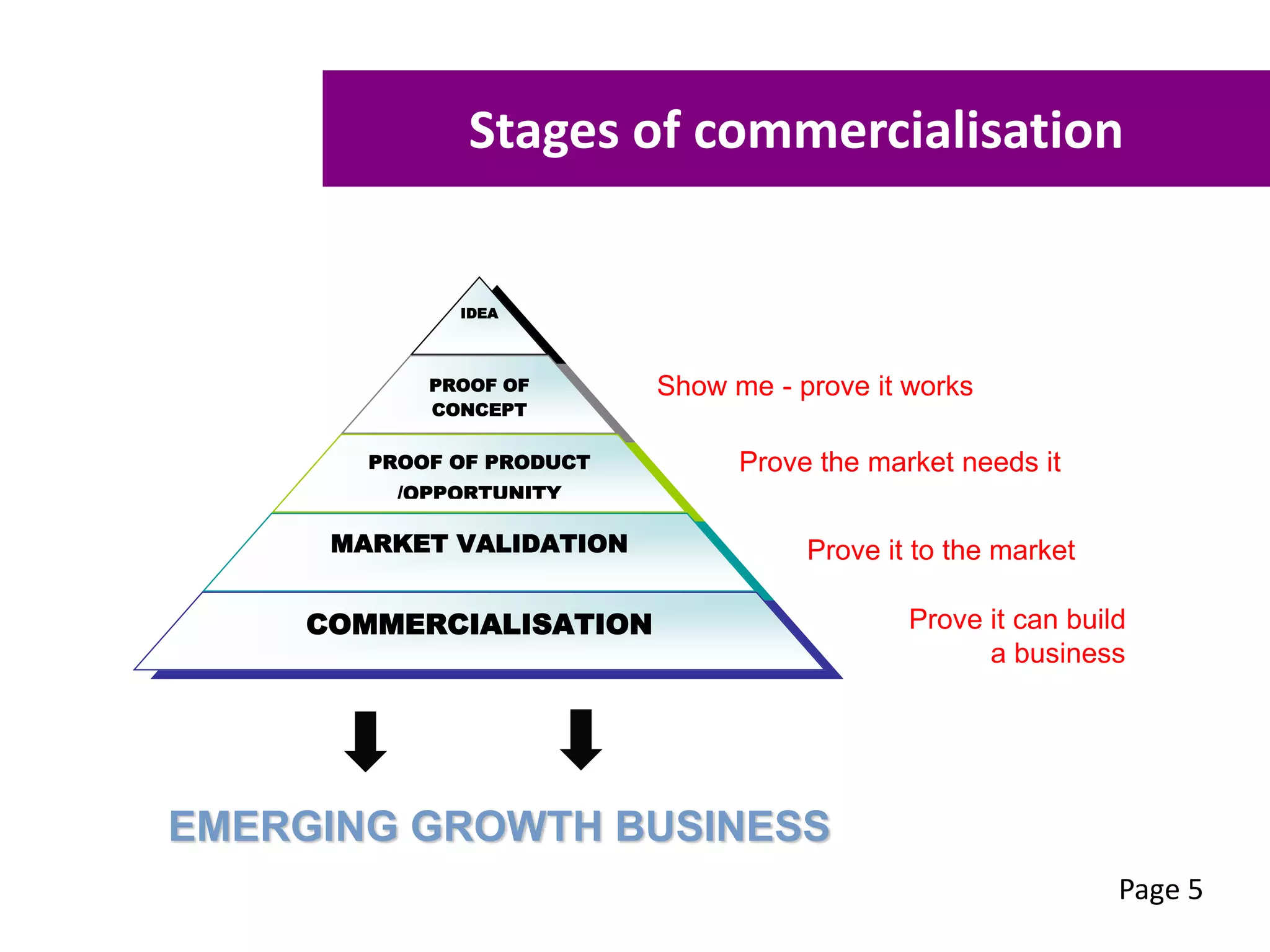
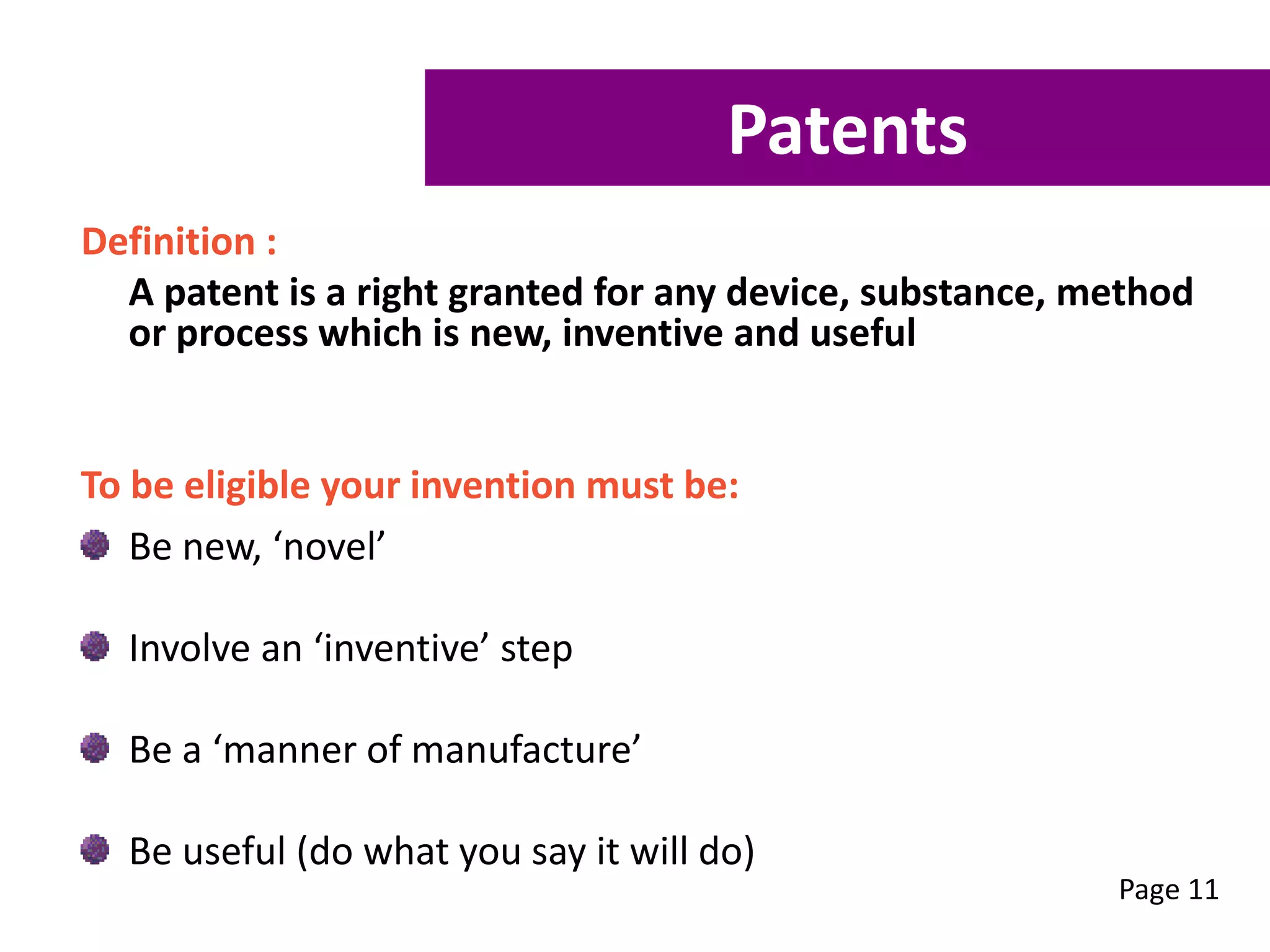
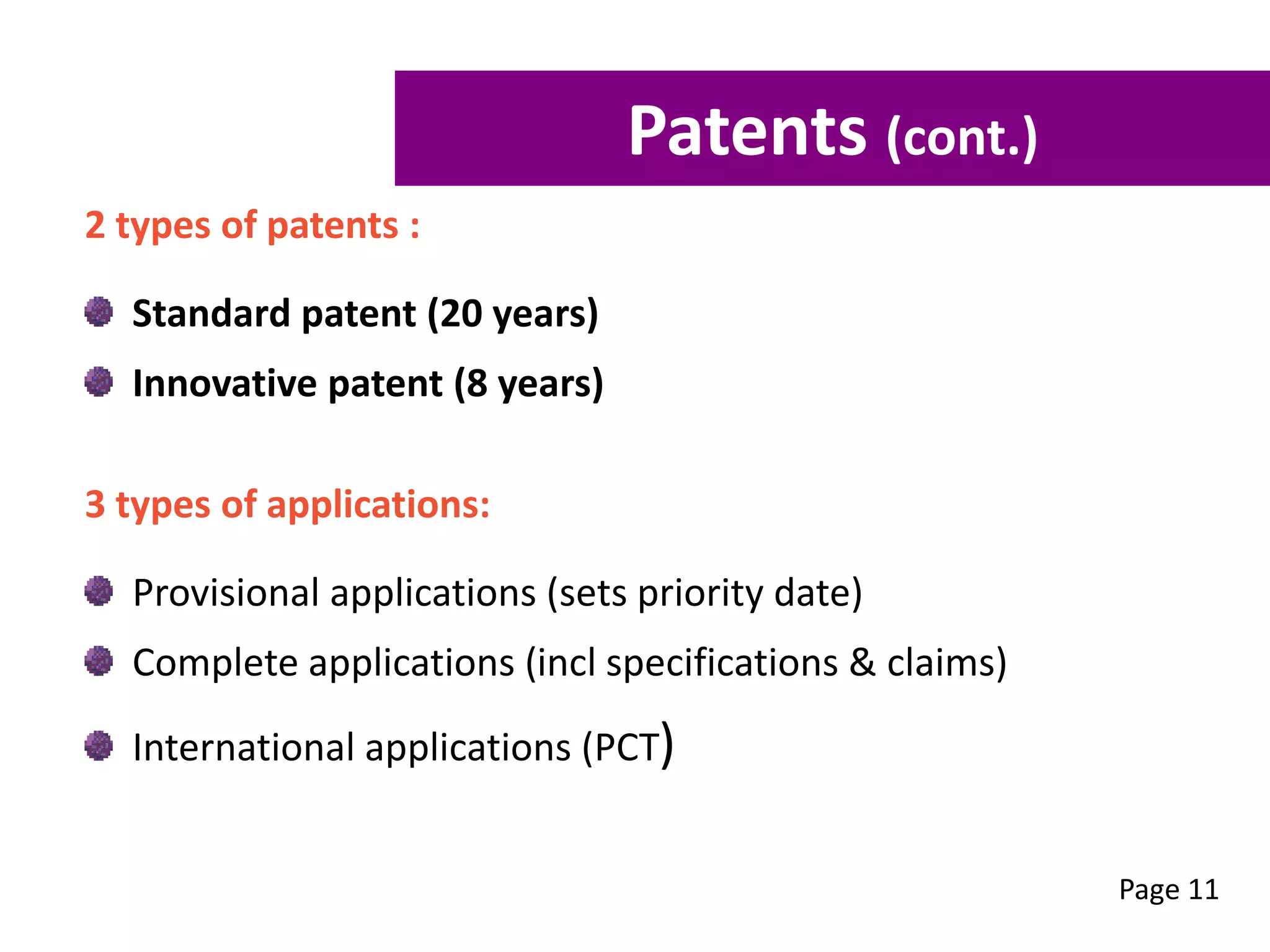
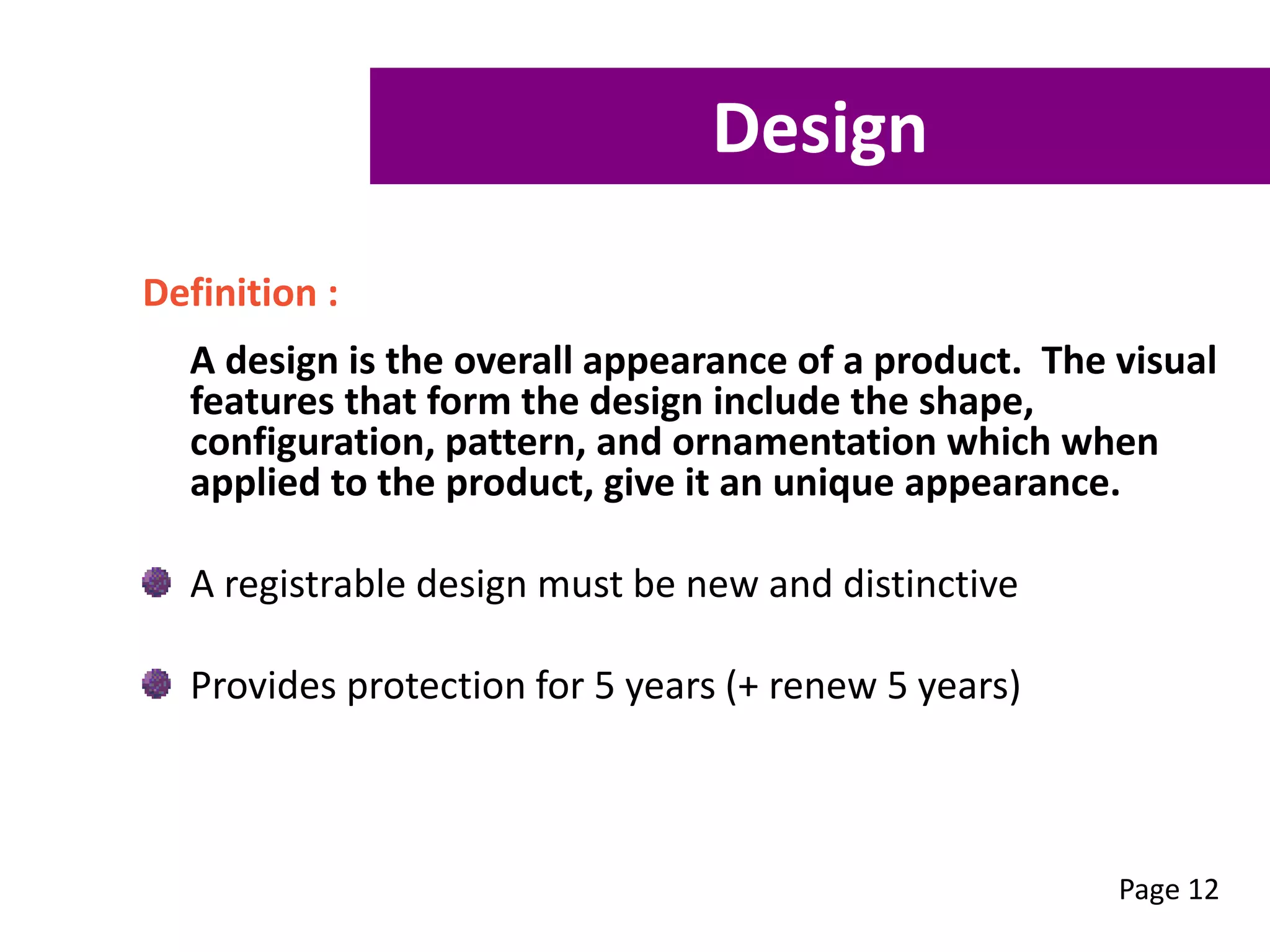
This workshop aims to equip participants with skills to understand the stages of commercialization, assess their ideas' feasibility, and create a focused commercialization plan. Key topics include intellectual property types, feasibility assessment criteria, and essential components of a commercialization strategy. Participants can also receive free mentoring to enhance their business development and commercialization efforts.