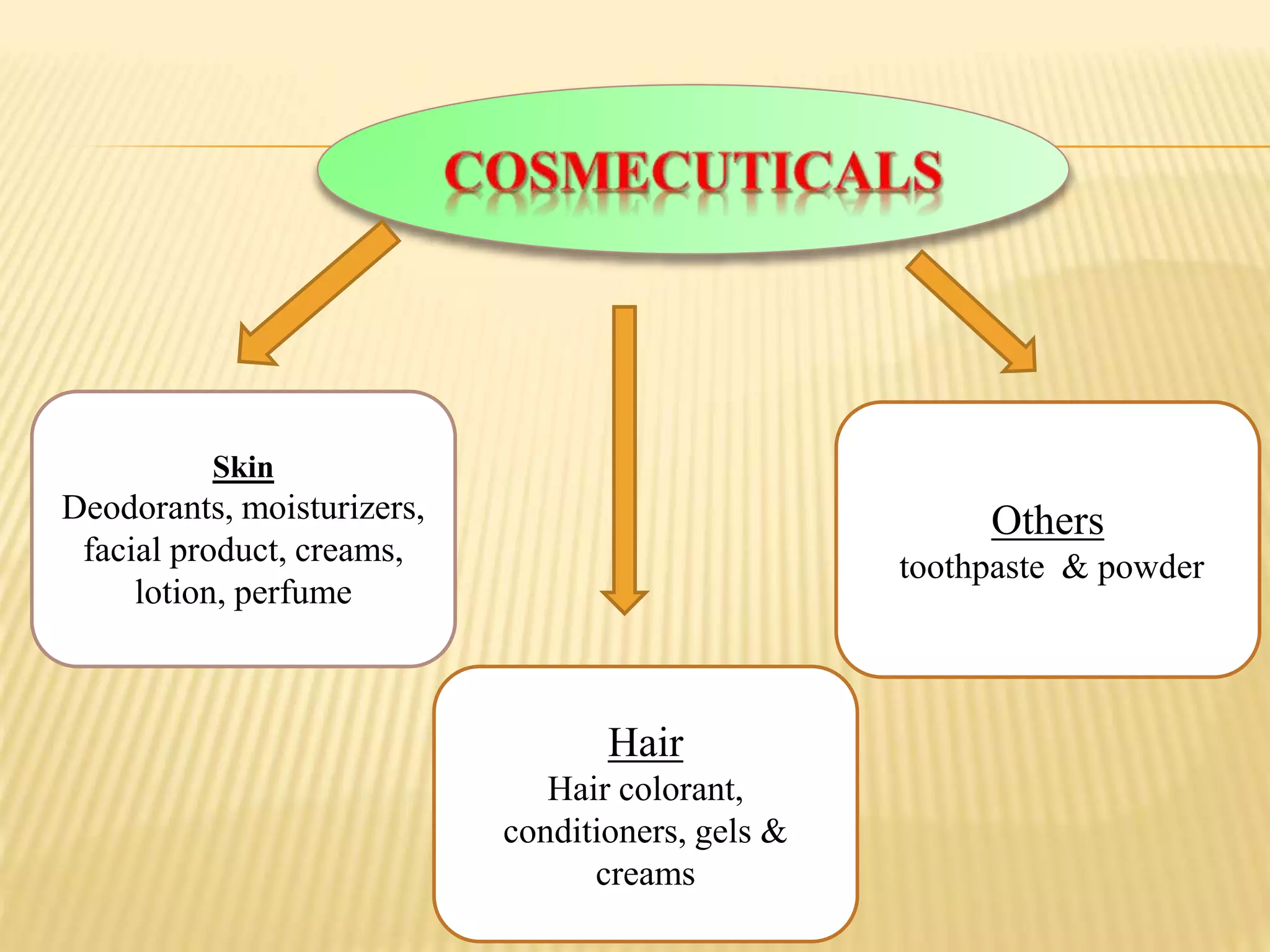
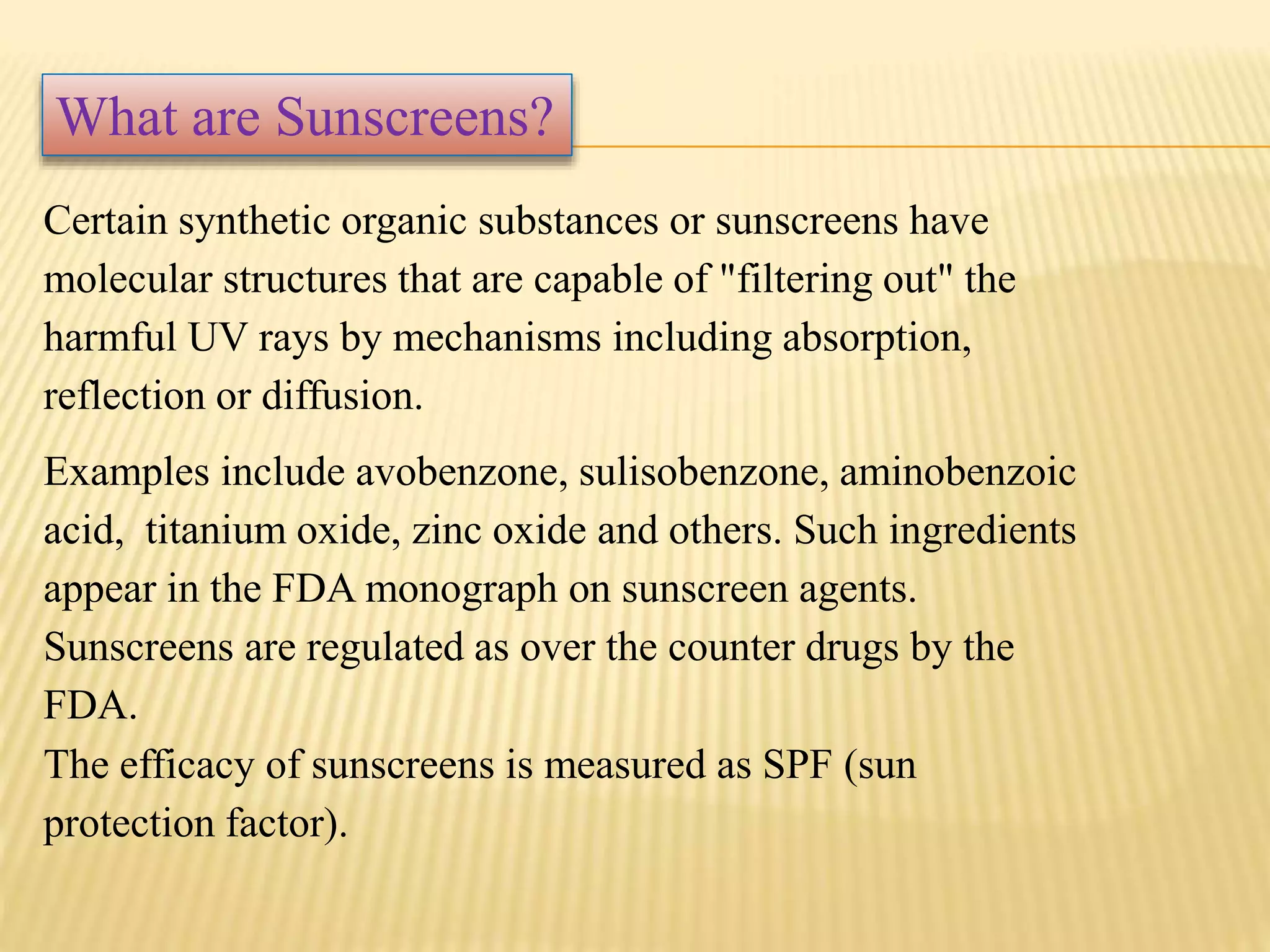
Cosmeceuticals are topically applied products with medicinal benefits for the skin. They fall between cosmetics and drugs. Some key points:
- Cosmeceuticals were coined in 1980 and contain ingredients that protect against skin damage.
- The FDA does not recognize cosmeceuticals as a separate category - a product is either a drug, cosmetic, or combination.
- Common cosmeceutical ingredients include antioxidants, peptides, retinoids, and exfoliants which treat signs of aging.
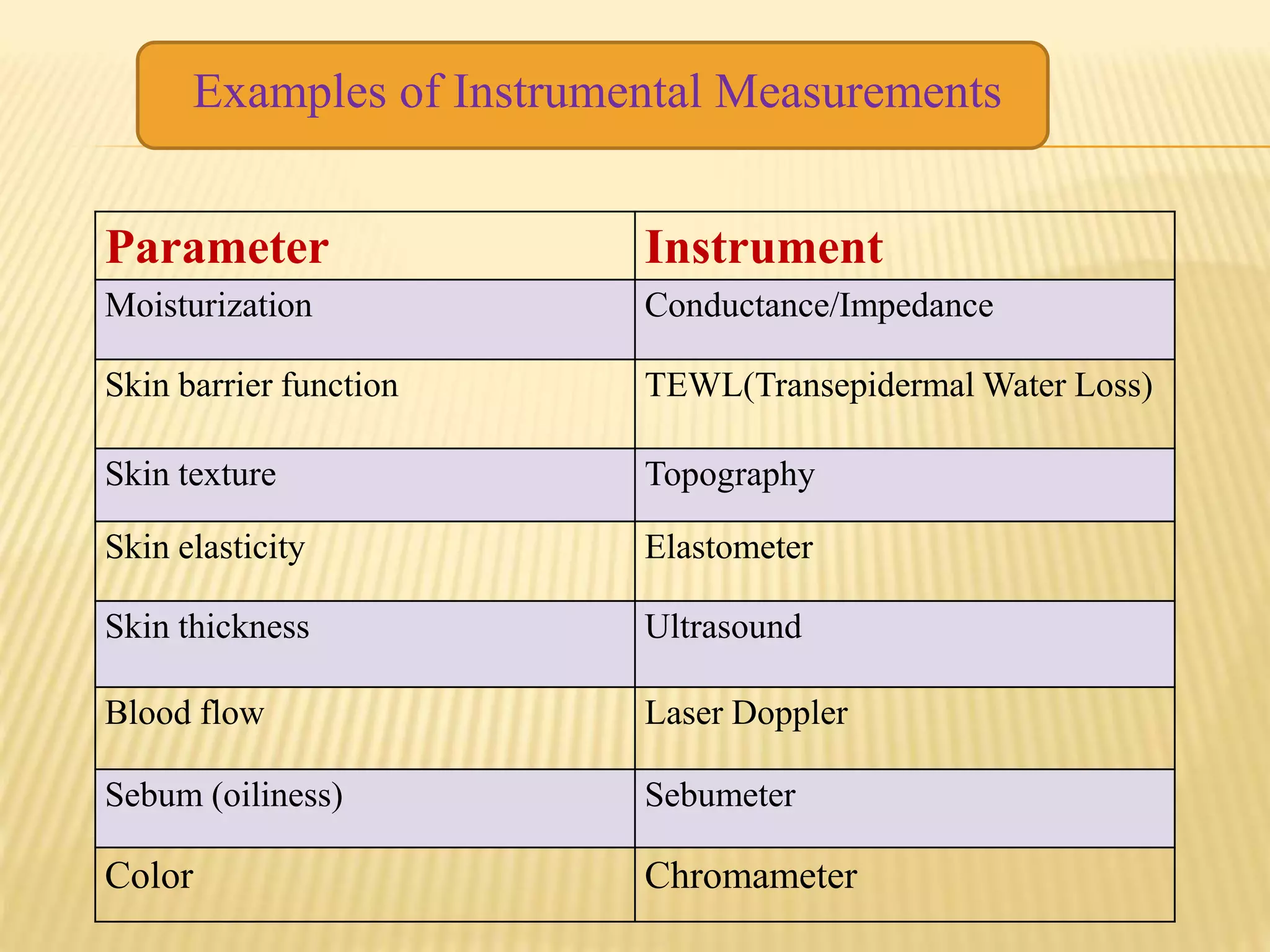
- Safety testing evaluates irritation potential, phototoxicity and other factors to ensure cosmeceuticals are safe for long-term use. Instrumental methods objectively measure skin