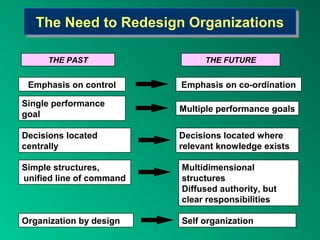
The document discusses current trends in strategic management, including new directions in strategic thinking, redesigning organizations, and new modes of leadership. It outlines some key trends of the 1990s like the quest for shareholder value and adjusting to increased competition. It also discusses emerging developments like knowledge management, rethinking organizational structures, and the leadership competencies needed for the future like creativity, flexibility, and relationship building.