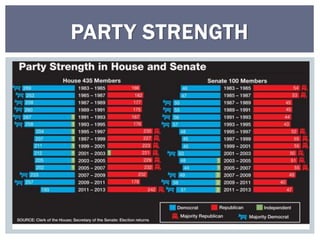
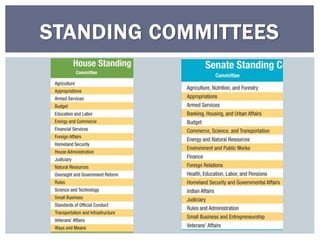
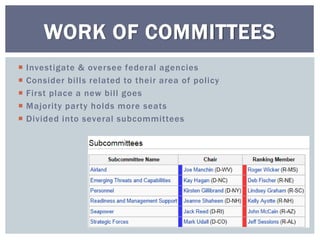
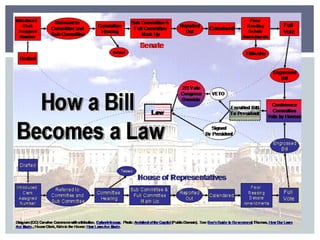
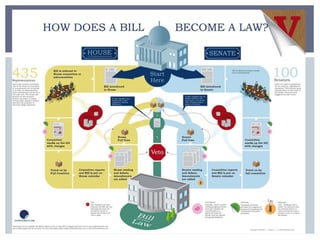
The document discusses the leadership structure and legislative process in the US Congress. It explains that the Speaker of the House and Senate Majority Leader act as leaders of their respective chambers and political parties. It also outlines the committee system and roles of committee chairs, and describes the process a bill goes through from introduction to final passage or veto. This includes consideration in committees, amendments, debates on the House and Senate floors, conferences to resolve differences, and potential presidential approval or veto.