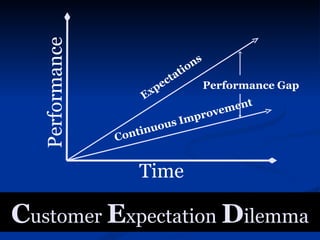
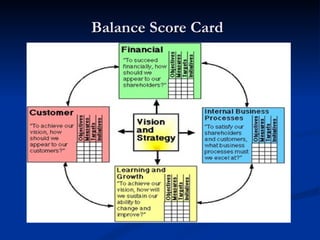
The document discusses various contemporary management practices such as MIS, end user computing, materials requirement planning, just in time manufacturing, total quality management, six sigma, capability maturity model, supply chain management, enterprise resource planning, performance management, business process outsourcing, business process reengineering, benchmarking, and balanced scorecard. It provides details on the objectives, methodologies, benefits, and key aspects of each of these management practices.







![BENEFITS OF JIT
Quality consciousness
Reduced scrap
Reduced cycle times
Smoother flow of production]
Low inventory
High productivity
High worker participation
Reduced space requirements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitviii-120411113705-phpapp01/85/Unit-viii-8-320.jpg)