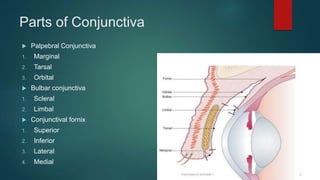
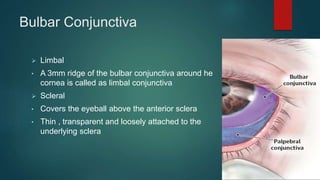
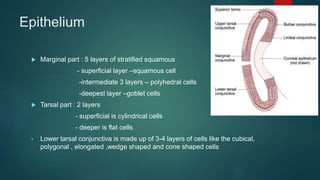
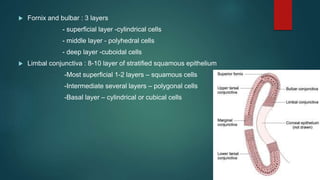
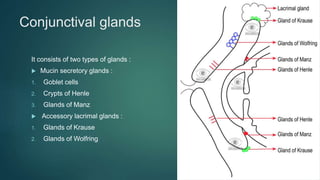
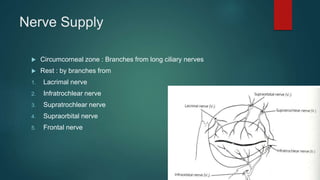
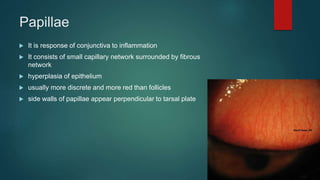
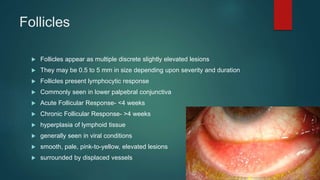
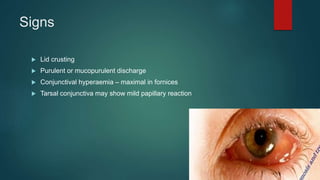
The document provides an extensive overview of the conjunctiva, including its structure, layers, and types, alongside common diseases and their management. It discusses the anatomy of the conjunctiva, types of conjunctival glands, blood supply, nerve supply, and lymphatic drainage, as well as various conjunctival conditions such as pinguecula, pterygium, and conjunctivitis. Management strategies are outlined for optometrists, including non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatments for different conjunctival diseases.