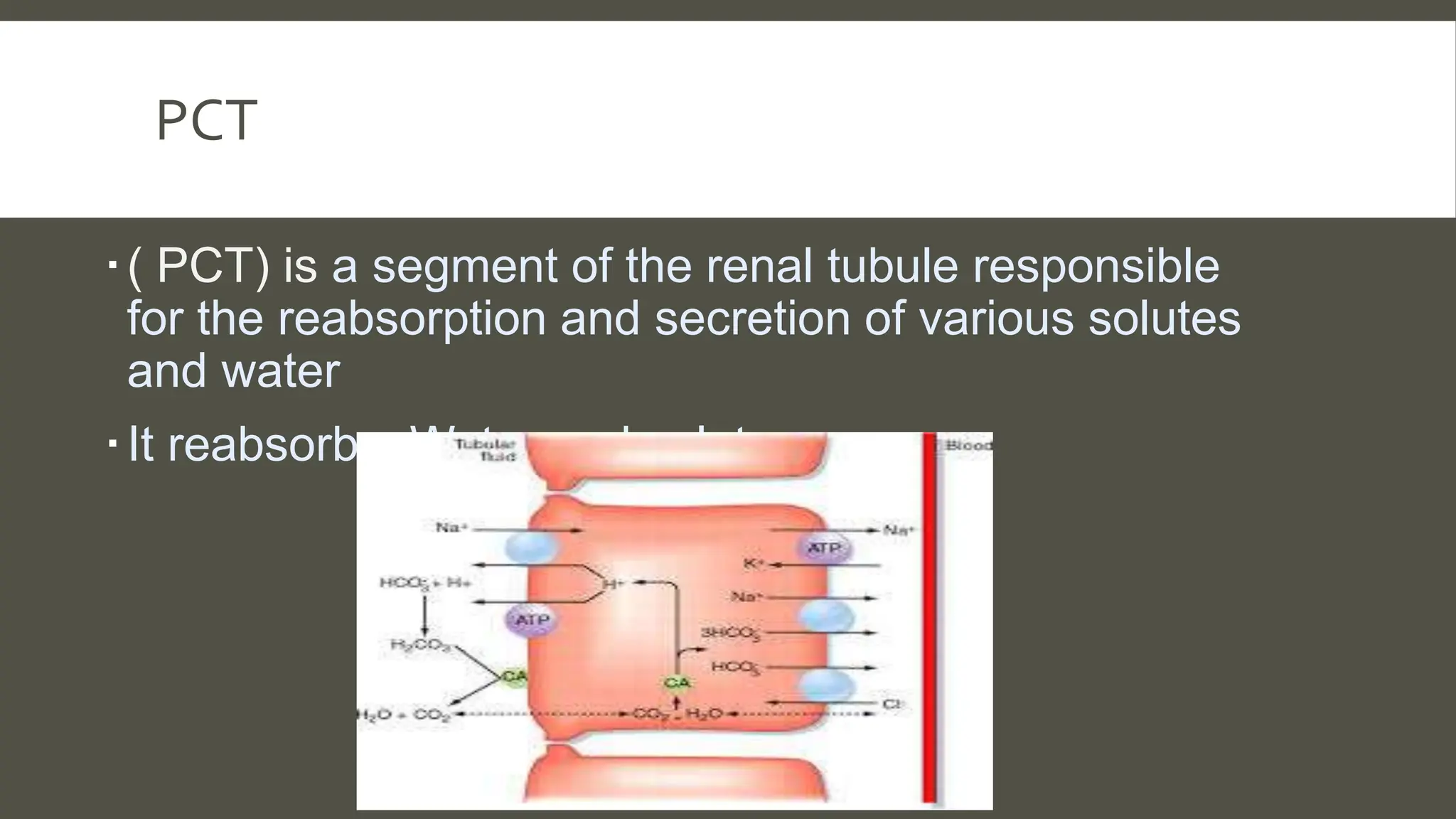
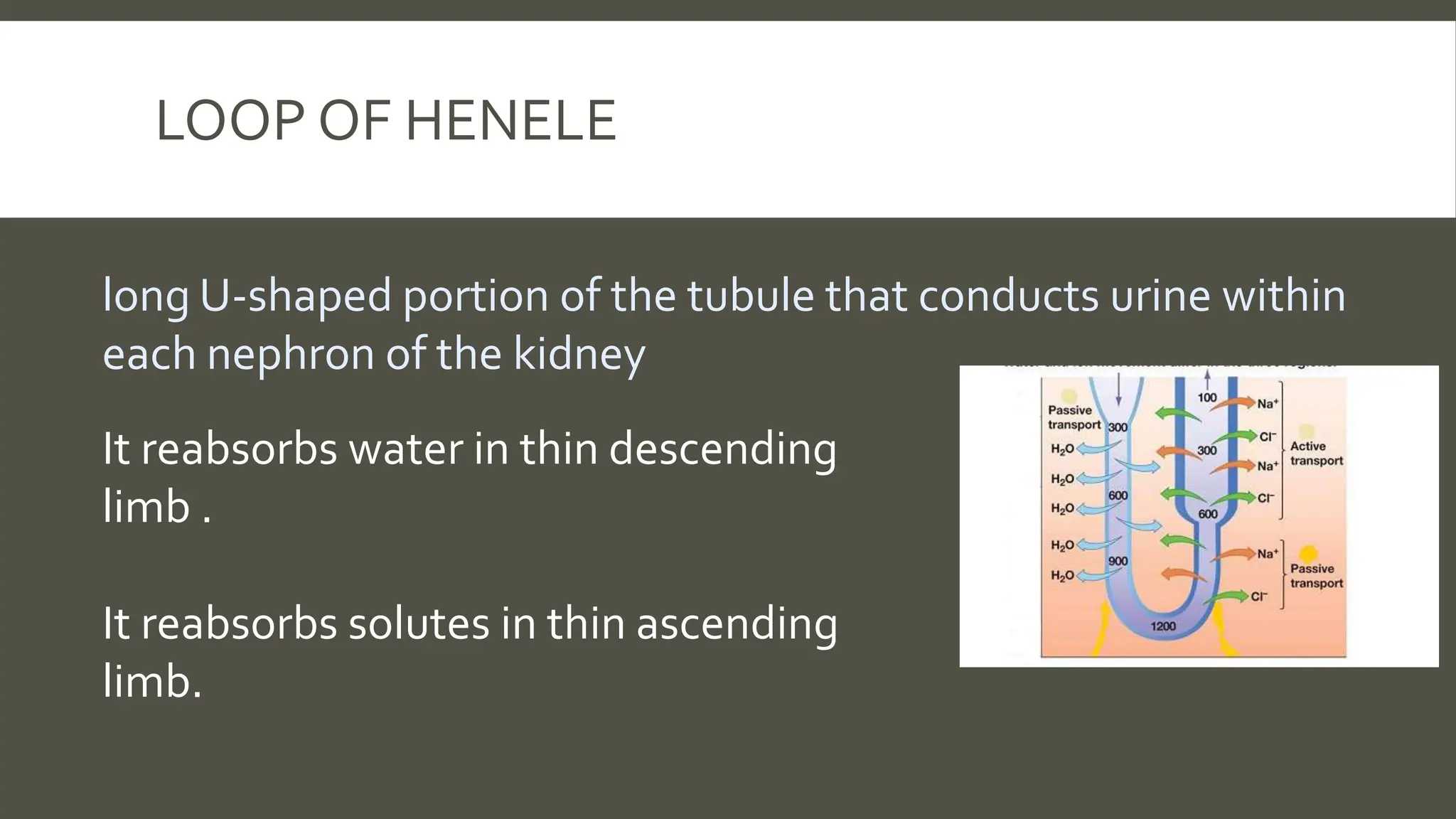
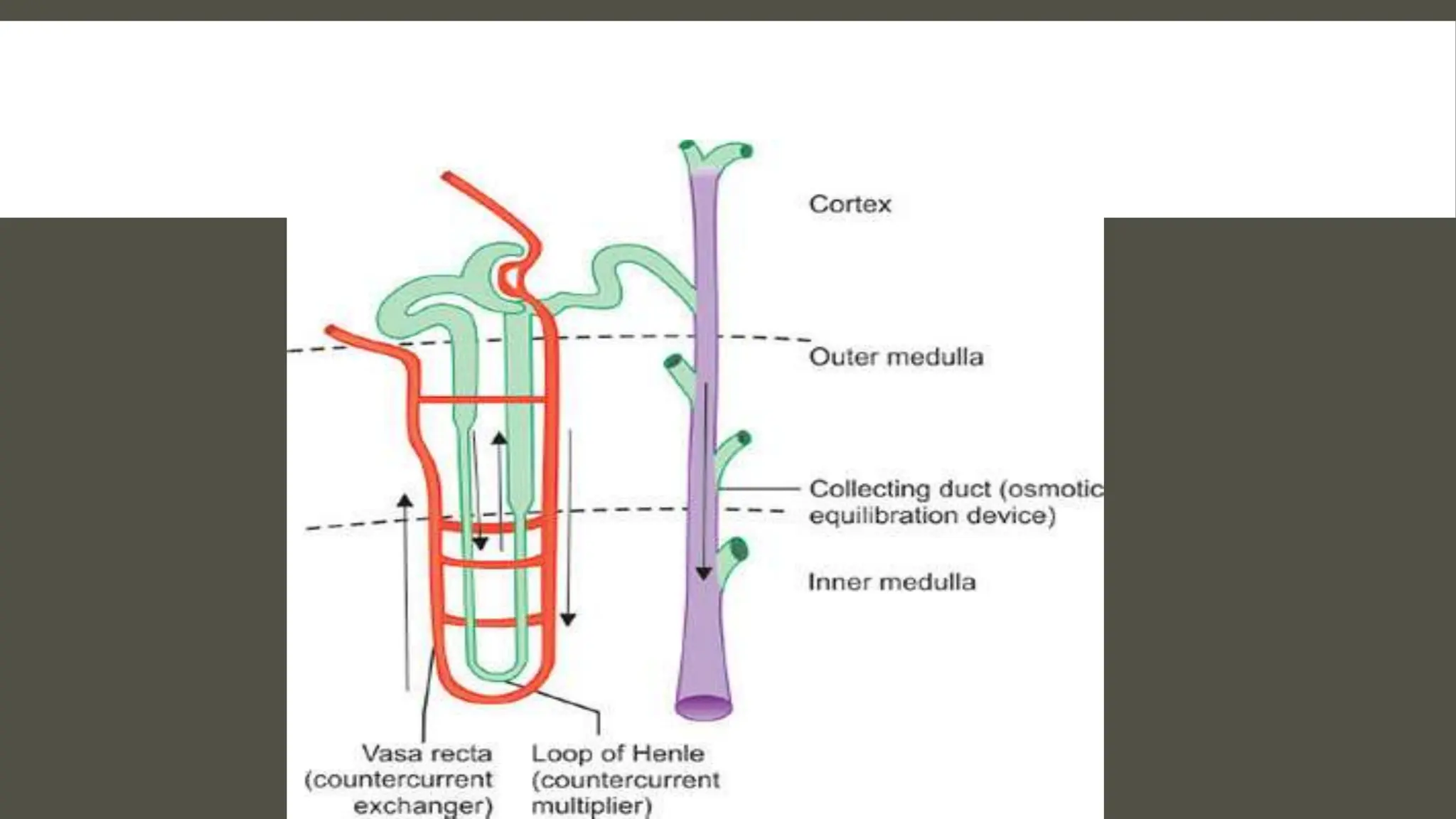
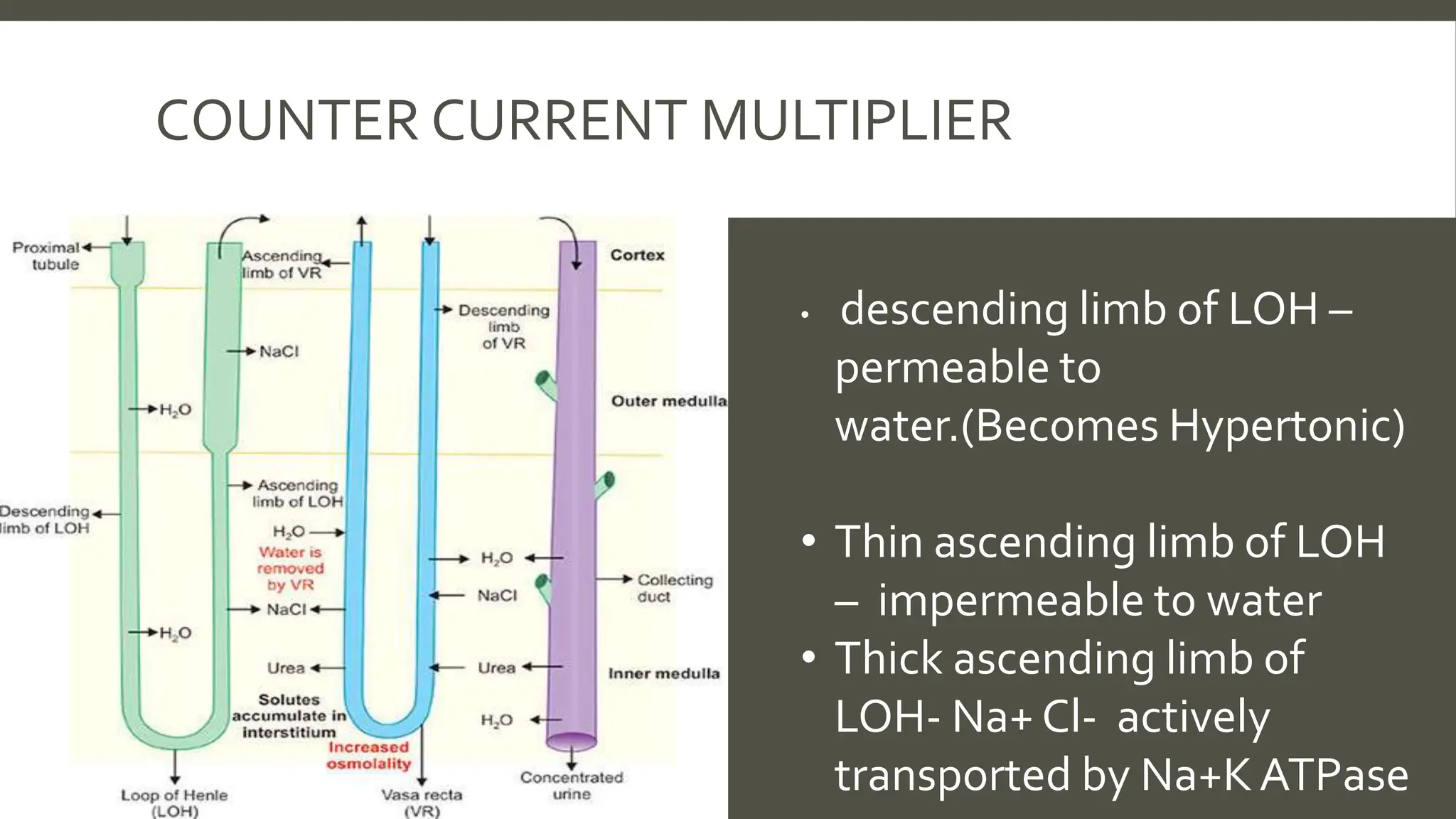
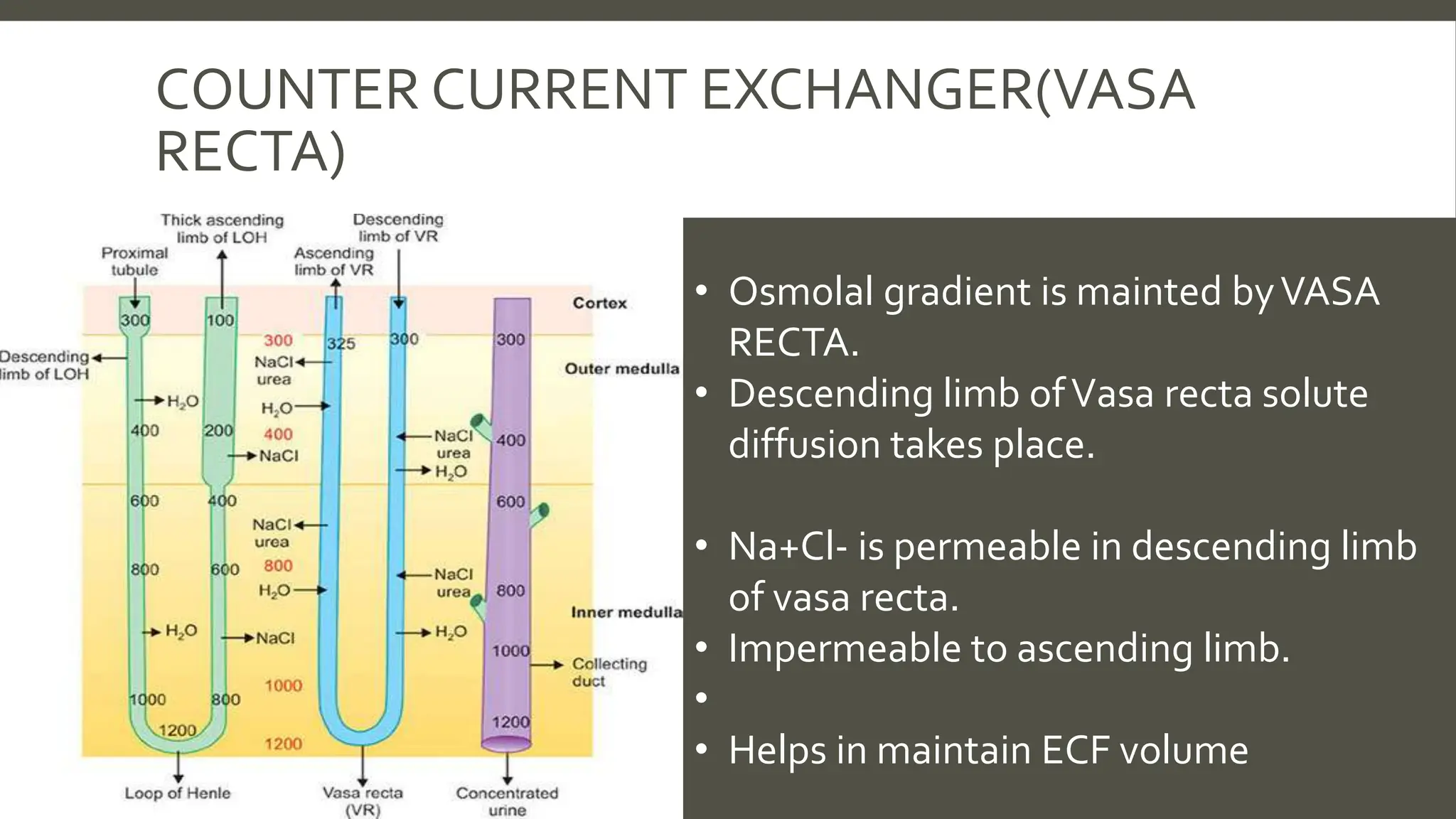
The document explains the counter current mechanism in the nephron, detailing osmolarity, diffusion, and the structure and function of different nephron segments. It describes how the descending and ascending limbs of the loop of Henle contribute to creating an osmotic gradient, which is maintained by the vasa recta. Additionally, it highlights the roles of the collecting duct and the importance of urea transport in regulating water movement in the kidney.