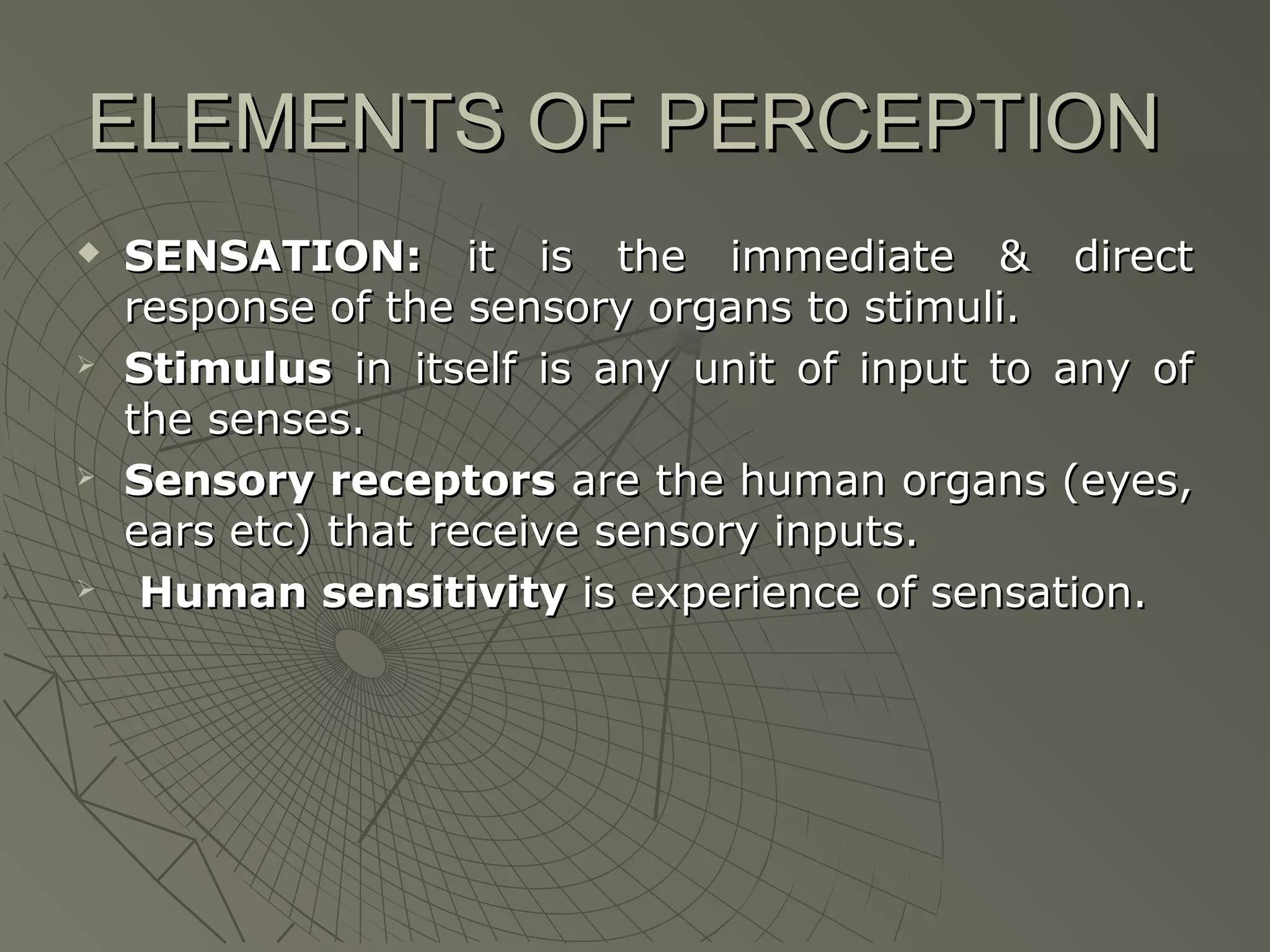
Consumer perception is how individuals select, organize, and interpret stimuli to form a meaningful understanding of the world. It involves sensation, where sensory receptors receive stimuli, and thresholds, such as the absolute threshold where something is barely detected and the just noticeable difference between two similar stimuli. Subliminal perception involves stimuli too weak to be consciously perceived but strong enough to be detected by receptors. Consumers develop images of products and brands based on symbolic meanings and evaluate brands on consistency with their self-images. Marketers position products through overall company images, competition, benefits, and multiple offerings under different brands to fill various positions. Repositioning may occur due to new competitors or saturated attributes, and perceptual mapping identifies product positions and gaps in