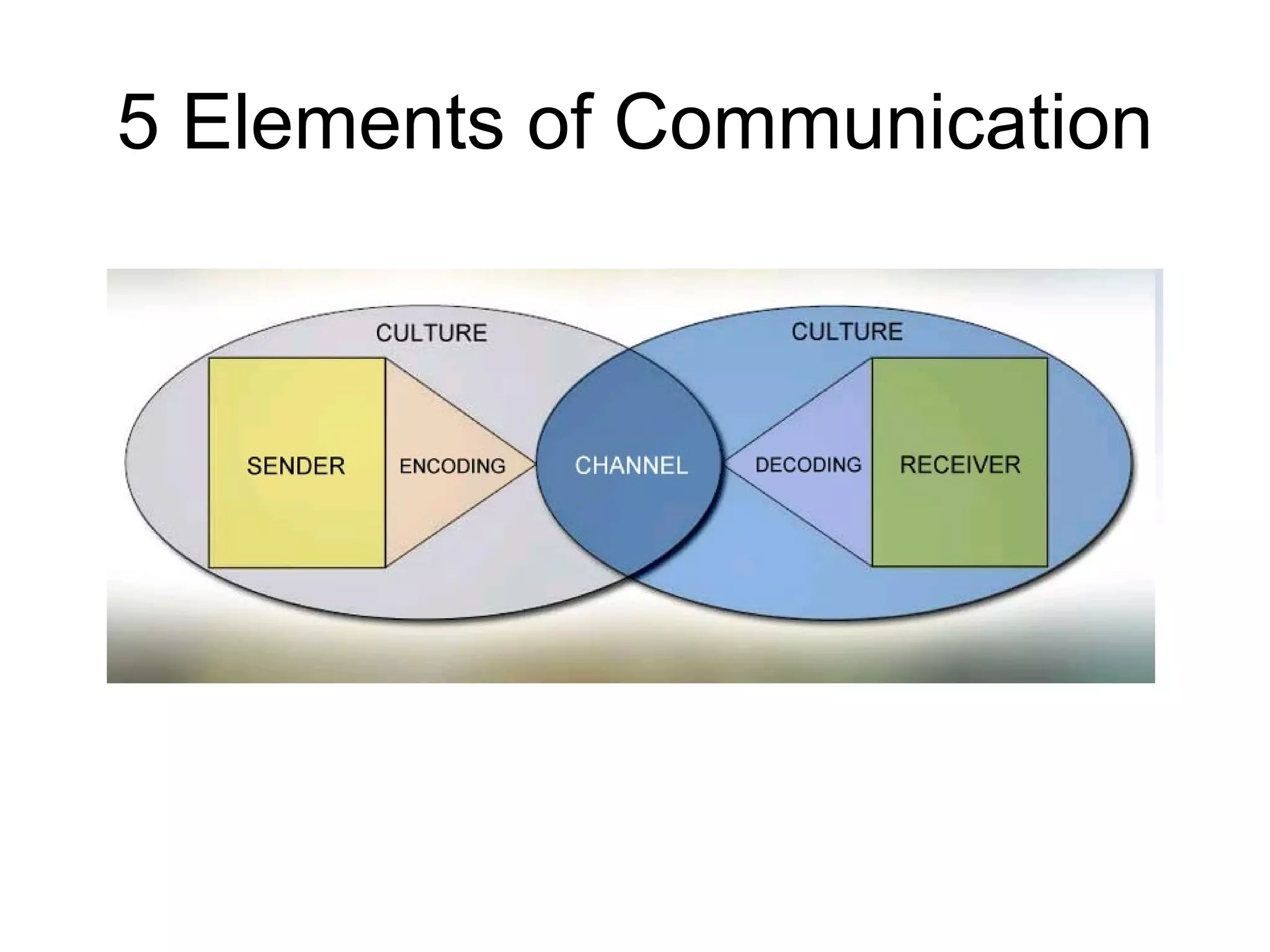
The document discusses communicating across cultures, noting there are high and low context cultures. High context cultures communicate more implicitly and avoid confrontation, while low context cultures are more direct, logical, and comfortable with opposing views. The document provides tips for tailoring communication to the cultural context, such as using formal titles and respecting silence for high context audiences versus being direct and keeping social talk brief for low context audiences.