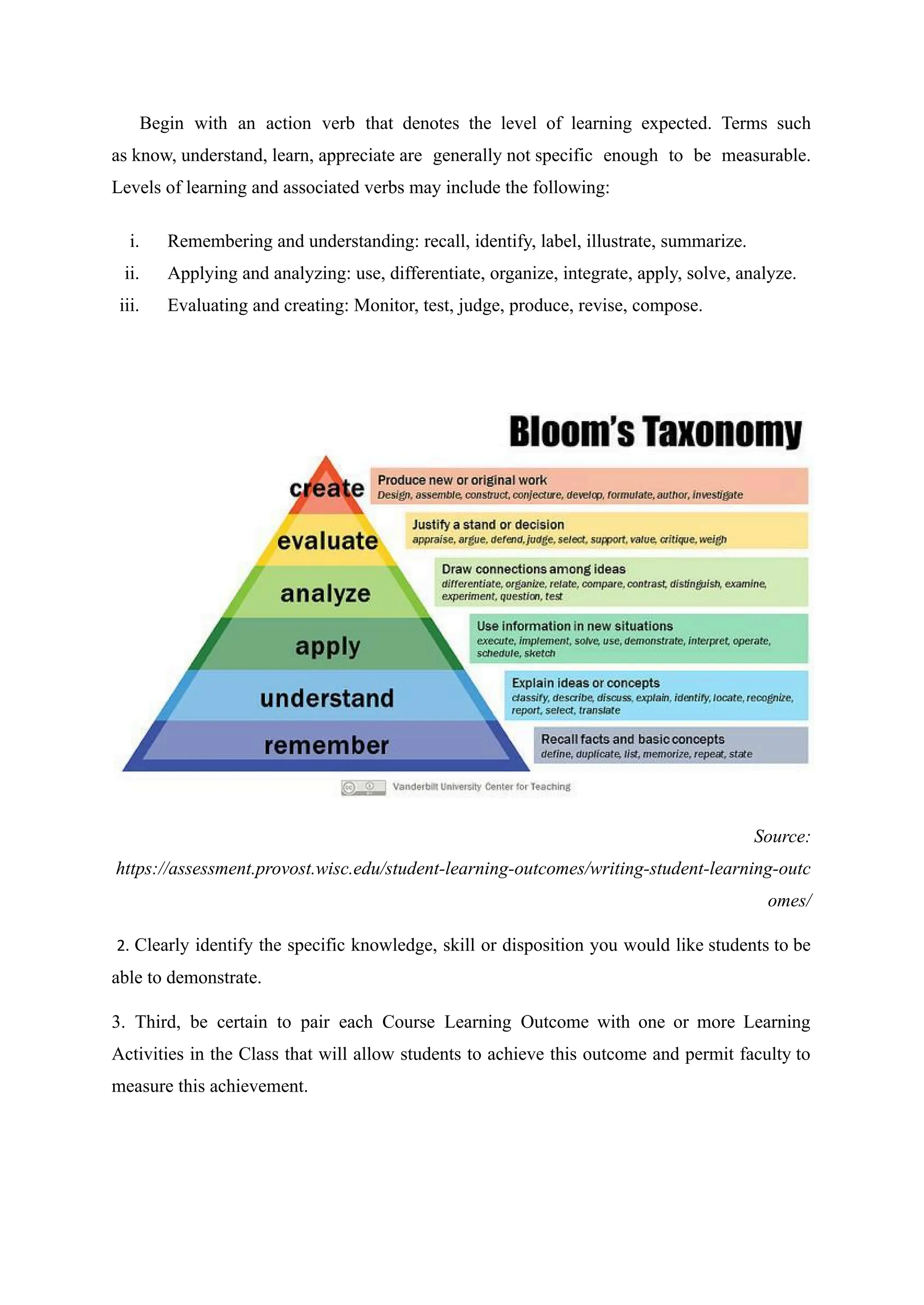
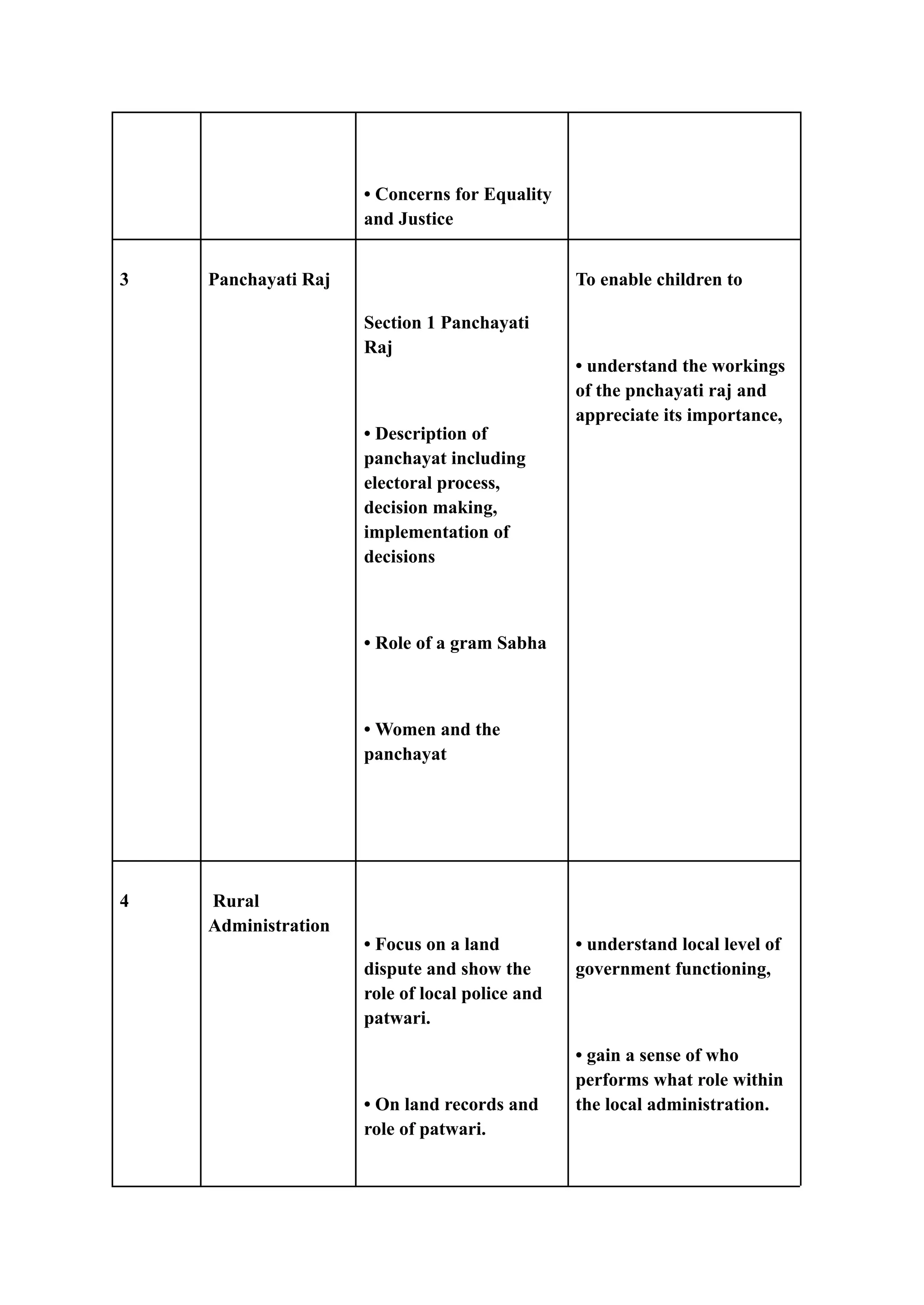
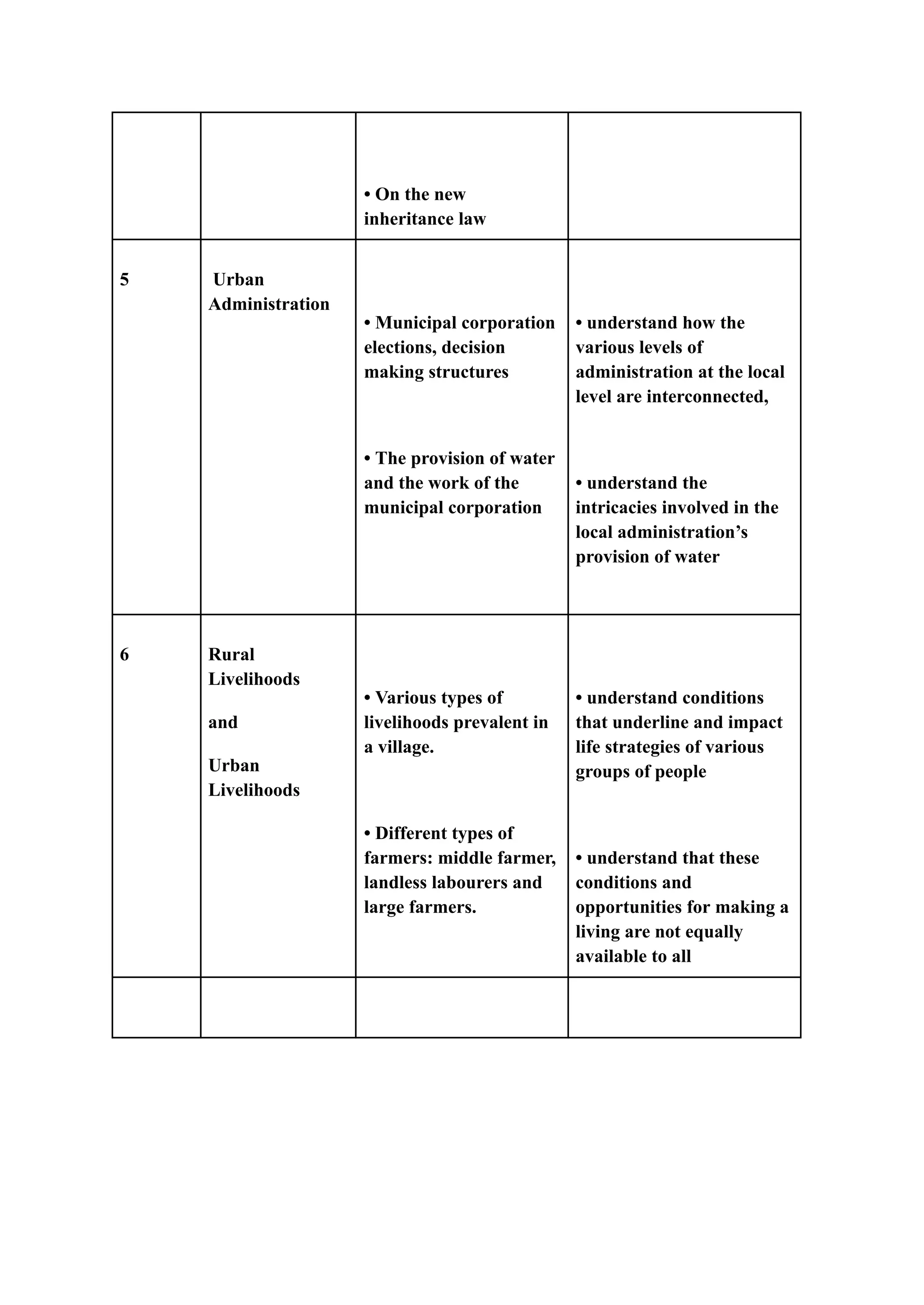
The document is an assignment focused on course learning outcomes in the psychosocial foundation of education, outlining their importance and steps for effective formulation. It emphasizes the need for clear and measurable outcomes to facilitate effective teaching and learning, highlighting various recommended practices and examples. Additionally, it discusses specific course topics and the corresponding learner objectives aimed at enhancing students' understanding of diversity, government, and administration.