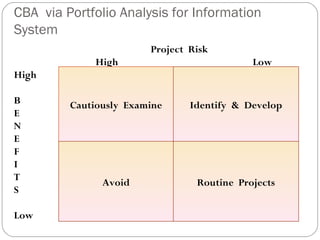
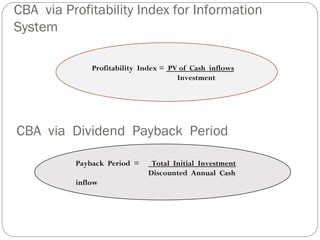
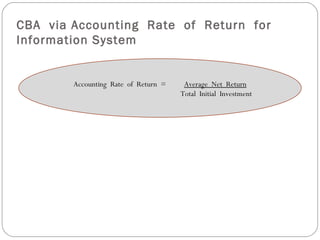
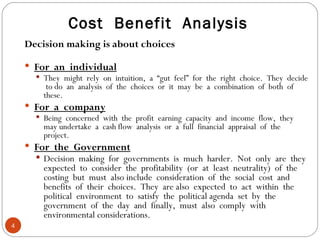
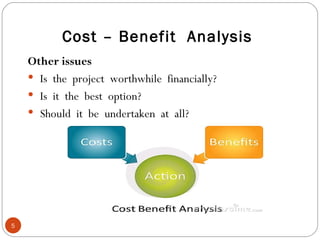
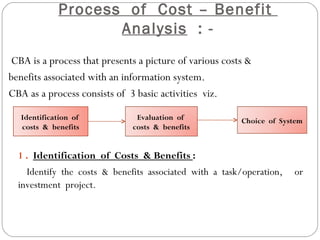
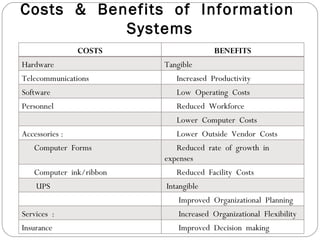
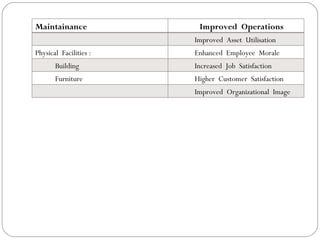
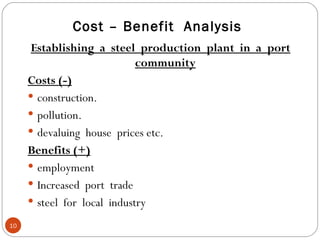
The document discusses the concept of cost-benefit analysis (CBA) for evaluating information systems projects. CBA measures and compares the costs and benefits of a project to determine if its benefits outweigh its costs. The CBA process involves identifying the tangible and intangible costs and benefits of a project, evaluating them, and choosing the system with the lowest costs but highest benefits. CBA is useful for decision making by individuals, companies, and governments.




![Cost - Benefit Analysis Method Identify all possible alternatives. Prepare table showing life of the project i.e. year to year basis. Establish Cost of project during the year including capital, operating and maintenance costs, social and other tangible costs Establish total benefits to be obtained from project by way of sales of goods and services including value of social benefits. Cost calculated at rate of interest such that NPV = Zero Ranking in order of [ benefit – cost ] or [ benefit / cost ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cba-111225024155-phpapp01/85/Cost-Benefit-Analysis-11-320.jpg)