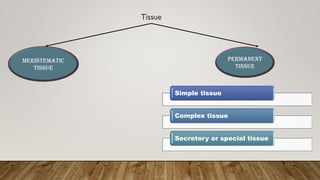
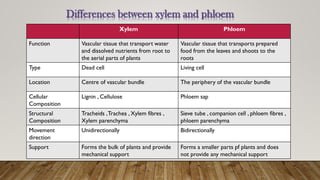
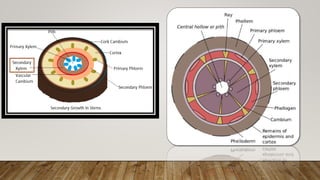
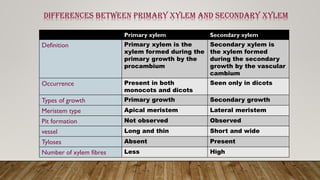
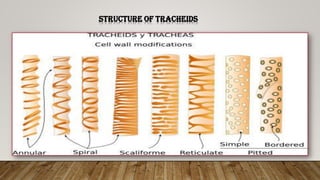
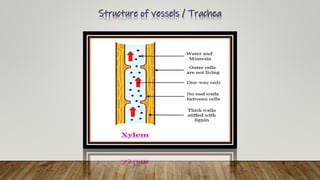
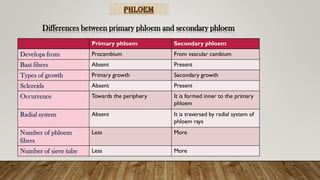
The document outlines the key differences between plant vascular tissues: xylem and phloem, including their structures, functions, and types. It distinguishes between primary and secondary xylem/phloem based on their origins and development during plant growth. Additionally, it describes the cellular composition and roles of various cells within these tissues, such as tracheids, vessels, and companion cells.