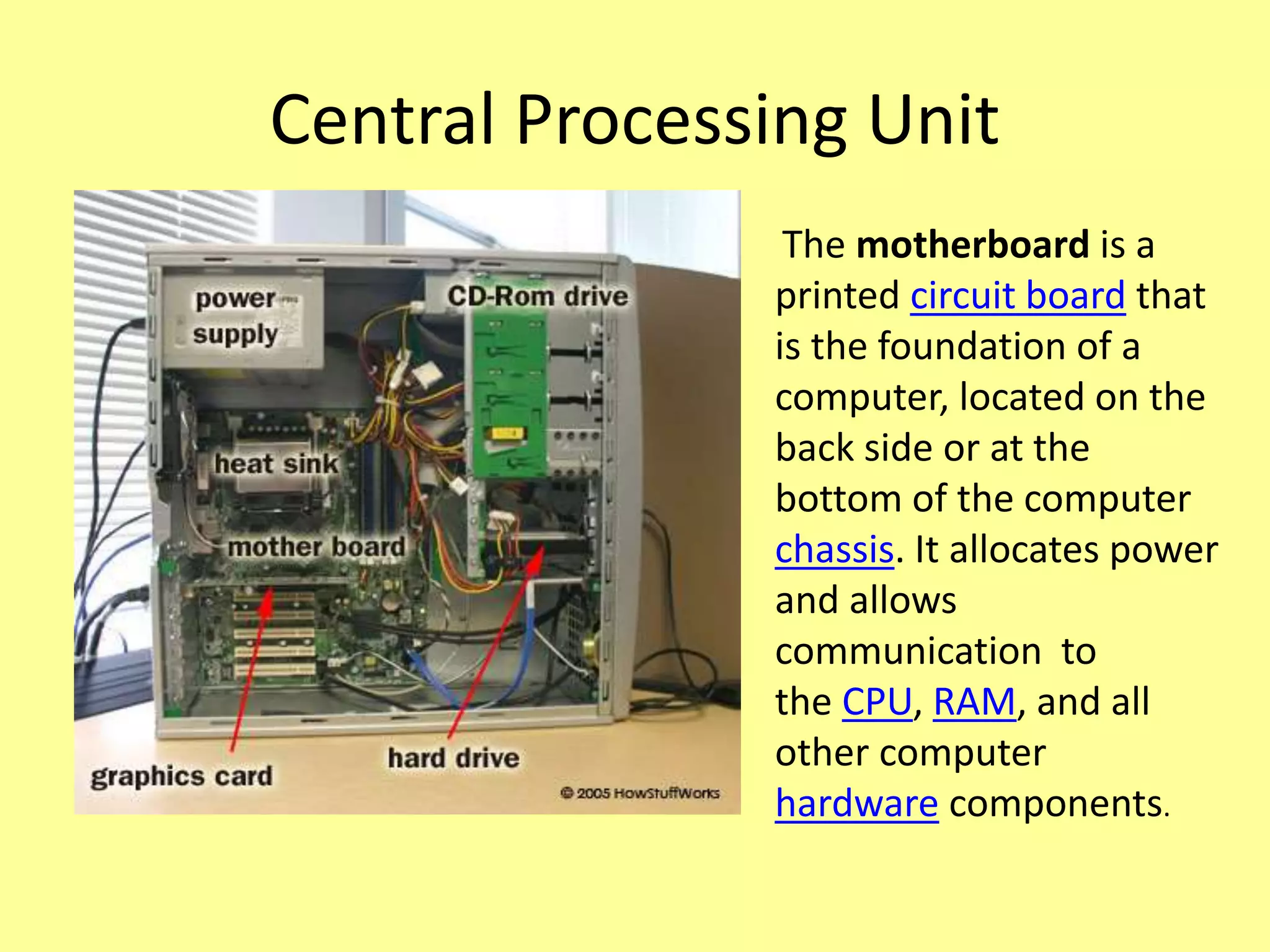
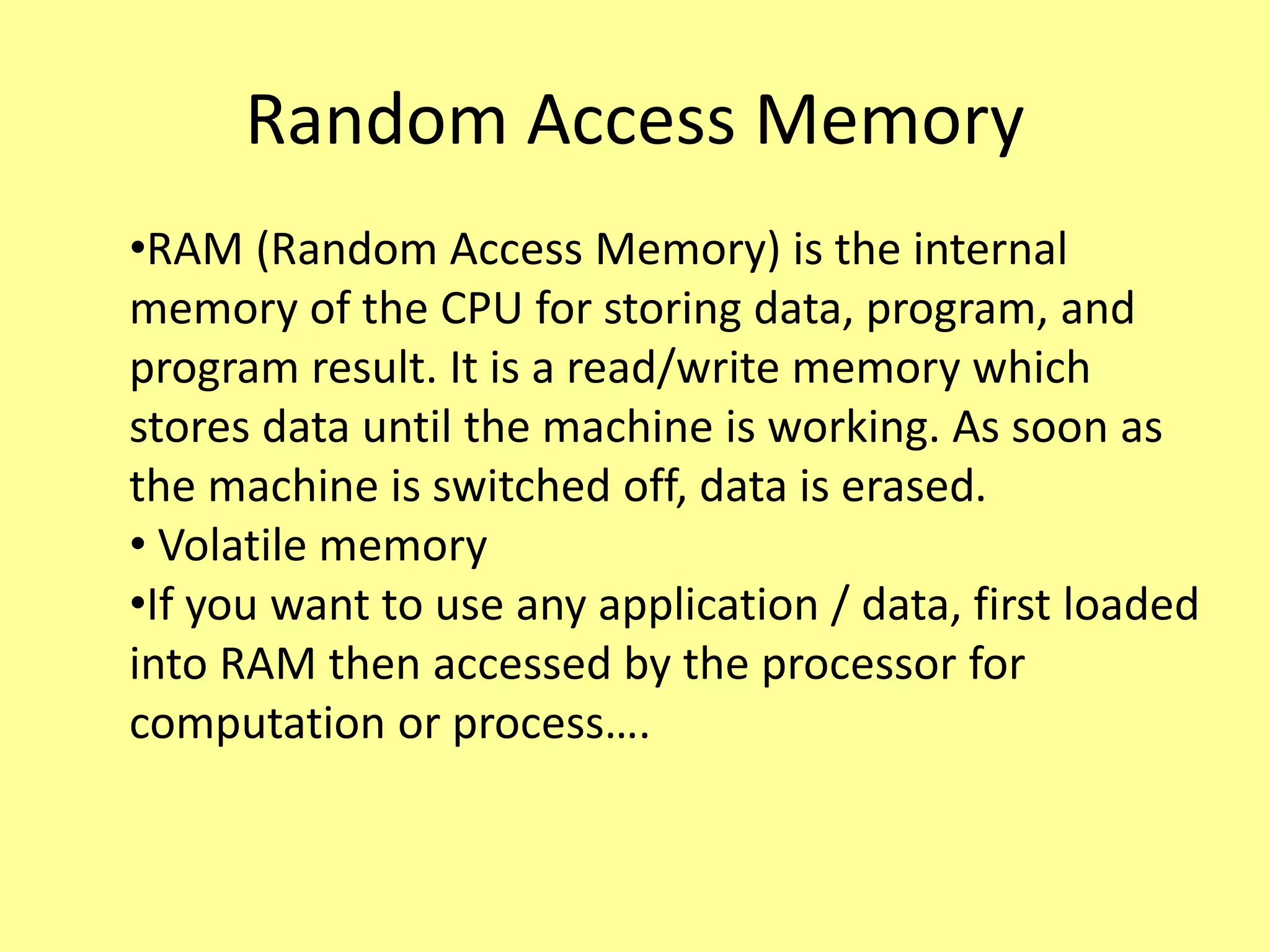
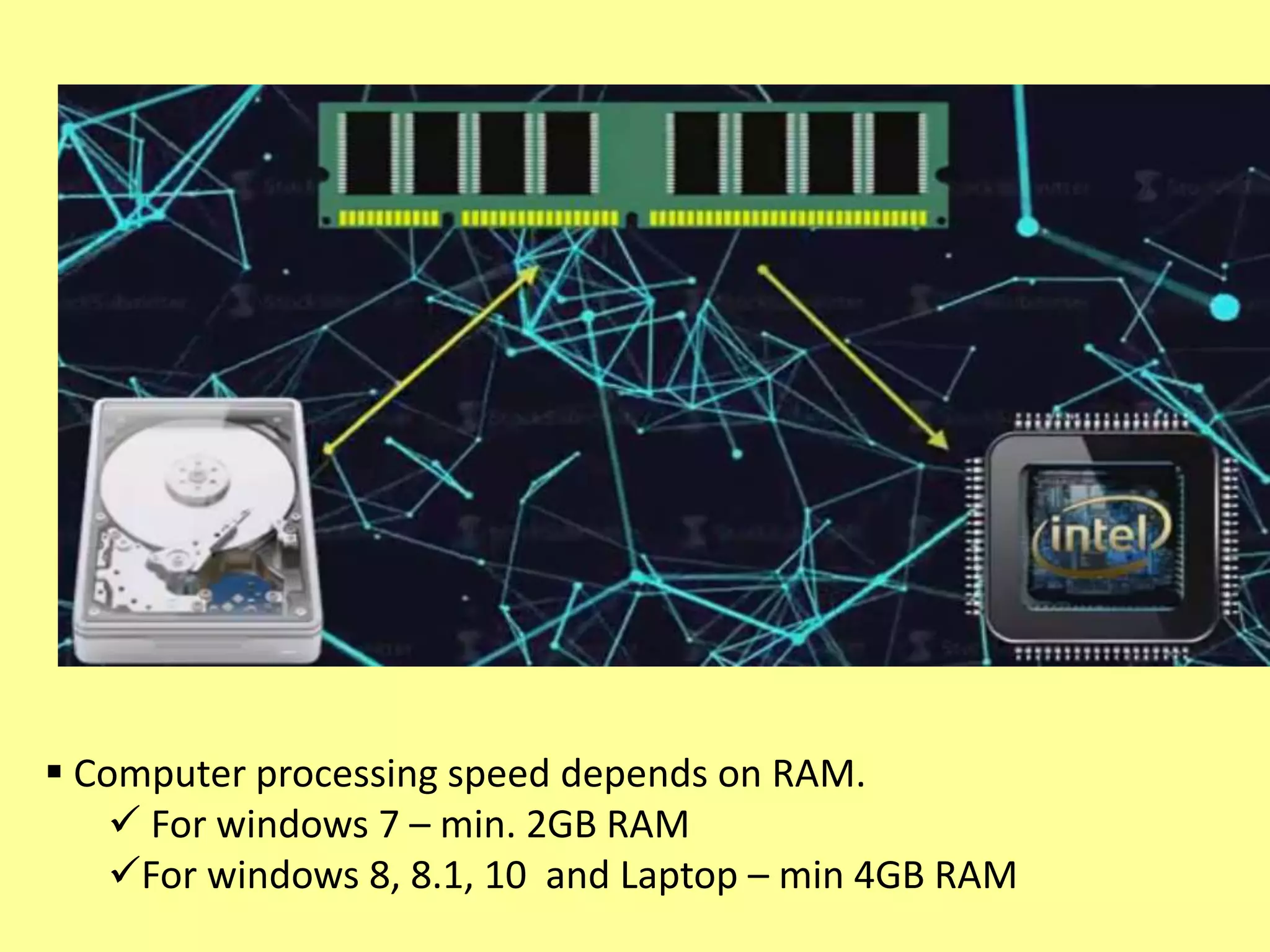
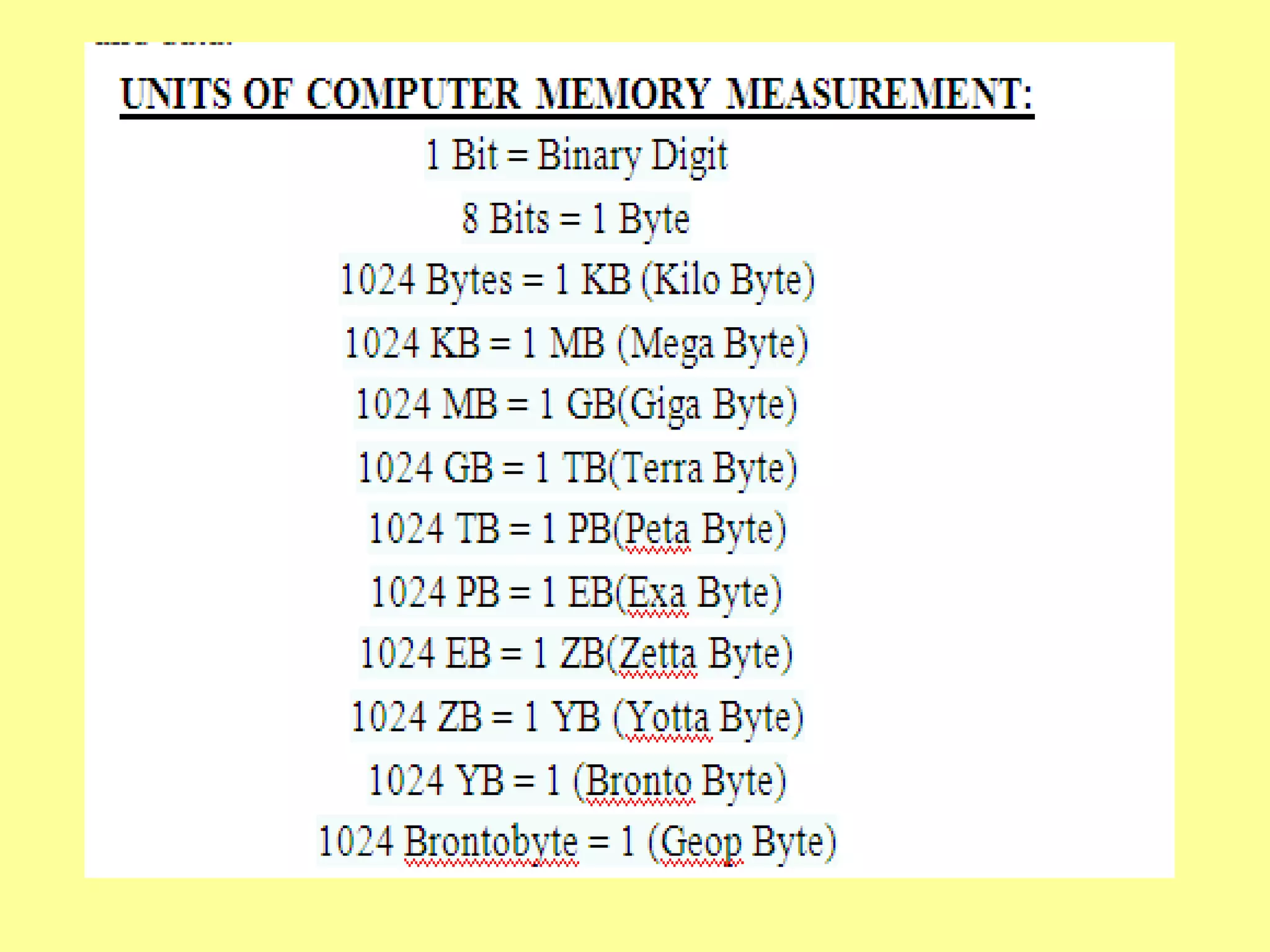
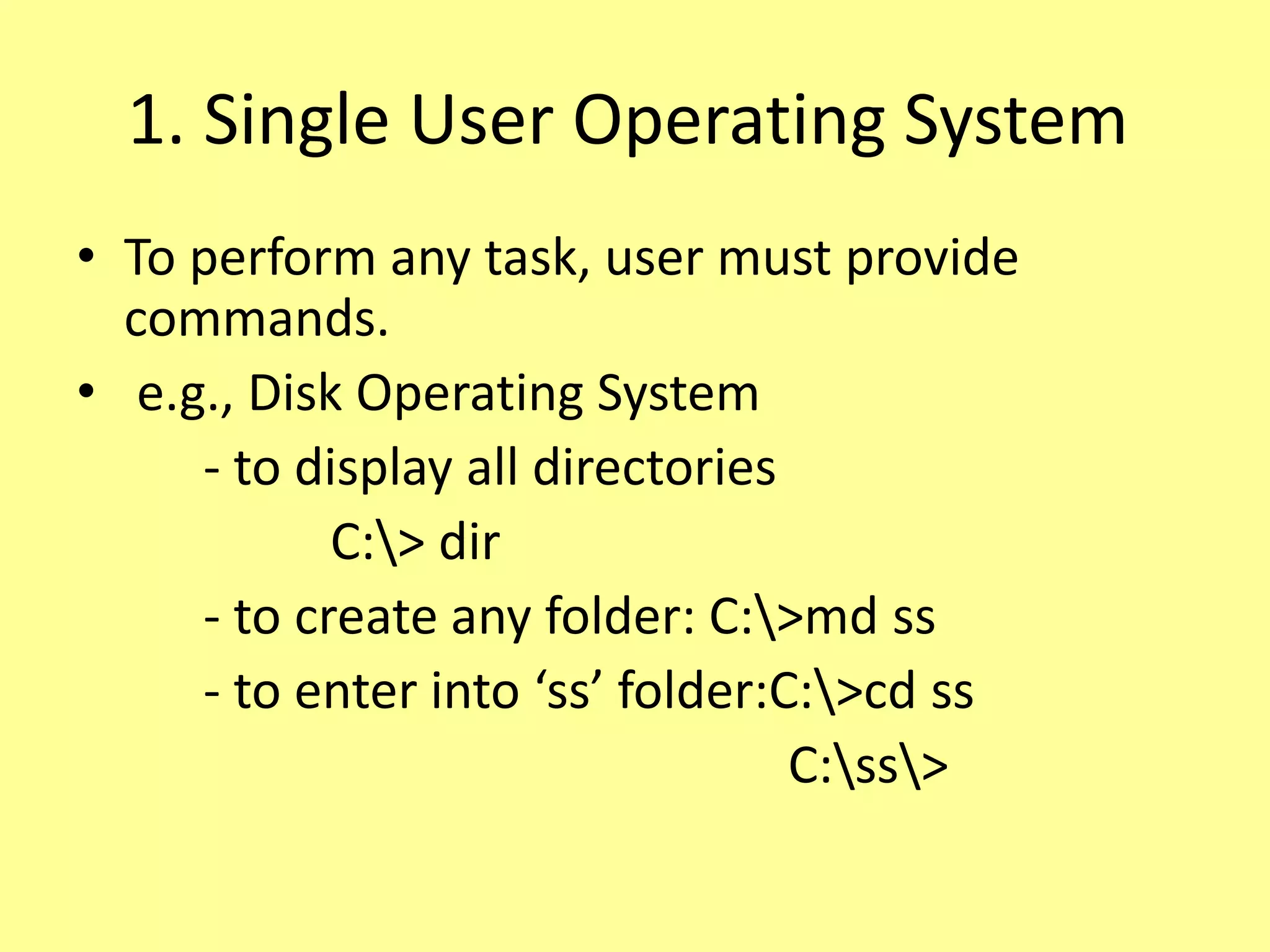
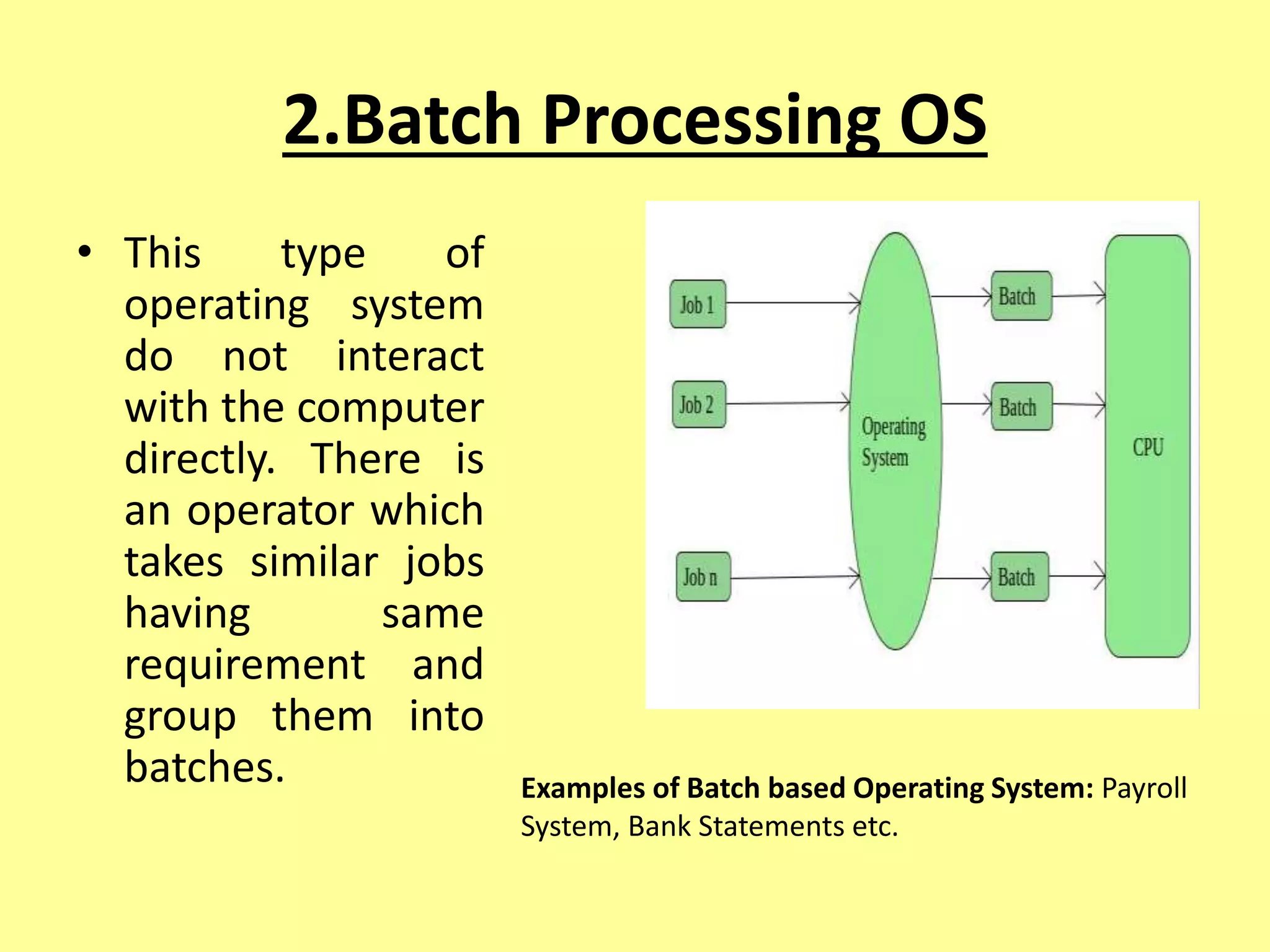
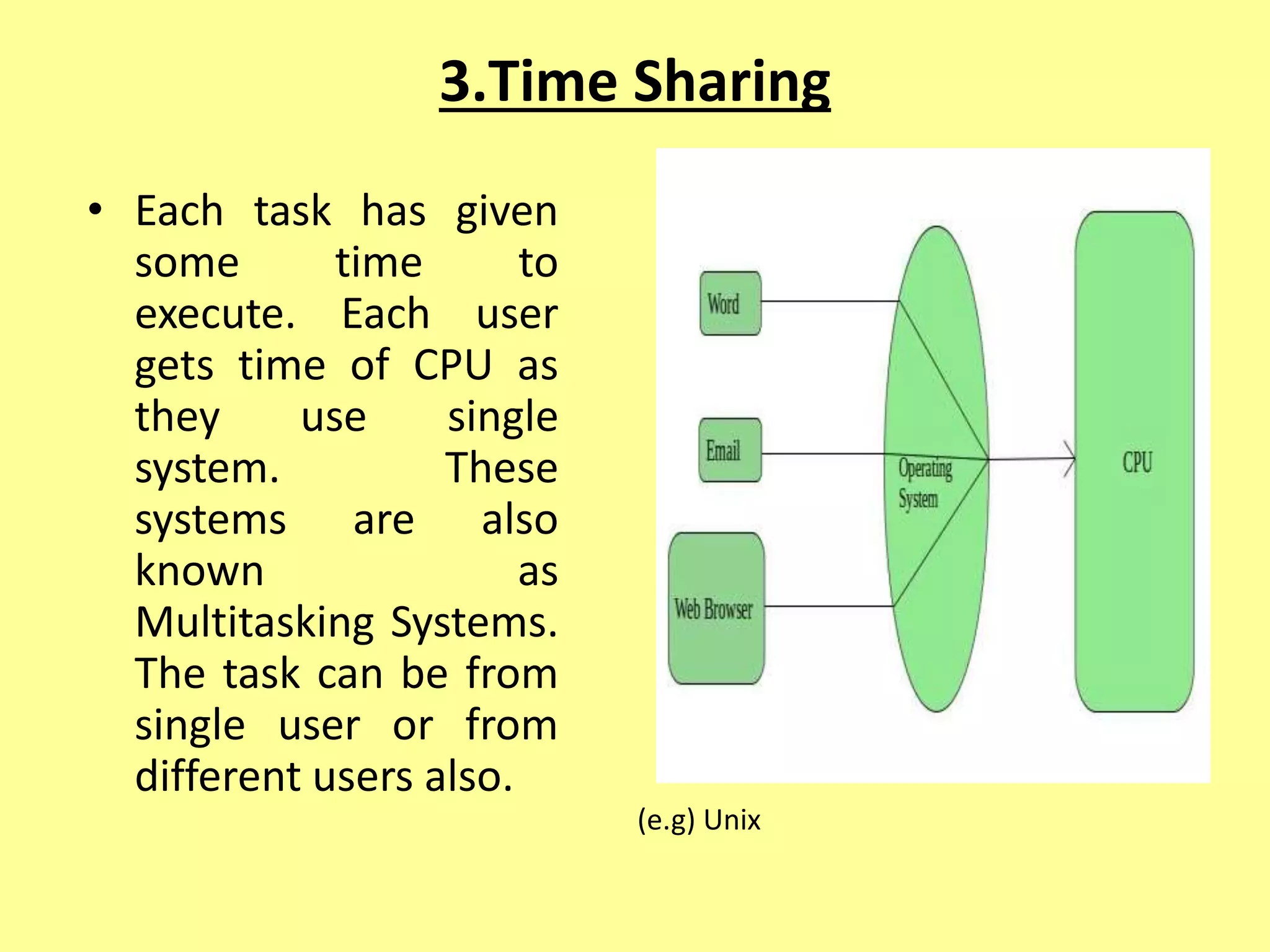
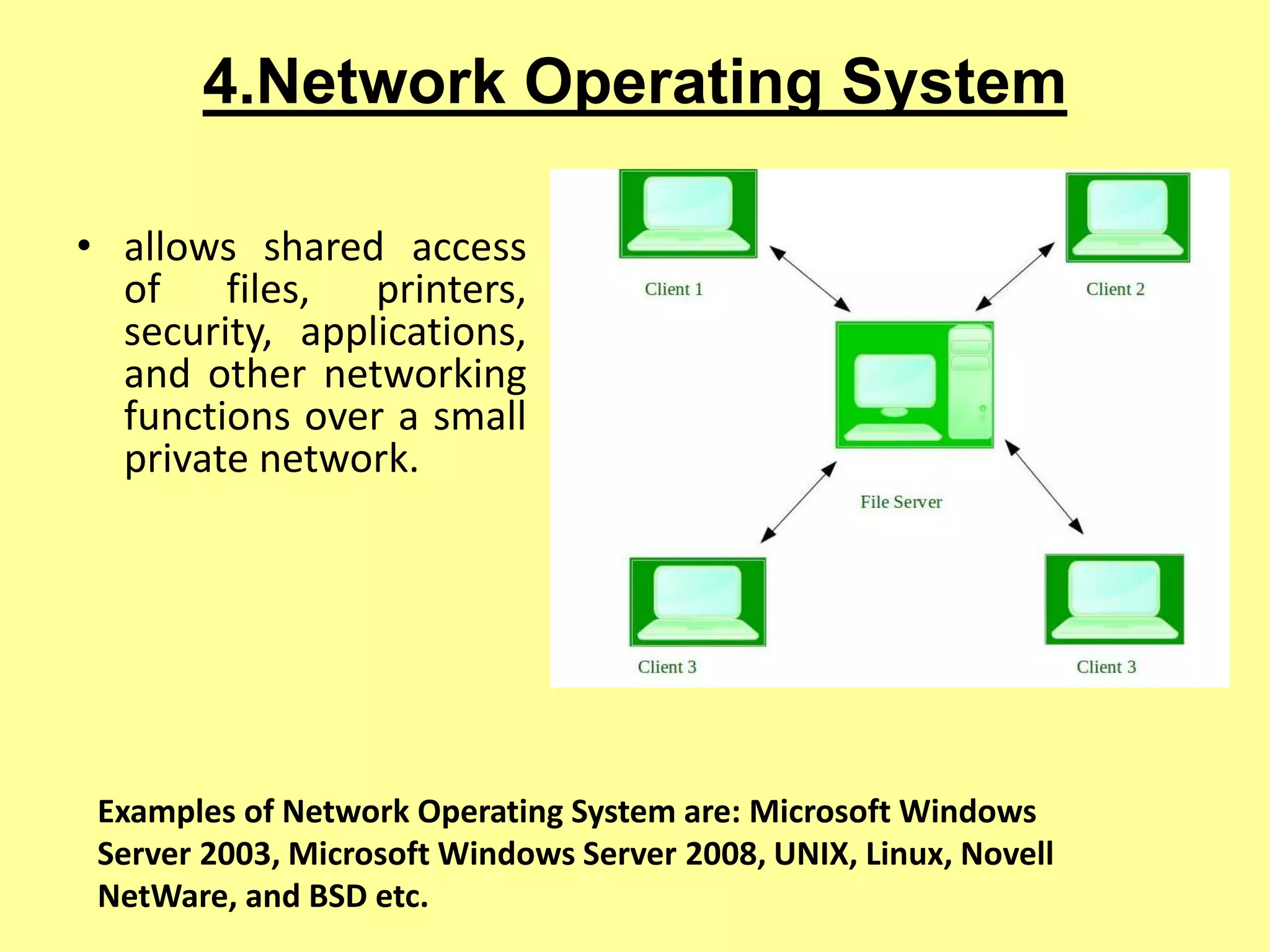
The document outlines the basics of computer input and output devices, detailing their purposes and types, including keyboards, mice, monitors, and printers. It also describes memory types including RAM and ROM, as well as storage devices such as hard drives and cloud storage. Additionally, it covers various operating system types, including single user, batch processing, time sharing, network, and real-time operating systems.