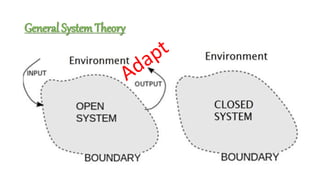
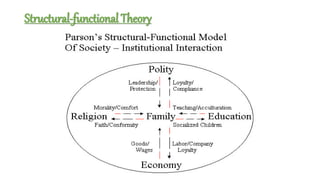
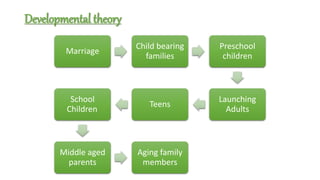
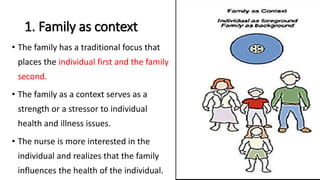
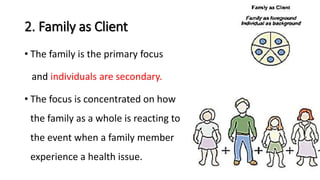
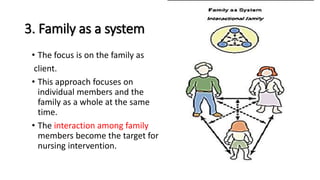
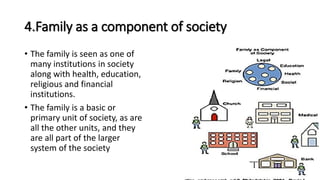
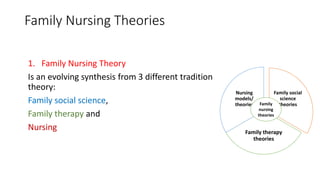
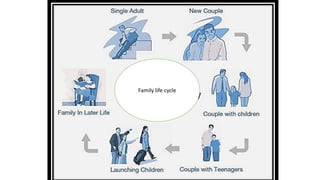
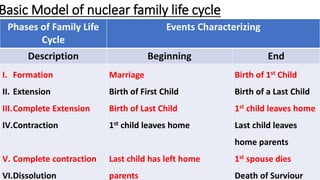
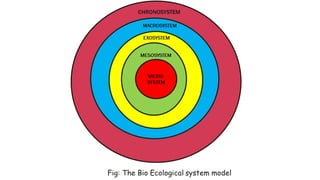
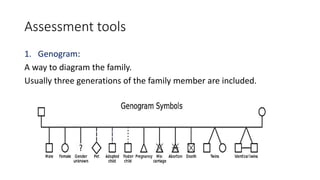
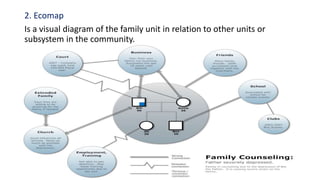
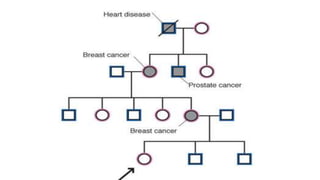
The document discusses family nursing and defines a family as a group of persons united through marriage, blood, or adoption. It discusses characteristics of healthy families and different types of families. The document outlines approaches to family nursing including viewing the family as context, client, system, and part of society. Several family nursing theories are described as well as the family nursing process which involves assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation.