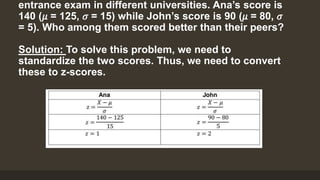
This document discusses converting between normal random variables and z-scores (standard normal variables). It provides the formula for calculating z-scores and examples of finding z-scores from raw scores and raw scores from z-scores. It also gives an example word problem involving comparing two students' scores on different exams by converting them to z-scores. The document aims to teach how to convert between normal random variables and z-scores.