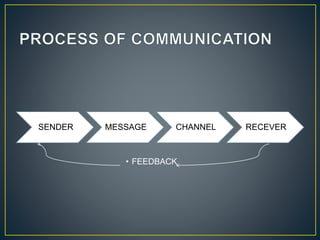
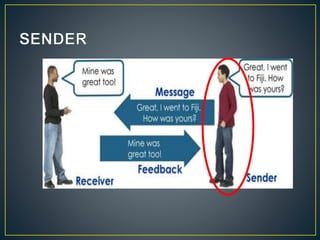
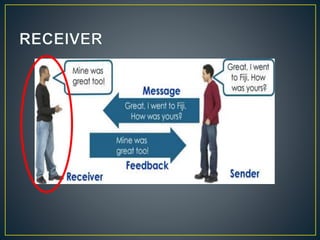
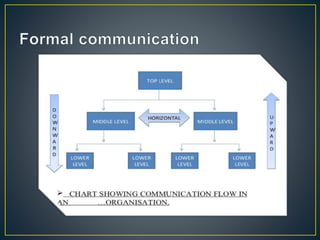
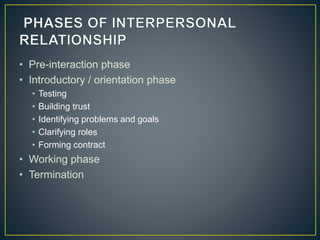
Communication is the process of exchanging ideas, feelings, and information between a sender and receiver using a channel. It involves transmitting a message from the sender, receiving feedback from the audience, and using different types of communication like verbal, nonverbal, and visual. Effective communication ensures the message is clear and any necessary supporting information is provided. Interpersonal relationships are strong associations between two or more people and involve different phases from initial interaction to termination. Problems can occur in interpersonal relationships, like loss of motivation, opposition, operational issues, task distortion, and authority problems, which reduce the effectiveness of groups.