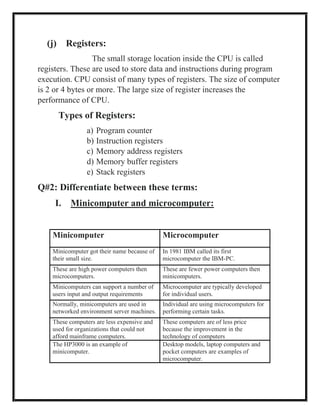
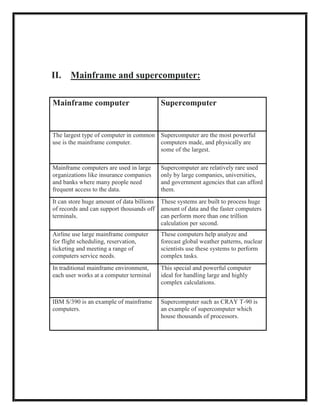
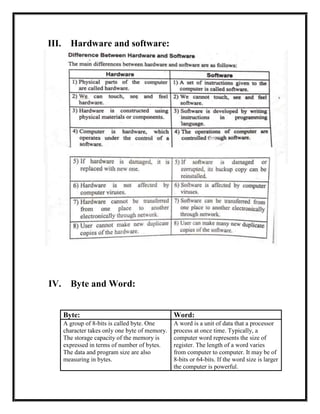
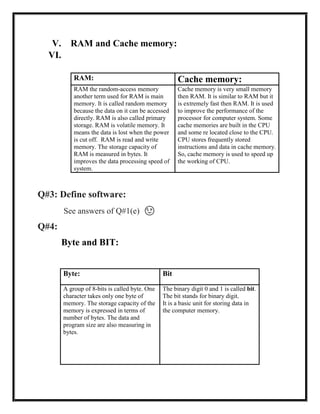
The document defines several computer-related terms:
RAM, byte, mouse, icons, software, control unit, LAN, modem, ALU, and registers. It also differentiates between terms like minicomputer and microcomputer, mainframe and supercomputer, hardware and software, byte and word, and RAM and cache memory. The document provides definitions for software and describes the procedure for how data is stored on a hard disk drive using binary code and read/write heads.




![(d) Icons:
An icon is a pictogram or ideogram displayed on
a computer screen in order to help the user navigate a computer
system. The icon itself is a quickly comprehensible symbol of
a software tool, function, or a data file, accessible on the system and
is more like a traffic sign than a detailed illustration of the actual
entity it represents.
It can serve as an electronic hyperlink or file shortcut to
access the program or data. The user can activate an icon using a
mouse, pointer, finger, or recently voice commands.
Their placement on the screen, also in relation to
other icons, may provide further information to the user about their
usage.[2]
In activating an icon, the user can move directly into and out
of the identified function without knowing anything further about the
location or requirements of the file or code.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computershortnote1-231220035515-33f915b7/85/Computer-Short-Note1-docx-5-320.jpg)