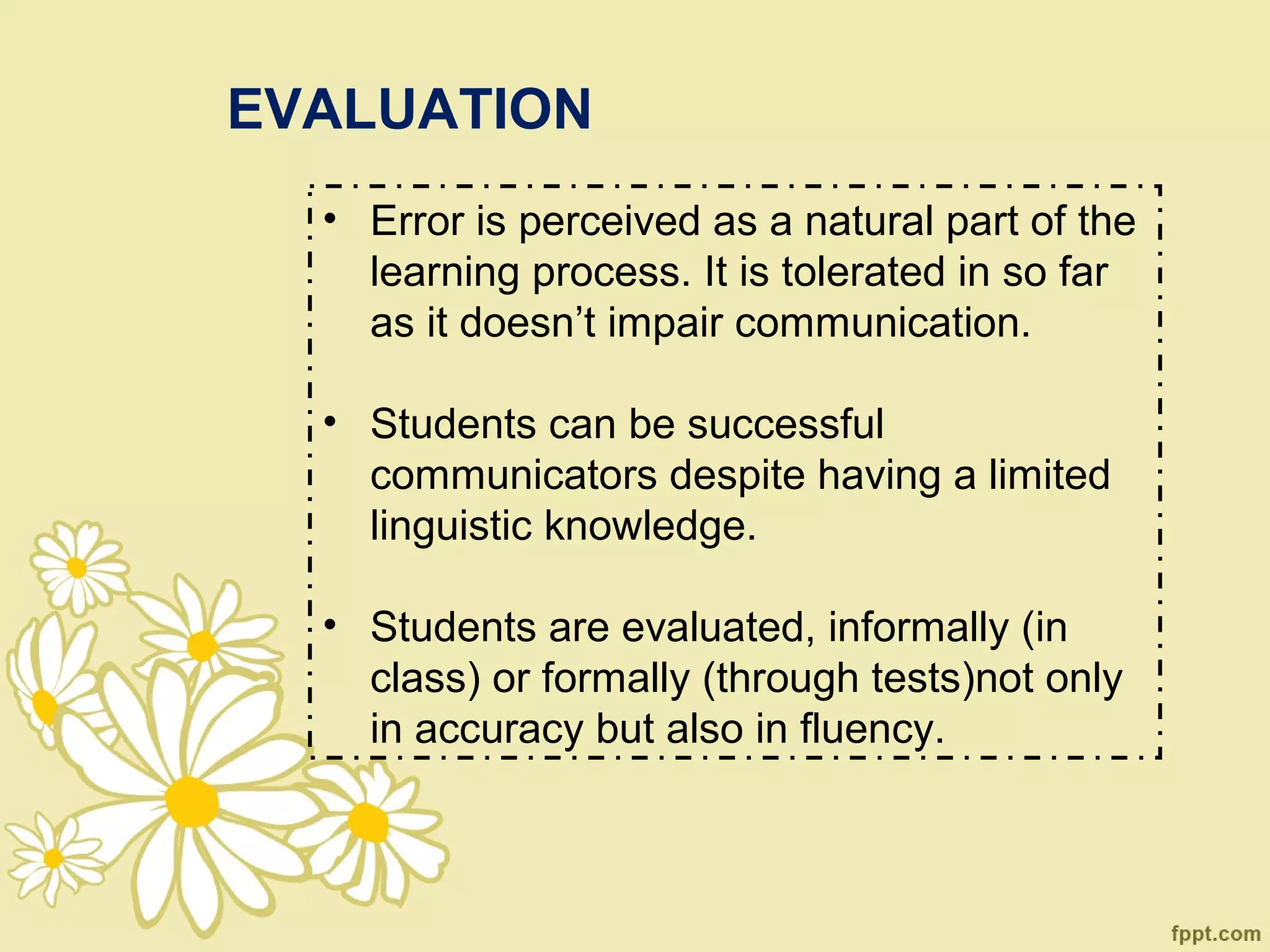
The document discusses Communicative Language Teaching (CLT), which emphasizes real communication and interaction in language learning, moving away from traditional methods like audio-lingual and grammar-translation. It outlines the roles of both teachers and learners in promoting communication through various authentic materials and exercises, while also addressing the place of grammar and evaluation methods. The approach aims to enhance communicative competence and motivate learners by engaging them in meaningful, context-driven activities.