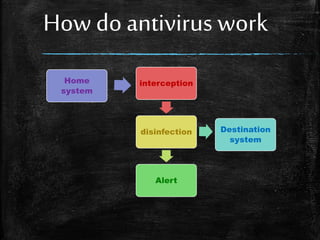
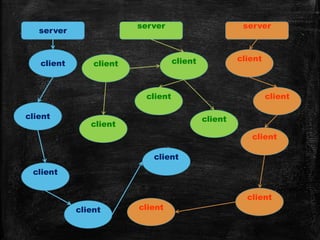
This document discusses computing safety and security threats. It defines safety properties in distributed computing and lists common threats like trojans, phishing, spam, and viruses. It also discusses antivirus software and how they work to detect, block, and remove viruses. Peer-to-peer networks and firewalls are described as ways to share information and block access. Tips are provided for protecting personal data and privacy online, but it cautions that the internet is not completely safe due to risks from hackers, grooming, cyberbullying, and sextortion.