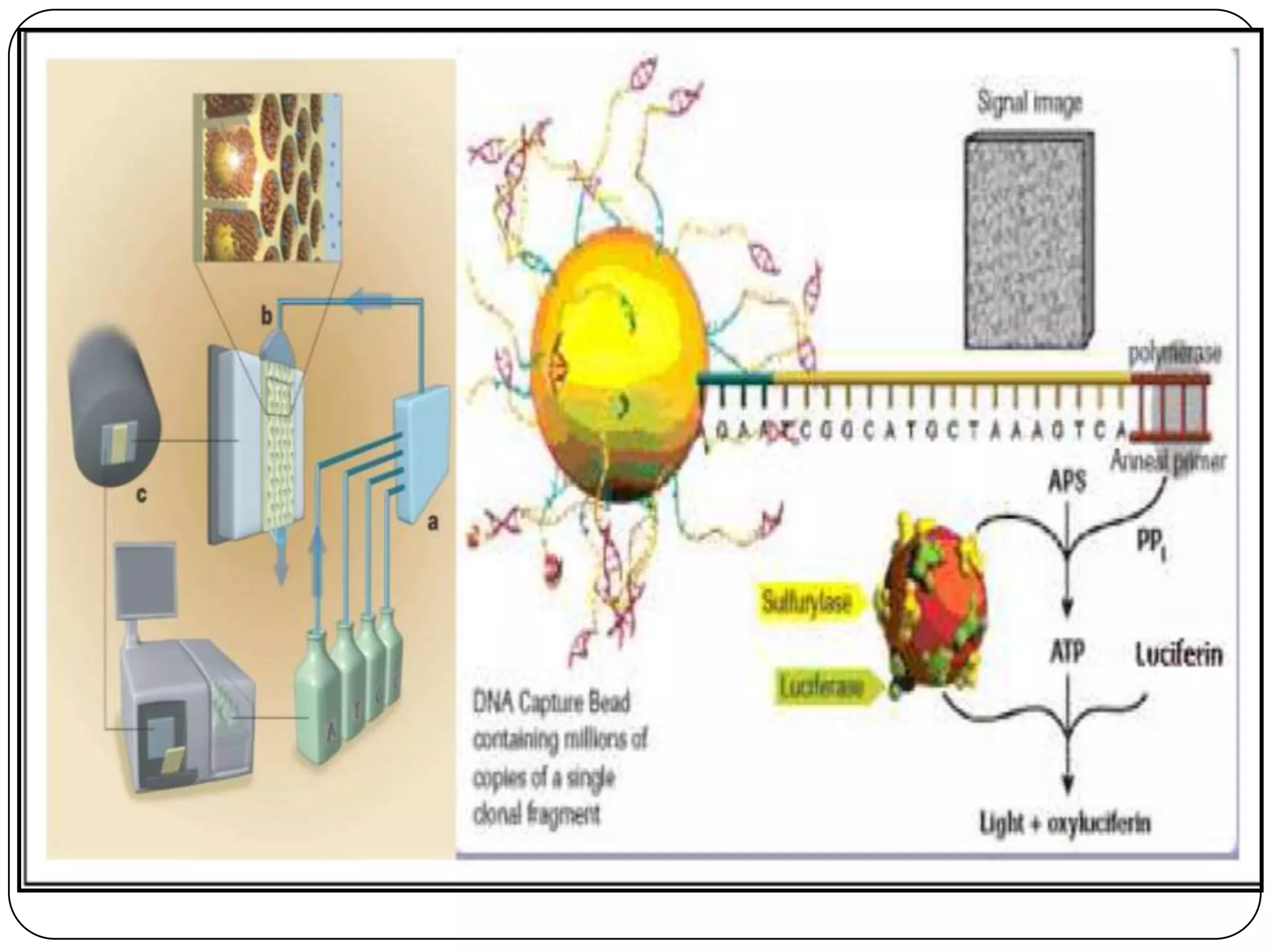
The document compares three high-throughput DNA sequencing techniques: the MegaBACETM method, 454 sequencingTM, and Single Molecule Real Time (SMRTTM) sequencing. The MegaBACETM method uses PCR and fluorescence-based capillary electrophoresis to sequence DNA fragments. 454 sequencingTM amplifies DNA fragments attached to beads in emulsions and sequences them using pyrosequencing on a picotiter plate. SMRTTM sequencing sequences single DNA molecules in zero-mode waveguides on an SMRT chip using fluorescent nucleotides and real-time detection. SMRTTM provides the highest throughput and read lengths over 1,000 bases, while 454 sequencingTM has an intermediate throughput