The document discusses the applications and evolution of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) in various fields, particularly focusing on its role in wastewater treatment processes. It emphasizes the importance of CFD modeling in optimizing designs and improving performance by simulating hydrodynamics prior to implementation. The text highlights the current state of wastewater treatment technology and the potential cost and time savings associated with CFD-based designs.

![What is CFD?
The physical aspects of any fluid flow are governed by the
following three fundamental principles [1]:
Mass is conserved; Continuity equation
F = m·a (Newton’s second law); Momentum equation
Energy is conserved. Energy equation
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-2-2048.jpg)
![Evolution of CFD applications:
Figure 1 - Mapping of the Evolution of Patent Figure 2 - Mapping of the Evolution of
Applications filing [2] Scientifics Articles over time [2]
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-3-2048.jpg)
![CFD Applications:
CFD can be used in [3]:
• Aerospace & Defense
• Automotive
• Construction
• Health care
• Energy
• Chemical Processing
• Etc.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-4-2048.jpg)
![Application of CFD in water waste treatment
Activated sludge process (ASP) plants includes the following stages
[3]:
Inlet works
Primary settlement
Activated sludge treatment
Secondary settlement
Tertiary treatment
CFD can be used to;
• Find capital cost savings,
• Achieve performance improvements,
• Energy savings.
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-5-2048.jpg)
![Application of CFD in water waste treatment [3]
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-6-2048.jpg)


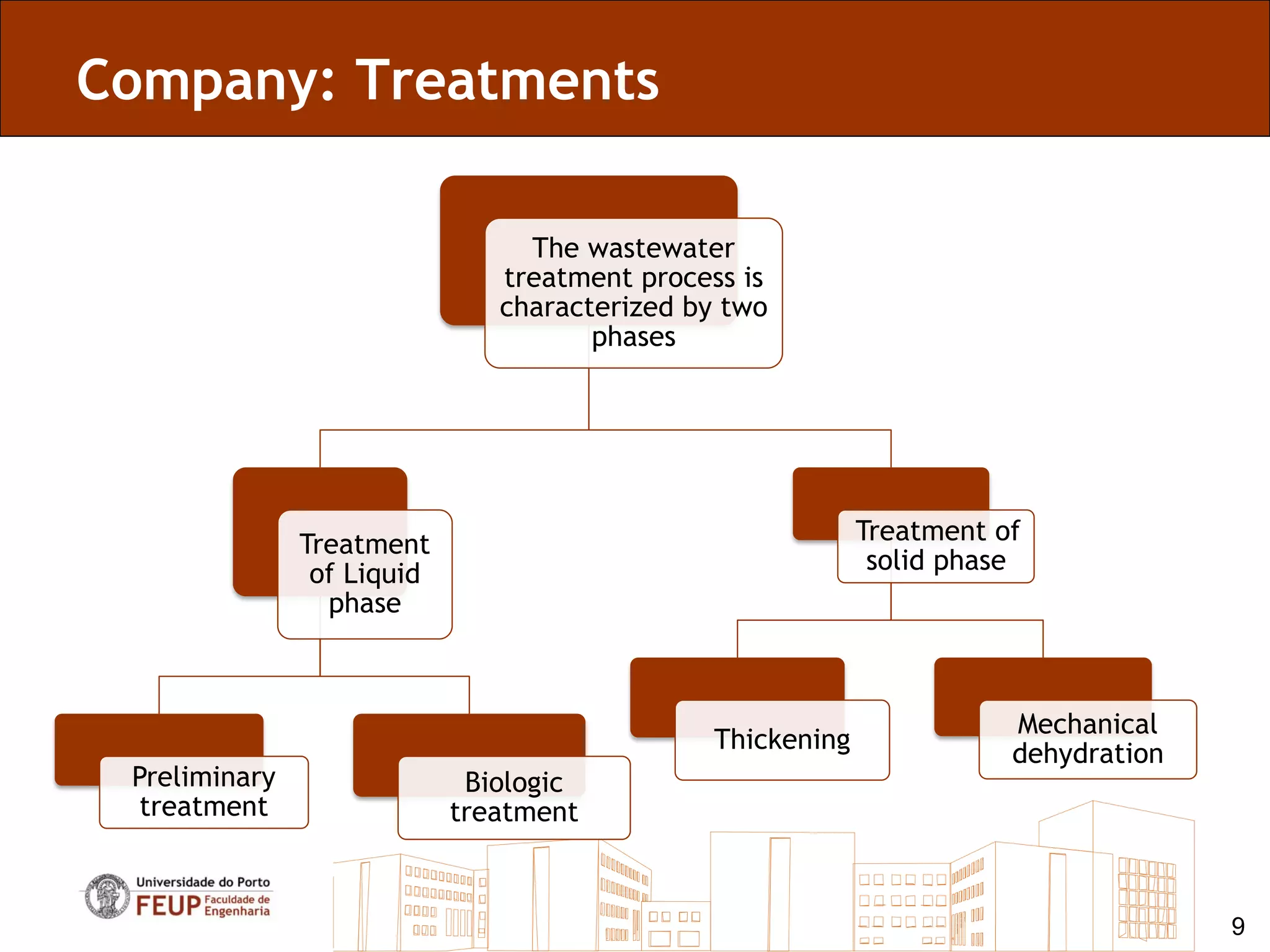
![Company: Treatments
• The decanted sludge is accumulated and then are returned
to the activated sludge tank. The decanted activated sludge,
when in excess, are send to a thickener tank to reduce the
moisture content. [4]
• After thickening, the sludge is dried, whose concentration
reaches 20% solids, and are destined for composing to the
Parada WWTP. [4]
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-10-2048.jpg)
![Current State of Design
Wastewater treatment vessels are sized according to required
pollutant removal: [5]
- Requires knowledge/assumptions of the flow regime (i.e.
hydrodynamics)
- Vessel configuration design to achieve flow type relies on
empirical correlations and heuristic techniques
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-11-2048.jpg)
![Hydrodynamics: Importance for Wastewater Treatment
The hydraulic behavior in an activated sludge tank, is of
fundamental importance for the efficiency of the process[6].
Hydraulic phenomena with negative effect on performance[6]:
-Short circuiting streams
-Dead volumes
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-12-2048.jpg)
![CFD: Alternatives
Models developed by the International Water Association are
useful tools for the process control. However, they are
unsuitable to model the influence of the reactor geometry; [7]
- Length/width ratio
- Presence of baffles
- Effluent inlet device
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-13-2048.jpg)
![CFD: Alternatives
Full-scale tracer tests are very informative when investigating
hydraulic situations in activated sludge tanks however [6];
-It claims a lot of personal
-And mean residence times are in order of days
So it becomes impracticable
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-14-2048.jpg)
![Why Design Using CFD in a WWTP?
A CFD model can simulate the hydrodynamics of a design before
implementation [8]:
- Reducing lead-up times and costs
- Ultimately lead to optimization of reactor configuration
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-15-2048.jpg)




![References
[1] Anderson, Jr., John D.; Computational Fluid Dynamics. ISBN: 0-
07-113210-4
[2] Islabão, G. et al (2010). Technological Trends in CFD Applications.
Journal of Technologyl, Managment and Innovation, 76-83.
[3] http://www.ansys.com/
[4] http://www.ambiente.maiadigital.pt
[5] L. Benedetti et al (2006). Benchmarking of WWTP design by
assessing costs,. Water Science & Technology, 95–102.
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-20-2048.jpg)
![References
[6] Kjellstrand R. et al (2005) Short Circuiting in a Denitryfying
Activated Sludge Tank. Water Science & Technology, Vol. 52, No. 10-
11, pp 79-87, IWA
[7] Moullec, Y. L. (2010). CFD simulation of the hydrodynamics and
reactions in an activated sludge channel. Chemical Engineering
Science, 492 - 498.
[8] Brannock, Matthew (2003). Computational fluid dynamics tools
for the design of mixed anoxic wastewater treatment vessels PhD
Thesis, School of Engineering, The University of Queensland.
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationalfluiddynamicsinwwtp-120417174949-phpapp02/75/Computational-fluid-dynamics-in-water-waste-treatment-plants-21-2048.jpg)