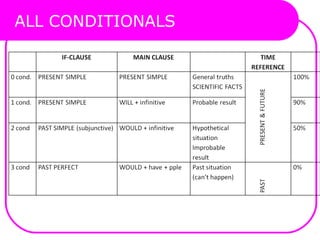
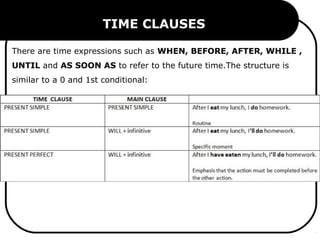
This document discusses various types of conditionals in English including zero, first, second, third conditionals and mixed conditionals. It explains the tense patterns used in the if-clause and main clause for each type of conditional. It also covers using modal verbs, conditional structures like "unless" and "as long as", time clauses, and expressions of wishes and regrets.