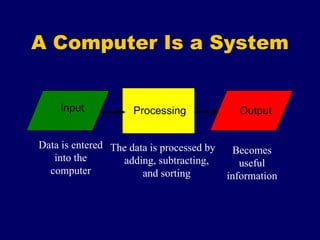
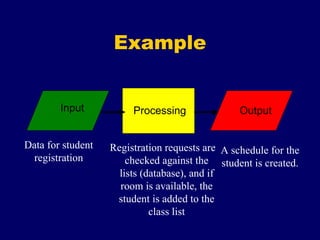
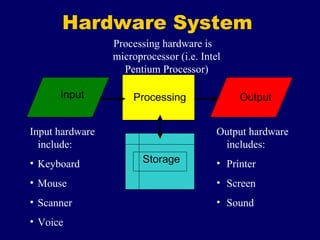
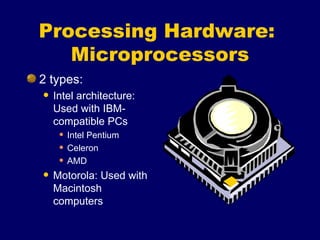
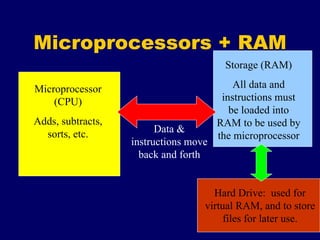
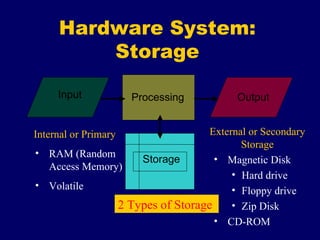
The document provides an overview of computer fundamentals including the components that make up a computer system and how they work together. It discusses that a computer takes in data as input, processes it, and provides output. It then describes the main hardware components including input devices like keyboards and mice, processing components like microprocessors, storage components like RAM and hard drives, and output devices like printers and screens. It also discusses the different types of software that run on computers including operating systems and application software.