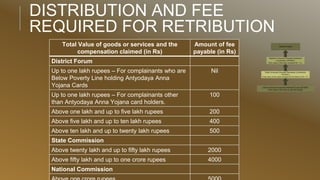
The document provides an overview of consumer awareness and consumer protection laws in India. It discusses key topics including what consumer awareness means, the importance of consumer awareness, consumer rights and responsibilities, consumer protection legislation and mechanisms in modern times and under the Consumer Protection Act of 1986. Specifically, it outlines the three-tier quasi-judicial system established at the district, state and national levels to address consumer complaints, the composition and jurisdiction of these redressal agencies, and the fees required for filing complaints.