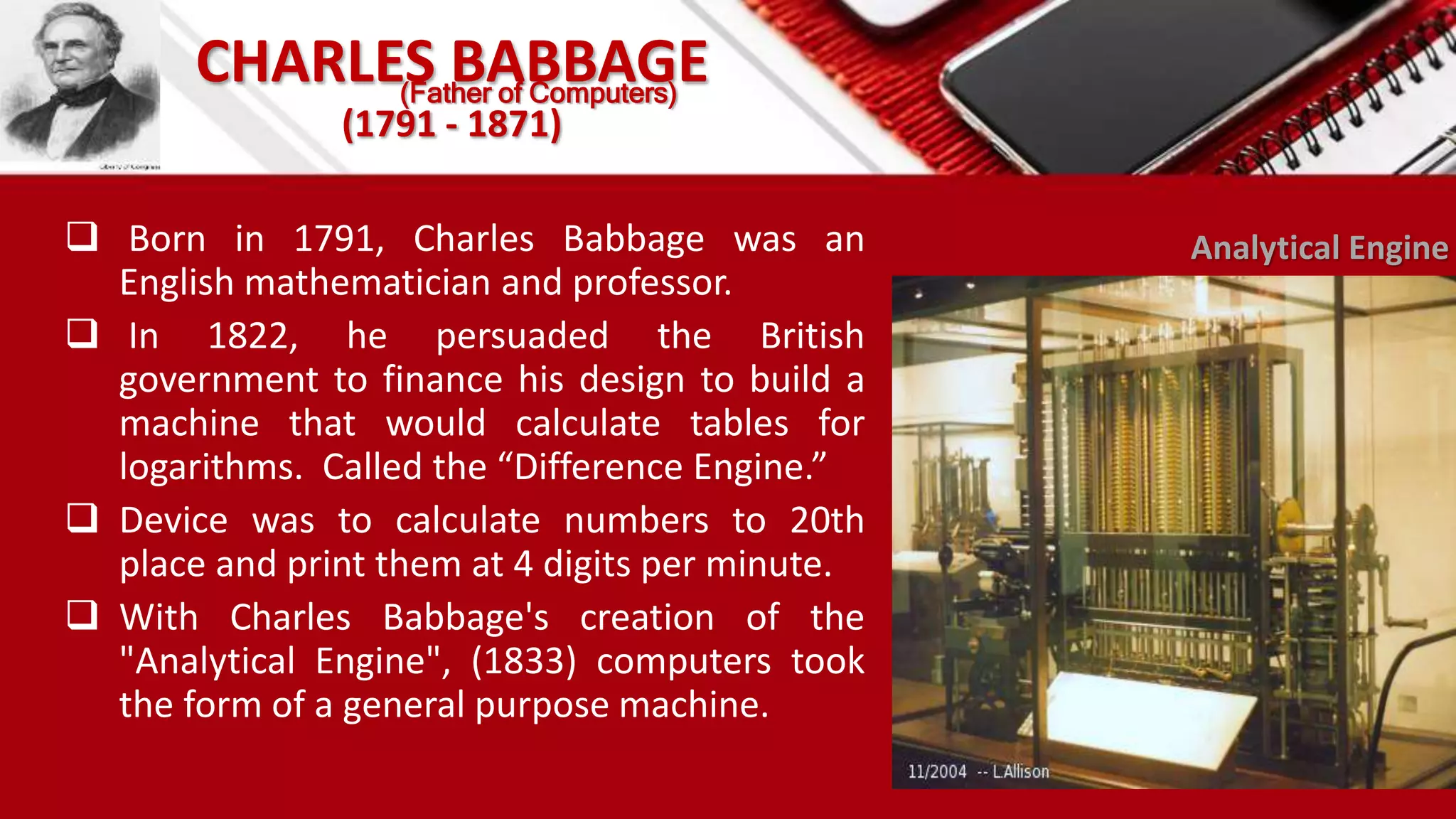
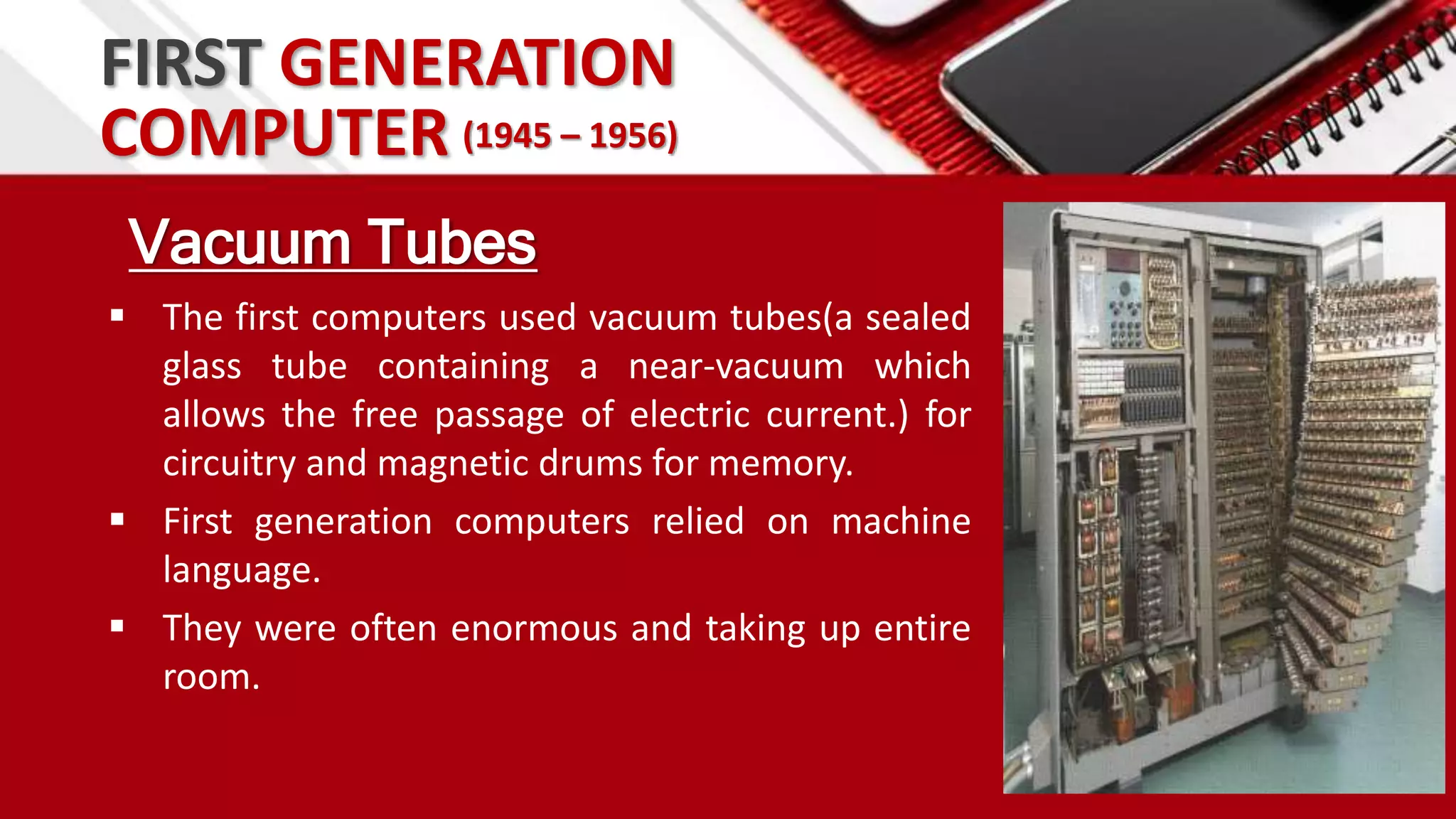
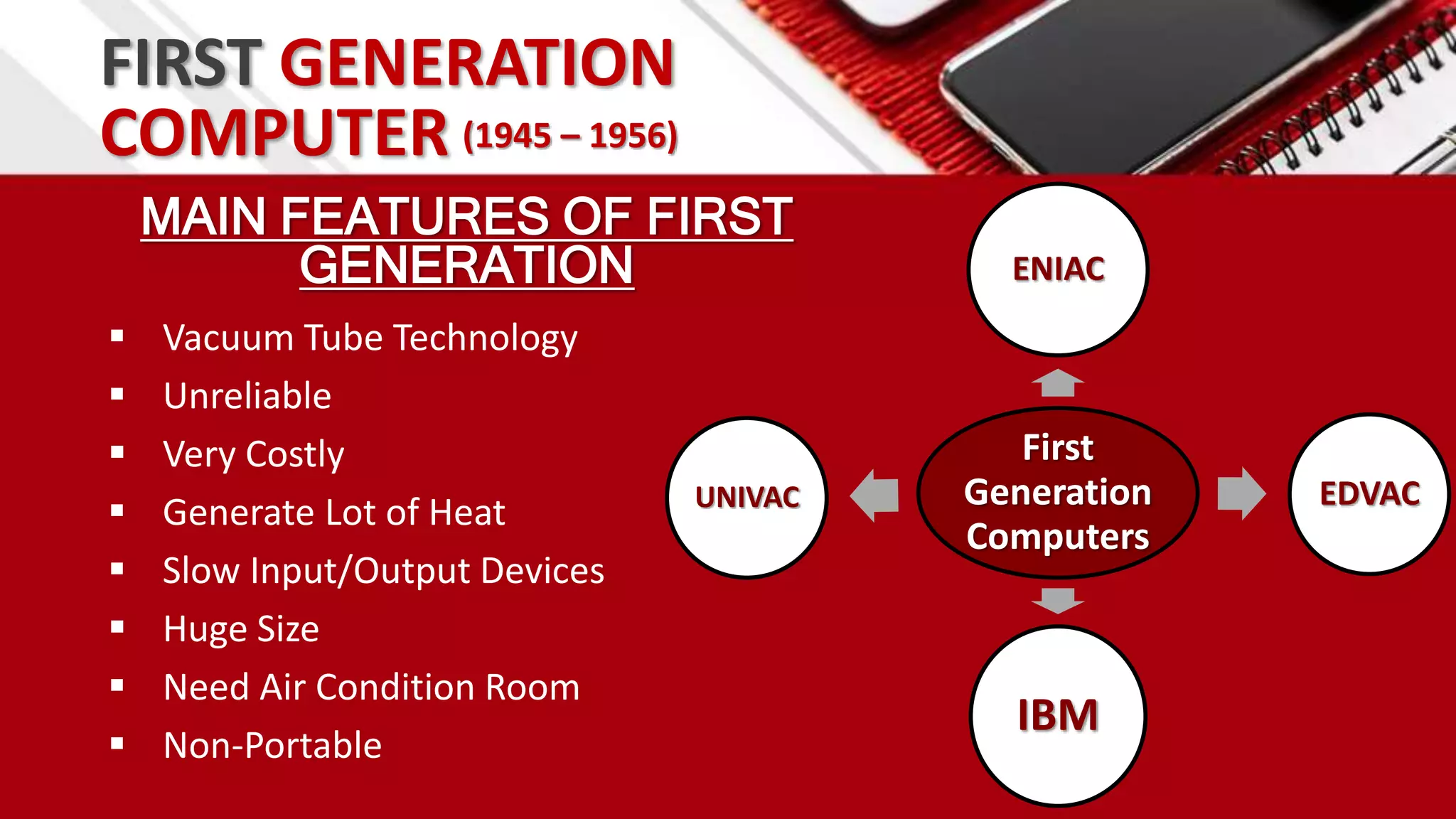
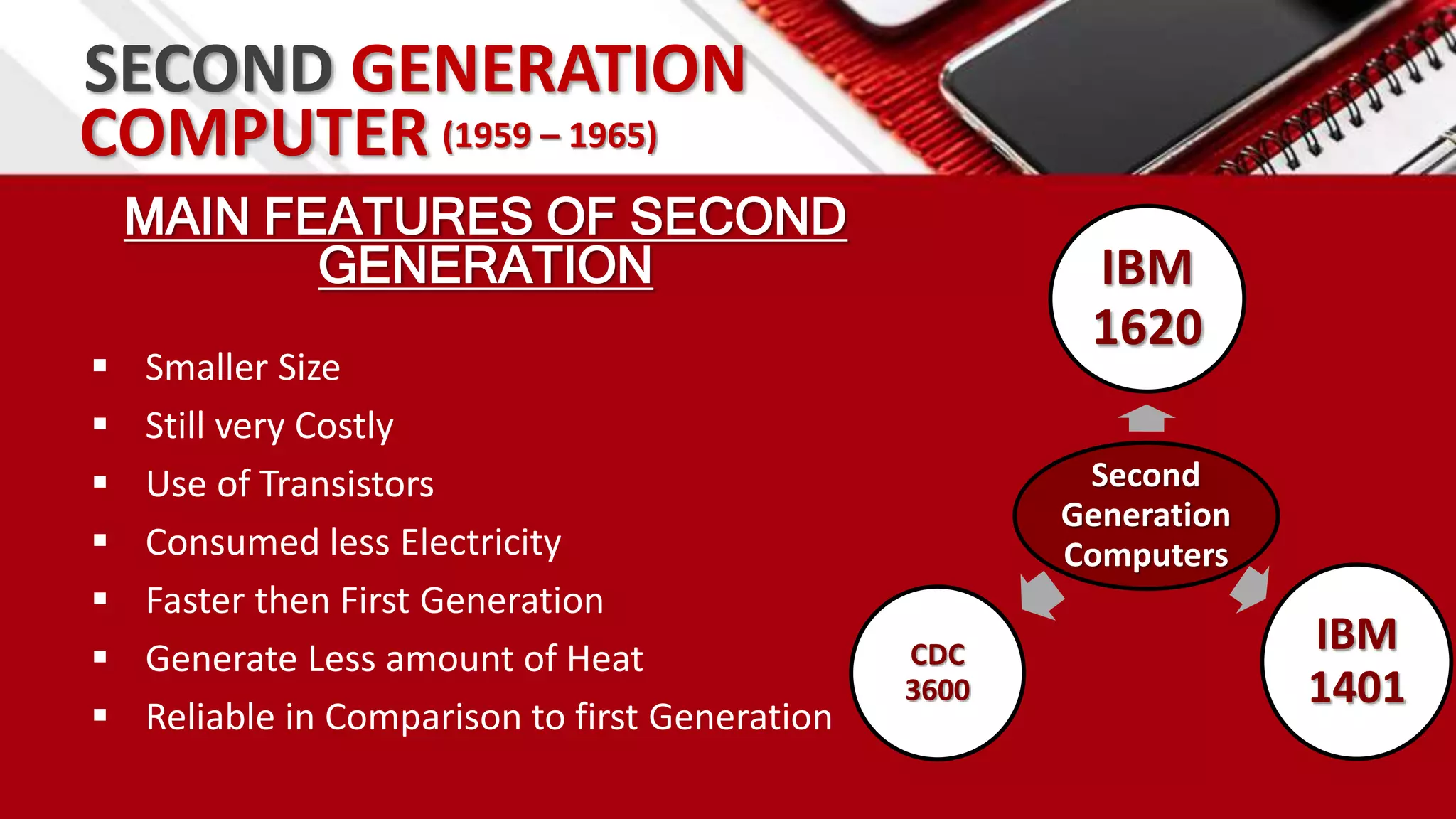
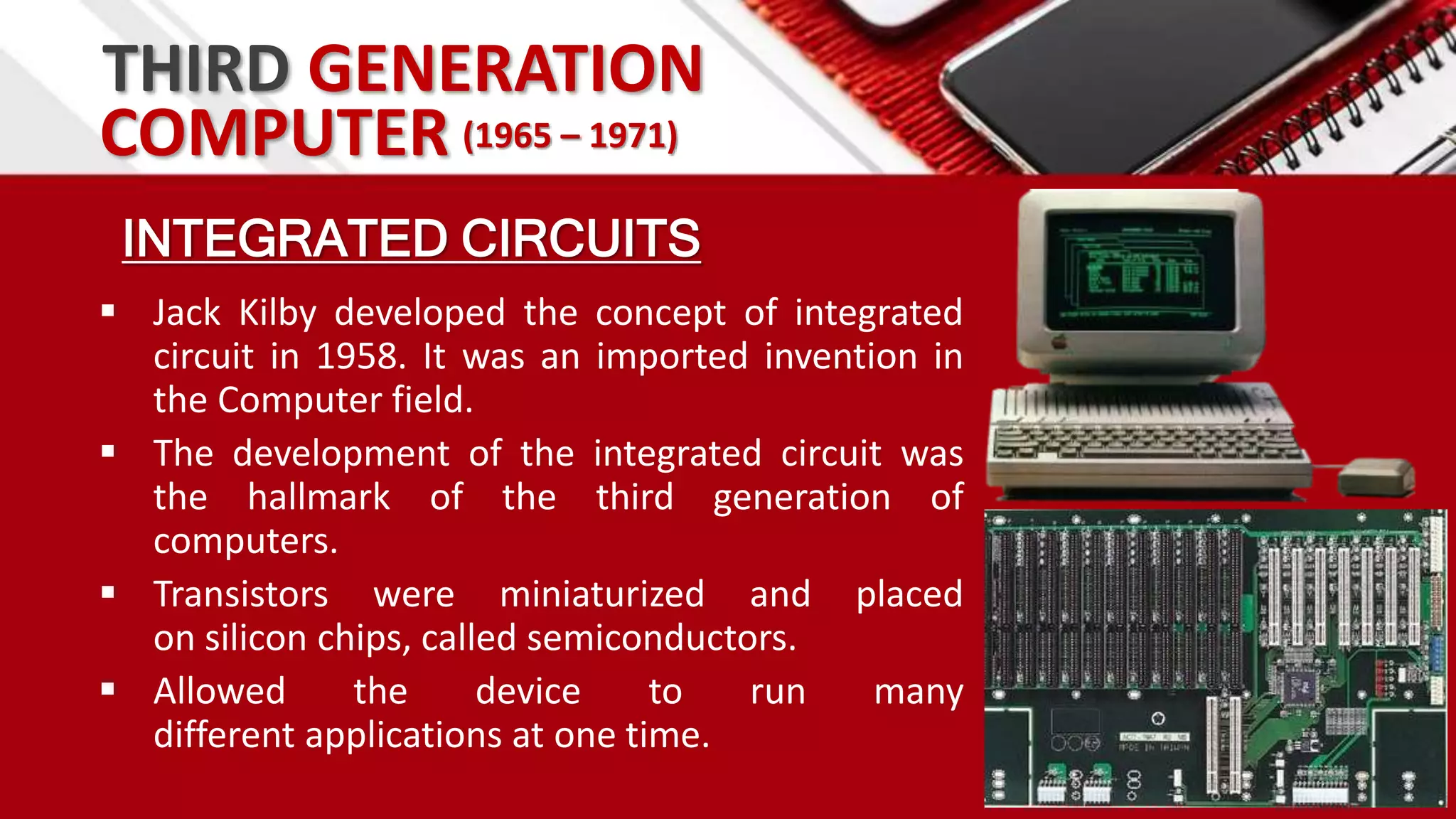
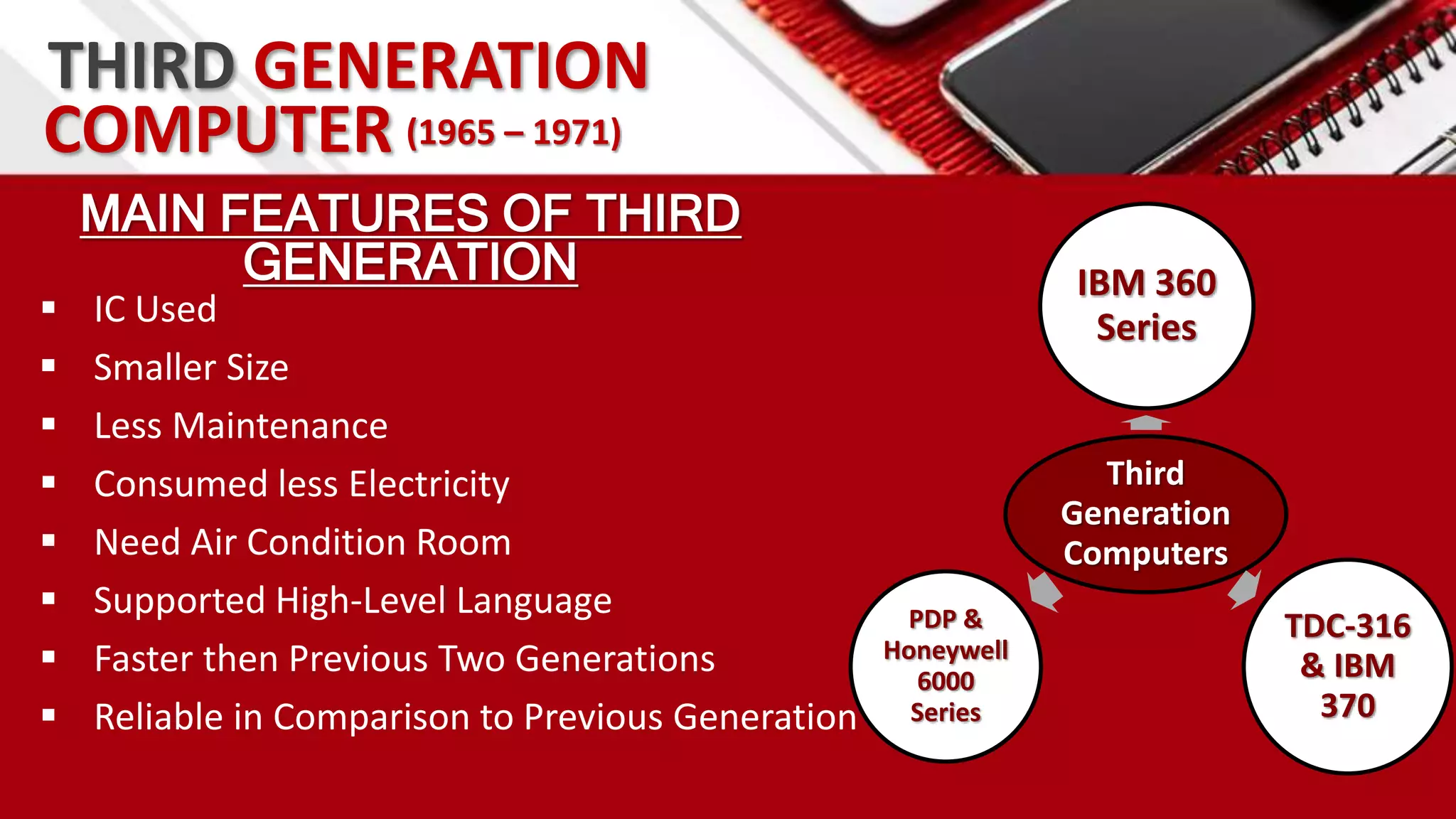
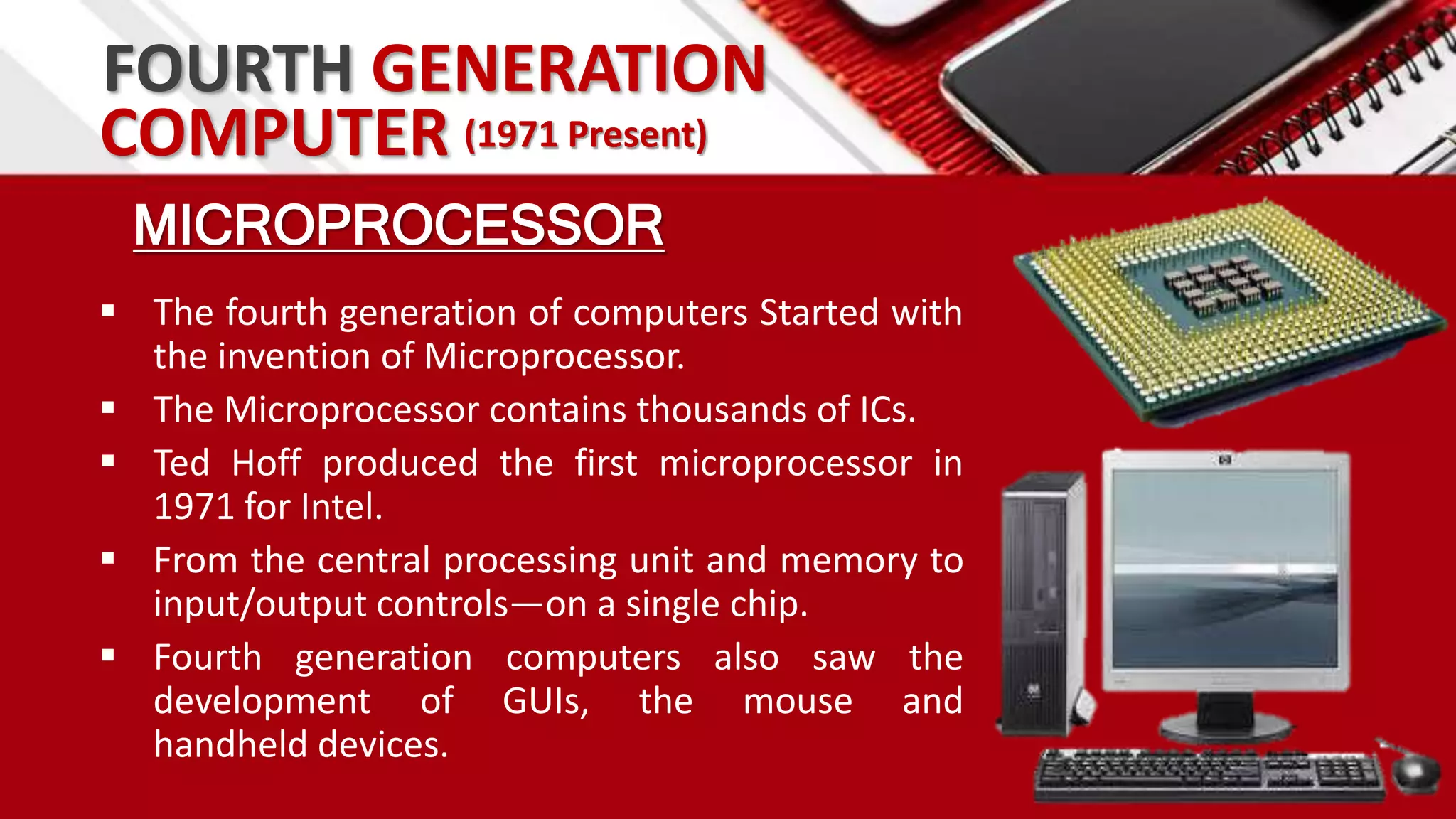
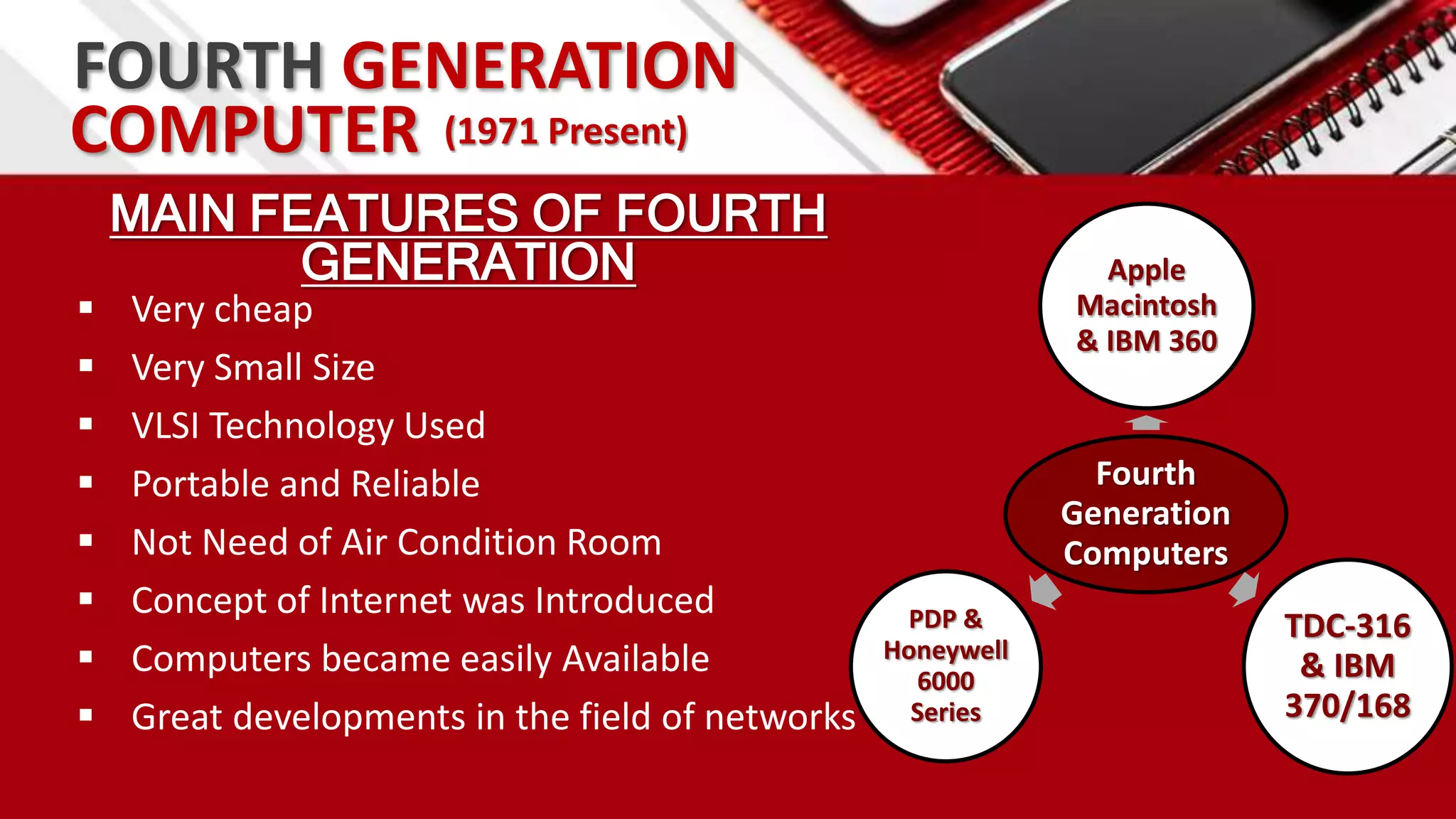
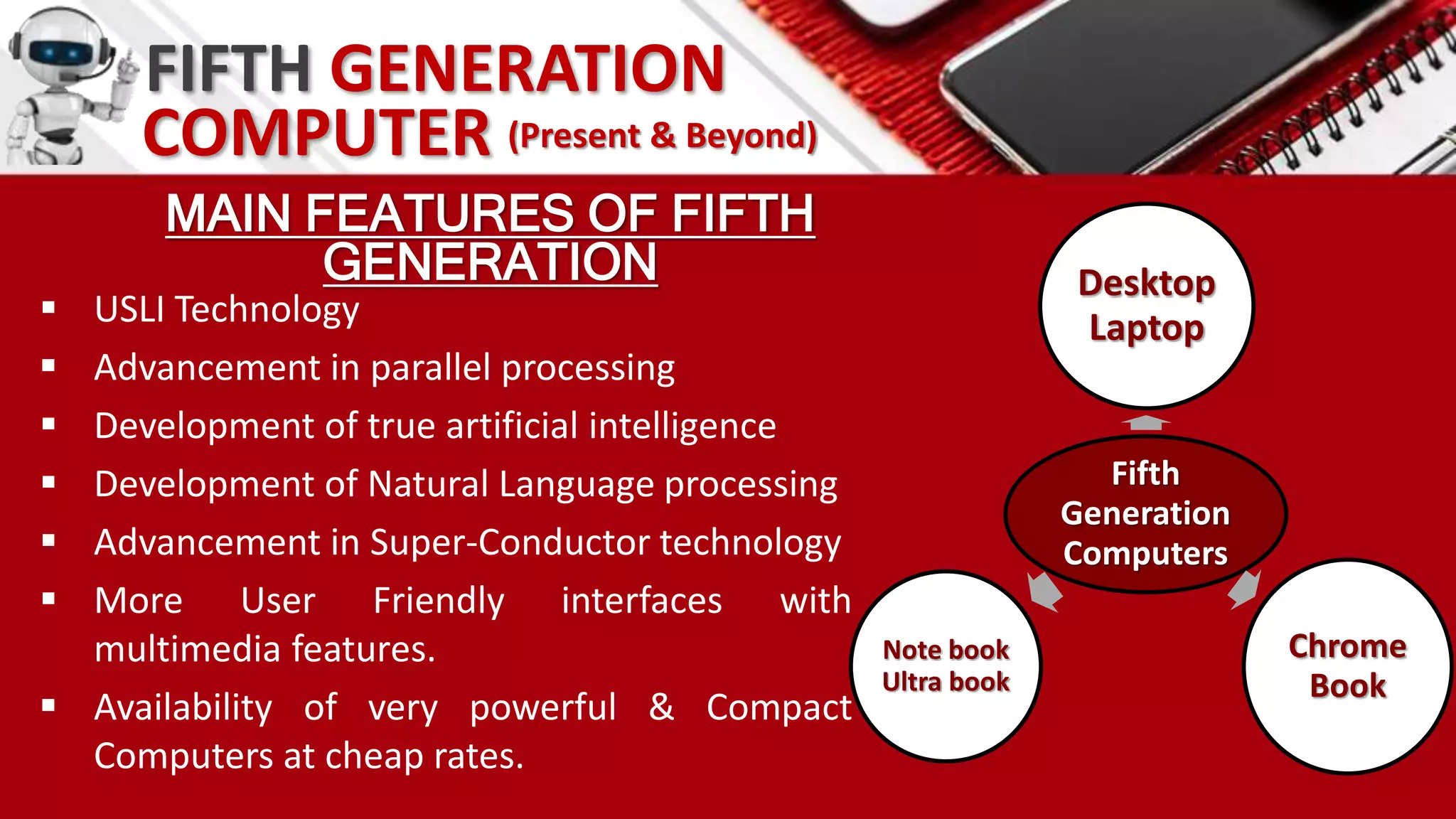
This document summarizes the history of computers from the 4th century BC to present day in 5 generations. The first generation used vacuum tubes and magnetic drums. The second generation used transistors, making computers smaller and more reliable. The third generation used integrated circuits, further miniaturizing computers. The fourth generation used microprocessors on a single chip, leading to smaller portable computers and the internet. The fifth generation aims to develop true artificial intelligence and natural language processing.