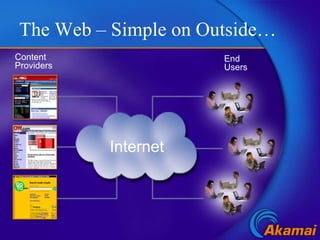
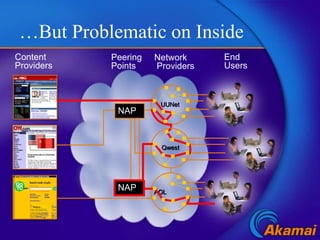
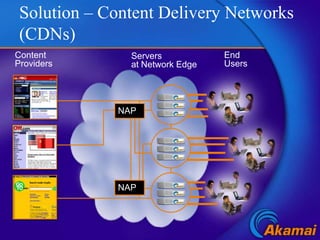
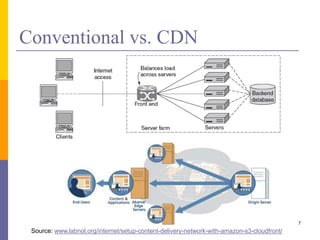
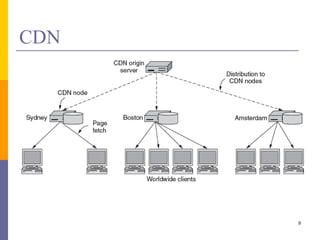
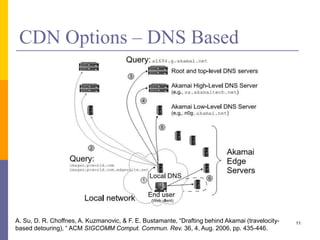
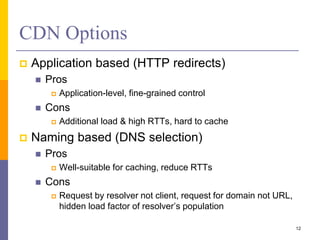
Content delivery networks (CDNs) improve content delivery over the internet by replicating content on servers located at the network edge. This reduces latency, packet loss, jitter, and server load issues that occur when content must travel long distances and through multiple network providers to reach end users. CDNs deliver content through either passive caching methods or active replication of content on their distributed server networks with redirection techniques like HTTP redirects or DNS selection.