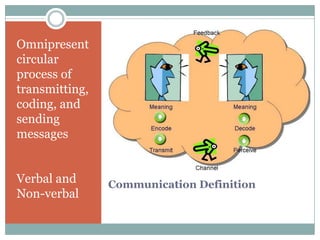
This document discusses different types of communication for nurses, including verbal and non-verbal communication. It explains that verbal communication can be subject to misinterpretation depending on language, intent, and cultural understanding. Non-verbal communication such as body language and facial expressions can also be culturally interpreted and is often more powerful than verbal communication. The document then describes effective communication, therapeutic communication, and professional communication for nurses and provides examples of each. It also lists facilitators and barriers to communication.