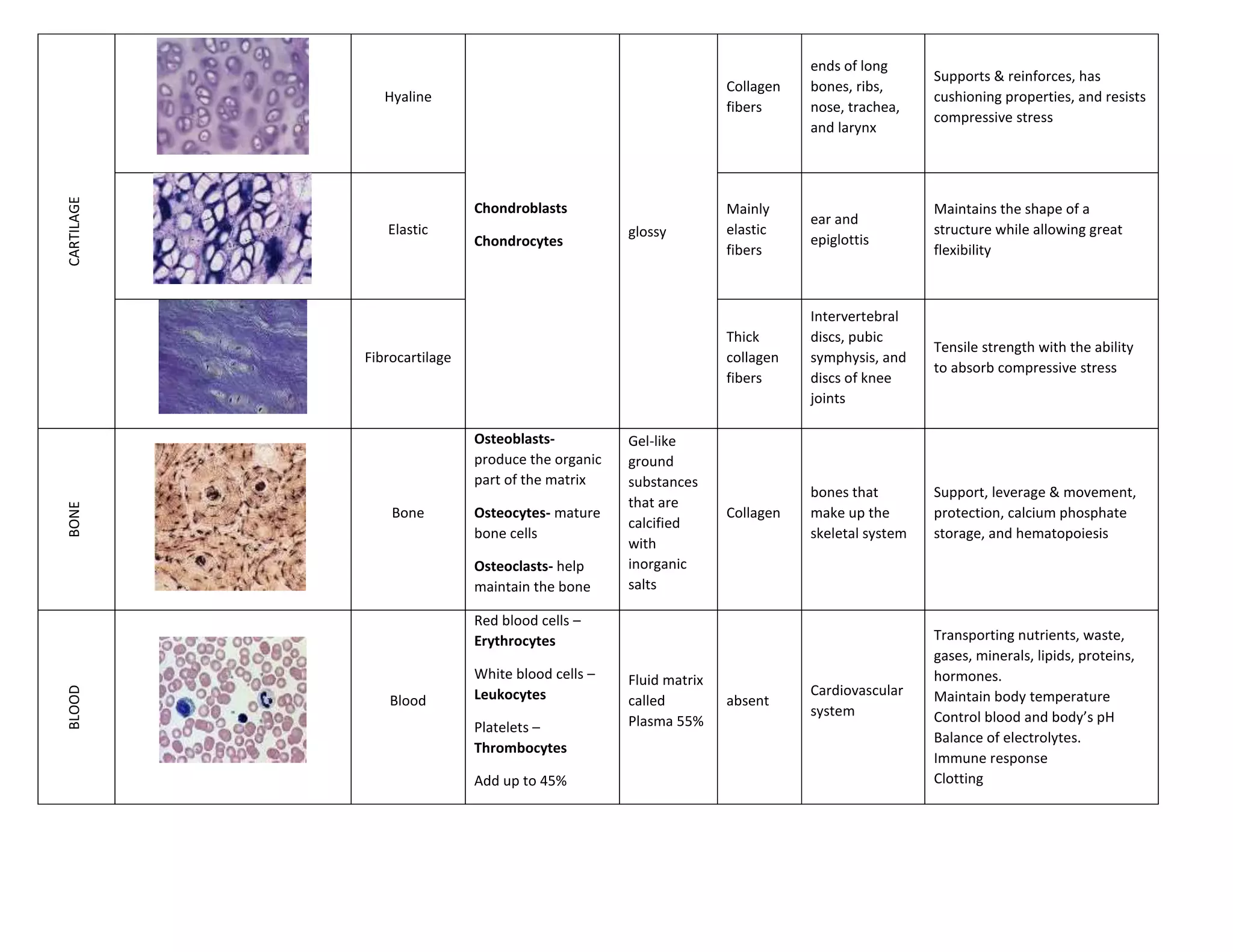
Connective tissue cells provide structure and support throughout the body. There are several types of connective tissue including dense connective tissue found in tendons and ligaments, loose connective tissue in the dermis and around organs, cartilage in joints, bone making up the skeletal system, and blood circulating through the cardiovascular system. Each type of connective tissue contains different matrix components and cell types that allow them to fulfill their specific functions.