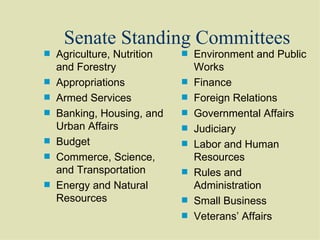
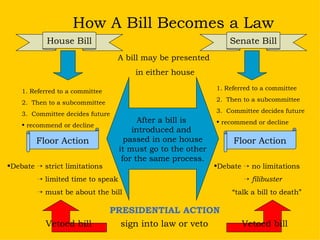
The document summarizes the structure and powers of the United States Congress. It describes Congress as a bicameral legislative body consisting of the House of Representatives and the Senate. It outlines the qualifications, terms, and election processes for both chambers. It also discusses the powers of Congress, including expressed powers directly granted by the Constitution as well as implied powers.