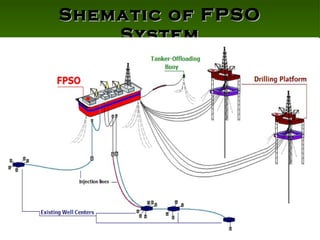
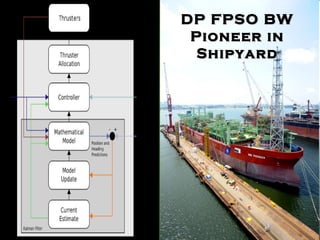
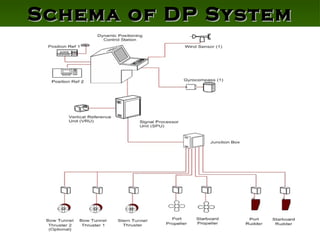
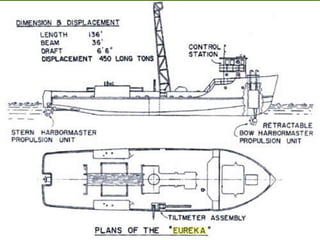
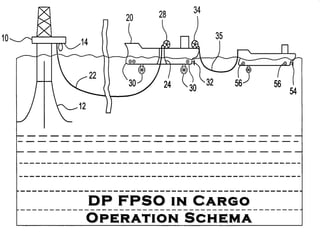
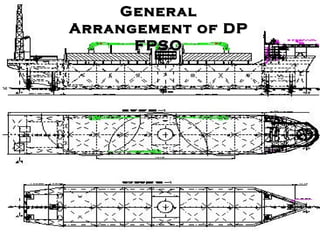
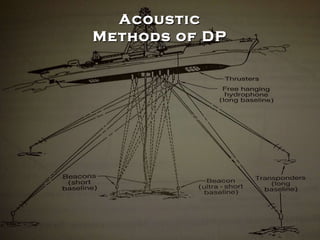
The document discusses the importance of dynamic positioning (DP) systems for floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) vessels. DP systems allow FPSOs to maintain position automatically using thrusters and propellers, which enables operations in ultra-deep waters. This is crucial as oil exploration moves to greater depths. DP technology has advanced significantly with satellite systems, improving positioning accuracy and allowing FPSOs to operate safely in waters over 1000m deep.