Embed presentation
Download to read offline


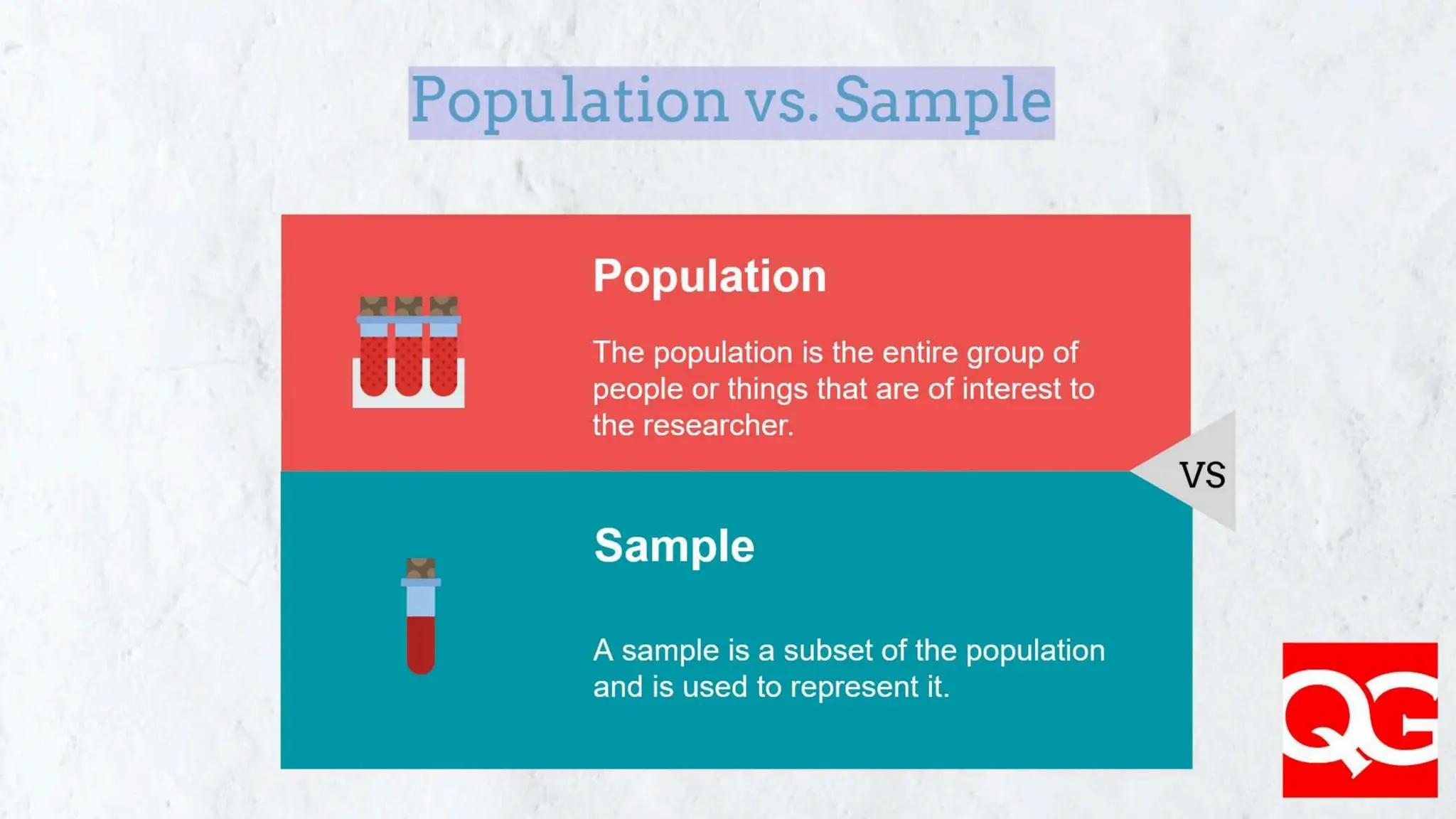
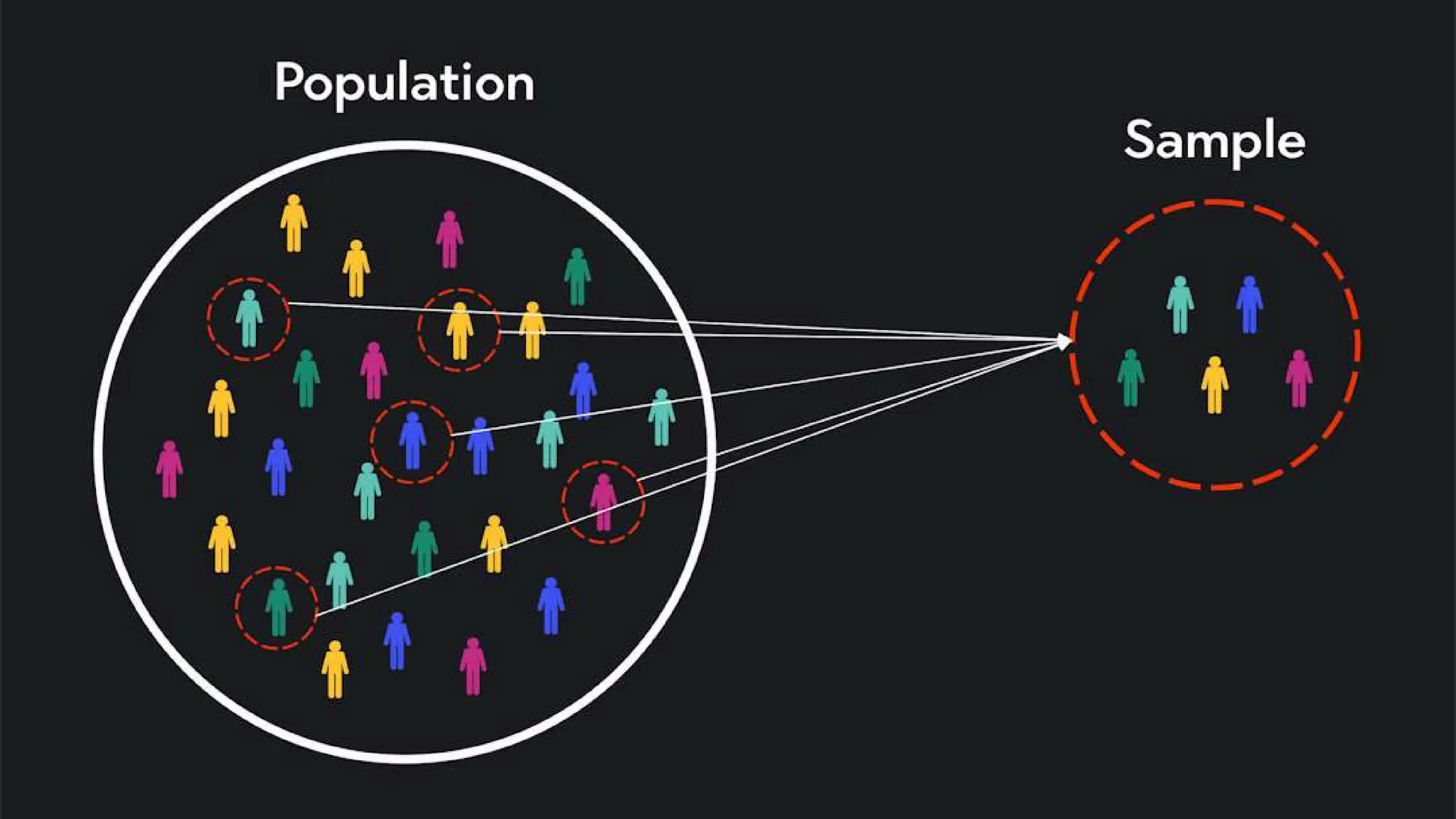






The document explains the concepts of population and sample in research, defining a population as the entire group of interest and a sample as a subset of that group. It describes two main sampling methods: probability sampling, which ensures equal chances of selection, and non-probability sampling, which can lead to bias. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of a representative sample to avoid biased outcomes.









