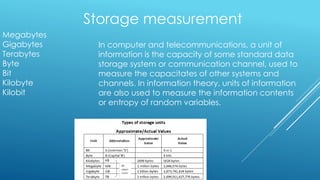
The document defines and describes common computer hardware components and related terms. It explains that the CPU processes all information in a computer and is often called the "brain". RAM allows temporary storage and immediate access to required data, while ROM retains its contents when the computer is turned off. Other components described include the cache, hard drive, motherboard, power supply, video/graphics card, sound card, and devices for measuring speed and storage such as kilohertz, megabytes, and gigabytes. Interface types like USB, VGA, HDMI, DVI, and audio jacks are also outlined. Finally, common peripheral devices such as printers, monitors, scanners, keyboards, mice, speakers, and USB flash drives are