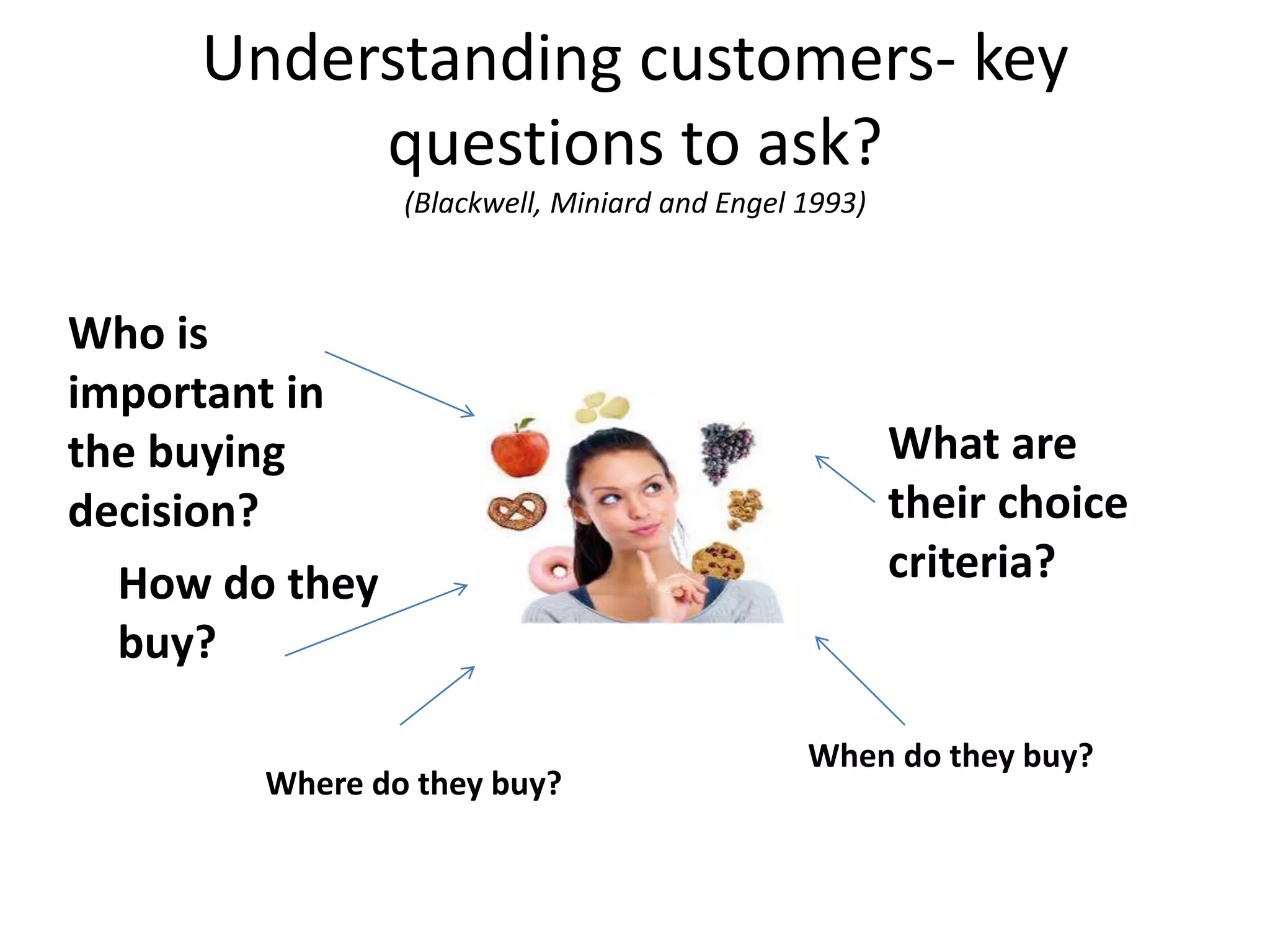
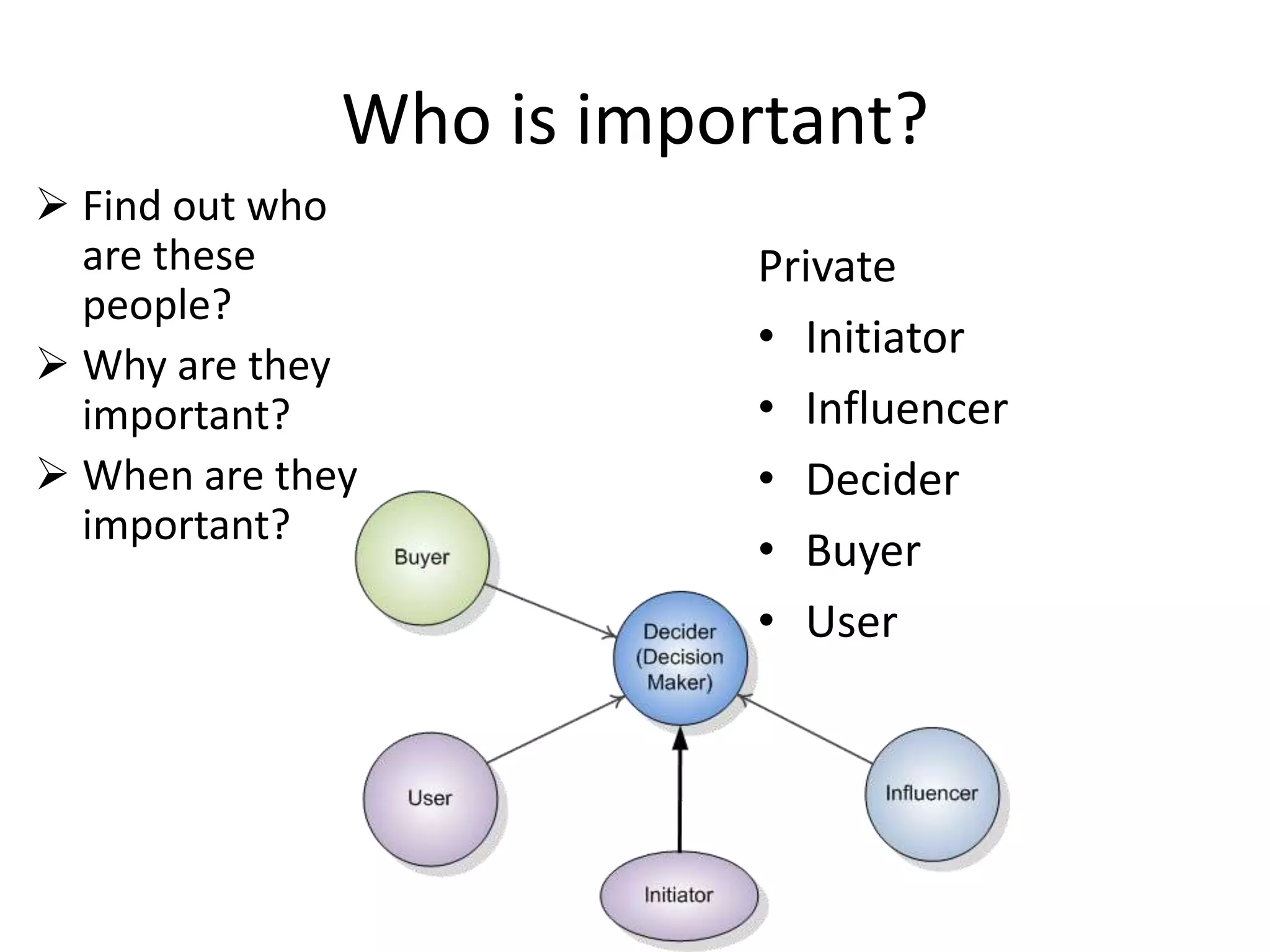
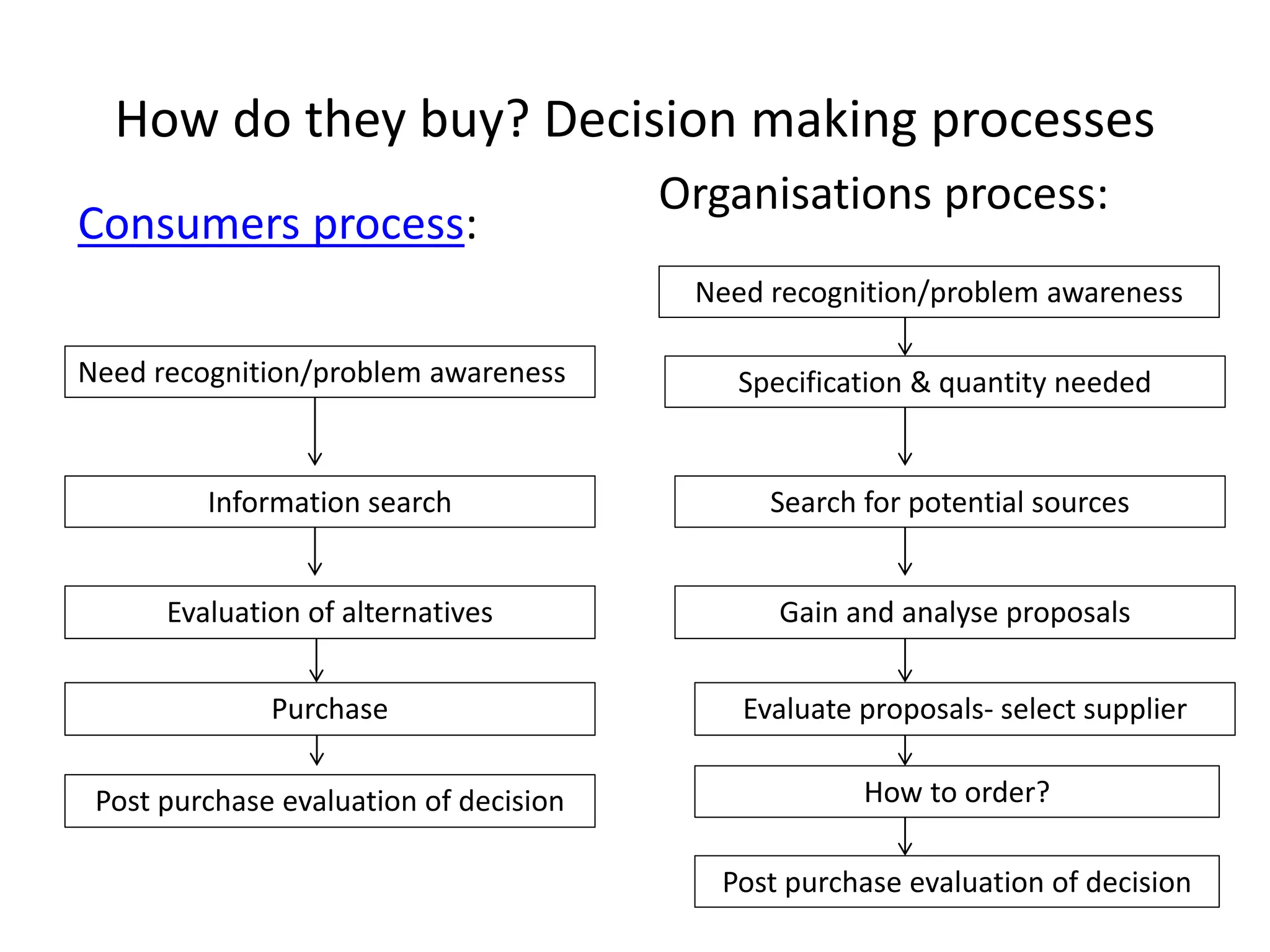
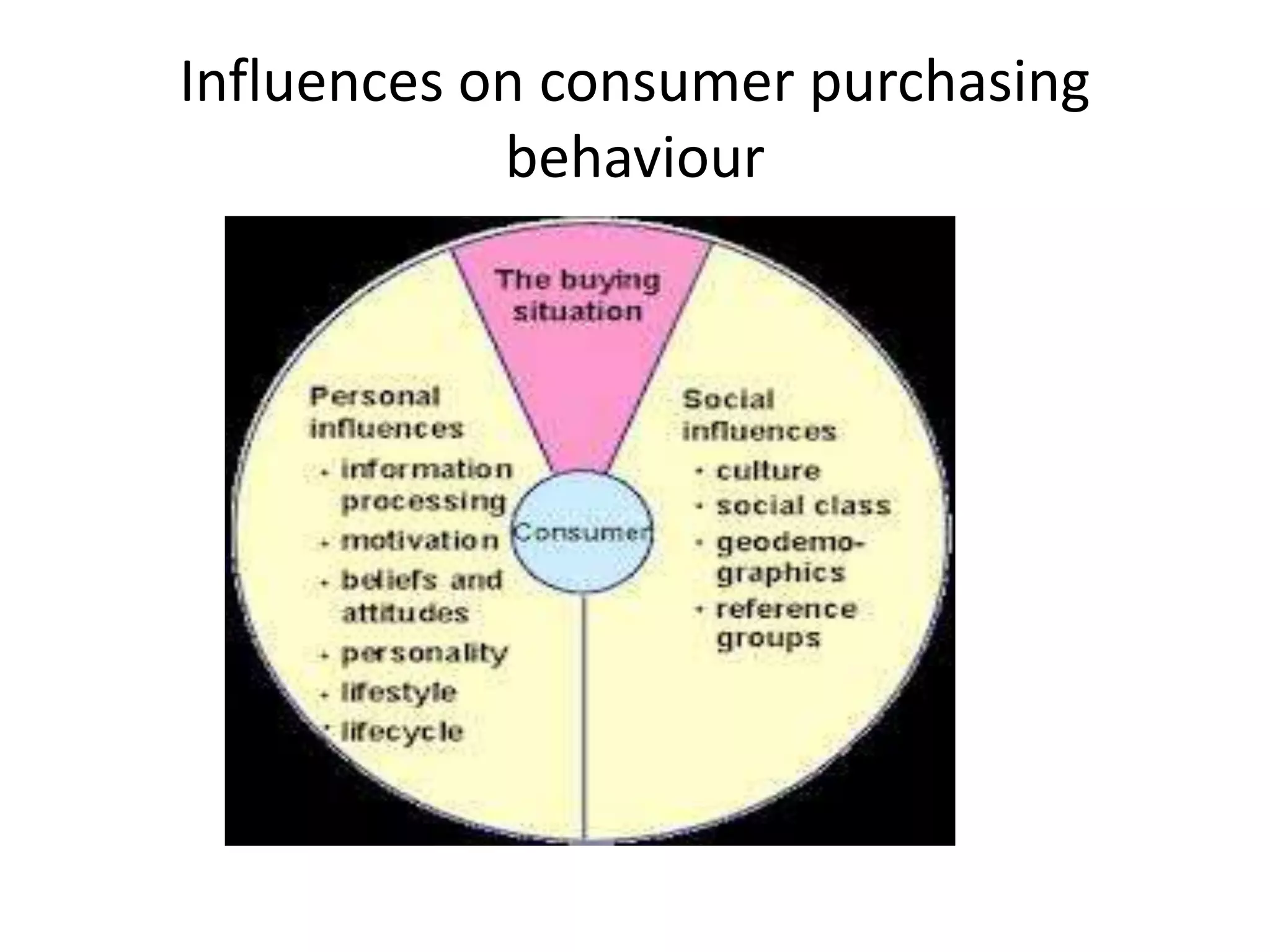
This document discusses understanding consumer behavior and key factors that influence purchasing decisions. It differentiates between private consumers and organizational buyers, and identifies important questions to consider like who is involved in the buying process, when and where purchases are made, and what criteria drive choice selection. Both consumer and organizational decision making processes are examined, along with common influences on purchasing behavior.