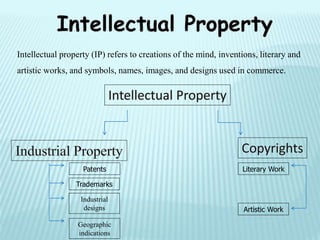
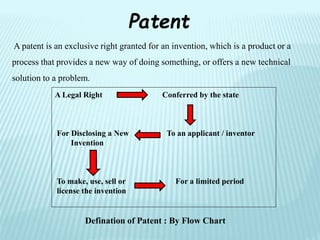
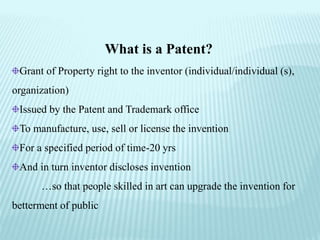
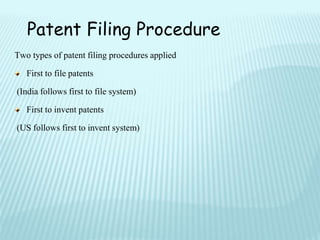
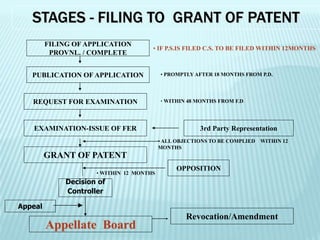
This document provides an overview of various types of intellectual property rights including patents, trademarks, copyrights, industrial designs, geographical indications, and trade secrets. It discusses what each type of intellectual property protects, requirements for protection, terms of protection, and registration processes. The key purposes of intellectual property rights are to incentivize creativity, provide official recognition to creators, create repositories of information, and facilitate industry and international trade.