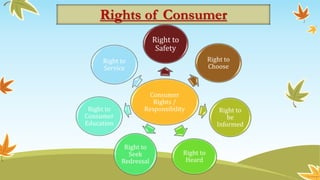
This document discusses consumer rights in India. It begins with definitions of a consumer and consumer rights, which include the right to information about quality, potency, quantity, purity and price of goods and services. It outlines the Consumer Protection Act of 1986 and some key rights of consumers such as the rights to safety, choice, being informed, and seeking redressal. It lists the three types of consumer courts in India that handle different monetary ranges of consumer complaints. It concludes with emphasizing the importance of consumer education and consumers' ability to influence the market.