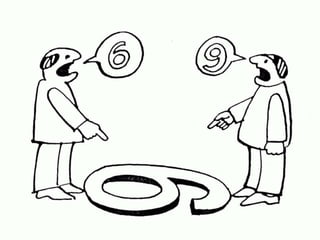
This document discusses consumer perception and imagery. It defines perception as how individuals interpret stimuli to understand the world. Perception involves selection, organization, and interpretation of stimuli. Consumer imagery refers to the images consumers form about products, services, prices and quality. Key topics covered include subliminal perception, elements of perception like selection and interpretation, issues with consumer imagery like perceived quality and risk, and how positioning and price influence consumer perception.