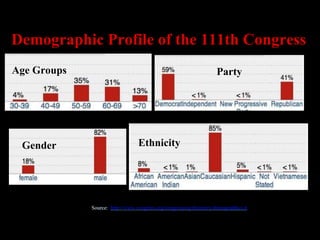
The document provides an overview of the structure and organization of Congress, including differences between the House and Senate such as term lengths and rules, as well as leadership positions and committees. It discusses the role of committees in considering legislation, oversight, and investigations and different types such as standing, select, joint, and conference committees. Party structure and unity are also examined.