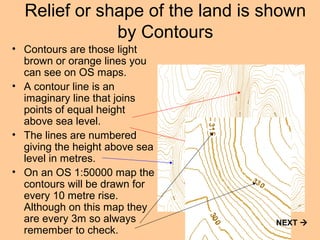
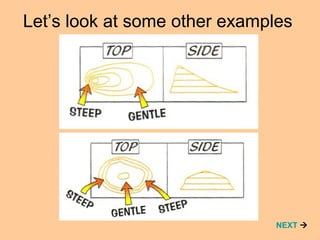
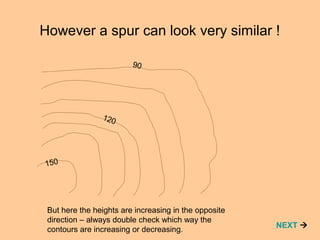
The slides explain contour lines on maps, which represent the relief or shape of the land by connecting points of equal height above sea level. Contour lines are numbered to indicate elevation, with closer lines indicating steeper slopes and fewer lines suggesting flatter terrain. The document also discusses features like valleys and spurs, encouraging users to engage with a test at the end.