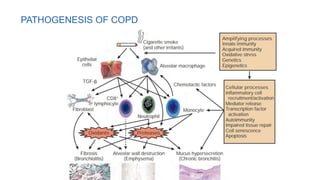
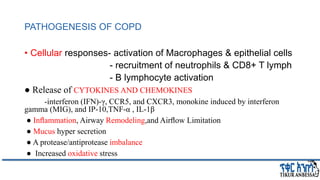
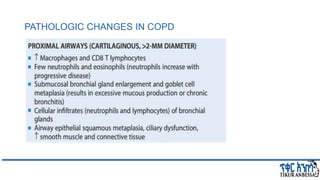
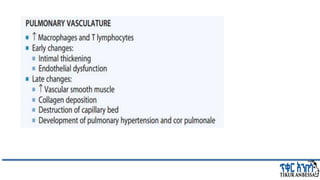
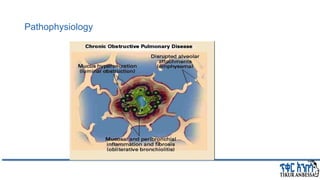
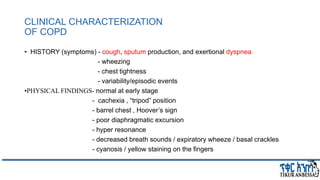
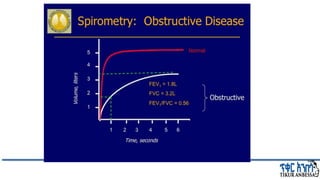
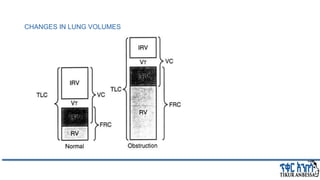
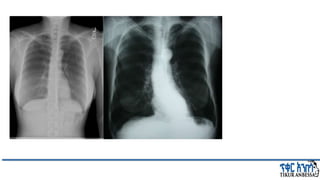
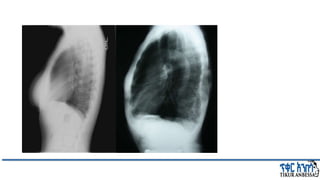
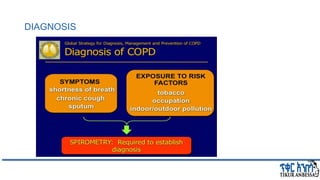
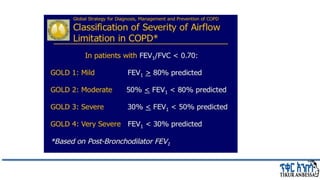
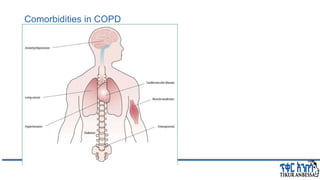
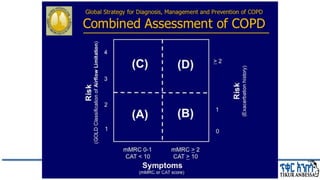
This document provides an overview of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It defines COPD and related terms like chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It then discusses the epidemiology, pathogenesis, pathologic changes, clinical characterization, diagnosis, assessment of severity and staging, differential diagnosis, and principles of management of COPD. The key points are that COPD is characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation caused by exposure to noxious particles/gases. Cigarette smoking is the most common risk factor globally. The major pathophysiology involves inflammation and narrowing of the small airways leading to decreased airflow. Spirometry is the gold standard for diagnosis and assessment of severity. Management involves assessing/monitoring